What is the SI unit of pressure?
Pascal
Bar
Atmosphere
Torr
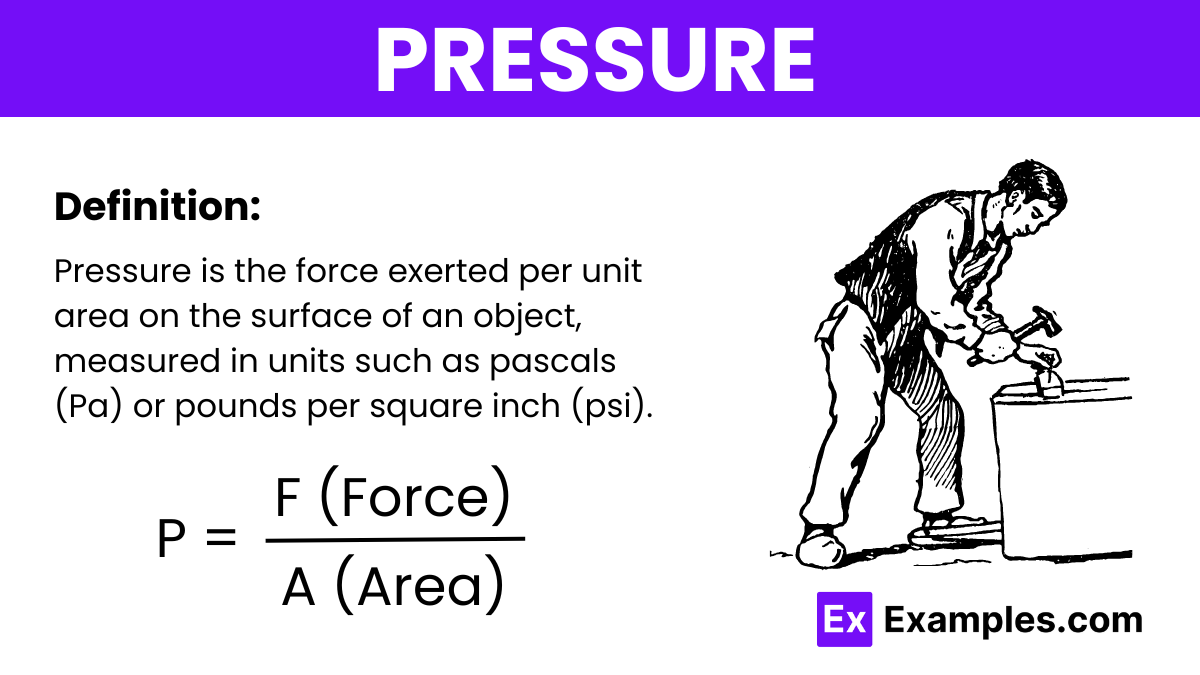
Pressure is defined as the force applied per unit area on the surface of an object. It is commonly measured in units of pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi). Pressure indicates how much force is exerted over a specific area and is a key concept in both physics and engineering.
Where:
The unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI) is the pascal (Pa), which is defined as one newton per square meter (N/m²).
This is the pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere above us. It decreases with altitude and is often measured using a barometer.
Gauge pressure is the pressure measured relative to the atmospheric pressure. For instance, the pressure in a car tire is typically given as gauge pressure, which does not account for atmospheric pressure. A gauge pressure of zero means it is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure.
Absolute pressure is the total pressure exerted on a system, including atmospheric pressure. It is gauge pressure plus atmospheric pressure and is crucial in calculations where vacuum or true total pressure is considered.
Differential pressure is the difference in pressure between two points. It is used in various applications, such as in measuring fluid flow or the level of a liquid.
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity. It increases with depth and is a critical factor in engineering and hydrodynamics.
Dynamic pressure is associated with the fluid flow. It is the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid particle. It plays a key role in fluid dynamics and aerodynamics.
| Aspect | Absolute Pressure | Gauge Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The total pressure exerted by a fluid, including atmospheric pressure. | The pressure of a fluid relative to the ambient atmospheric pressure. |
| Reference Point | Measured relative to a perfect vacuum (zero reference point). | Measured relative to the local atmospheric pressure. |
| Indication | Always positive, as it measures the total pressure including the atmospheric component. | Can be positive or negative; negative gauge pressure indicates a vacuum compared to the ambient. |
| Measurement | Includes the atmospheric pressure plus the pressure exerted by the fluid. | Excludes atmospheric pressure; it is the difference between the absolute pressure and the atmospheric pressure. |
| Typical Use | Used when it is important to have a true measurement of pressure, such as in scientific research and in conditions where vacuums are measured. | Common in everyday applications, such as tire pressure, HVAC systems, and blood pressure measurements. |
| Unit | Often still measured in pascals (Pa), bars, or psi. | Also measured in pascals (Pa), bars, or psi, but referenced as gauge (e.g., psi gauge). |
Pressure in physics is measured in pascals (Pa), where one pascal equals one newton per square meter (N/m²). Other units include atmospheres and psi.
Pressure is measured using devices like barometers, manometers, and pressure sensors, which indicate pressure by measuring the force exerted over a known area.
Pressure is the result of force distributed over an area. It increases as the force increases or as the area over which the force is applied decreases.
Any force exerted over an area creates pressure. This can be due to gravity, mechanical forces, or fluid dynamics in gases and liquids.
Pressure is crucial for understanding fluid dynamics, weather patterns, engineering applications, and many physical phenomena like buoyancy and the behavior of gases.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the SI unit of pressure?
Pascal
Bar
Atmosphere
Torr
What does one atmosphere (atm) of pressure equal in Pascals?
1.013 x 10⁵ Pa
1.013 x 10⁶ Pa
1013 Pa
1013 x 10⁴ Pa
Which instrument is commonly used to measure atmospheric pressure?
Thermometer
Barometer
Hygrometer
Anemometer
How does pressure in a fluid change with depth?
Increases with depth
Decreases with depth
Remains constant
Varies randomly
What is the relationship between pressure, force, and area?
Pressure = Force x Area
Pressure = Force / Area
Pressure = Area / Force
Pressure = Force - Area
What happens to the pressure of a gas if its volume is decreased while the temperature remains constant?
Increases
Decreases
Remains constant
Varies randomly
Which law states that the pressure of a given mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature?
Charles's Law
Boyle's Law
Gay-Lussac's Law
Avogadro's Law
How is the pressure of a gas related to its temperature at constant volume?
Directly proportio
Inversely proportional
Unrelated
Exponentially related
What is absolute pressure?
Pressure relative to atmospheric pressure
Pressure relative to a vacuum
Pressure at sea level
Pressure without any reference
What is gauge pressure?
Total pressure including atmospheric pressure
Pressure measured relative to atmospheric pressure
Pressure in a vacuum
Pressure at absolute zero
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

