What type of radiation is most penetrating and requires heavy shielding to stop?
Alpha radiation
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
Neutron radiation

Radioactivity is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves. This phenomenon occurs naturally in certain elements, such as uranium, radium, francium, astatine, polonium, and radon, as their atoms decay over time to achieve a more stable state. Radioactive Decay Law describes the rate at which these unstable nuclei disintegrate.. This process is crucial in various applications, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, and as a power source in nuclear reactors and space missions.
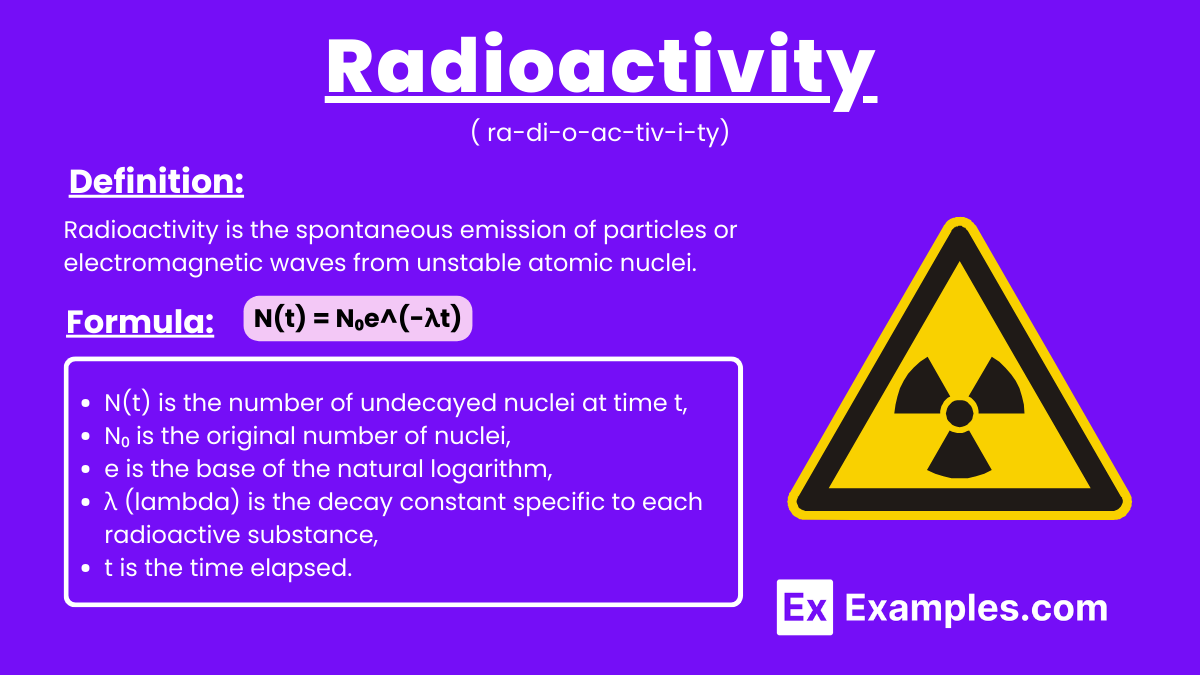
Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of particles or electromagnetic waves from unstable atomic nuclei. This process results in the release of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays, transforming the nuclei into more stable forms. Radioactivity occurs naturally in elements like uranium and can also be induced artificially, playing a vital role in medical treatments, energy production, and scientific research.
The formula that describes the rate of radioactive decay is given by:
N(t) is the number of undecayed nuclei at time t,
N₀ is the original number of nuclei,
e is the base of the natural logarithm,
λ (lambda) is the decay constant specific to each radioactive substance,
t is the time elapsed.
Here, units of radioactivity are listed below
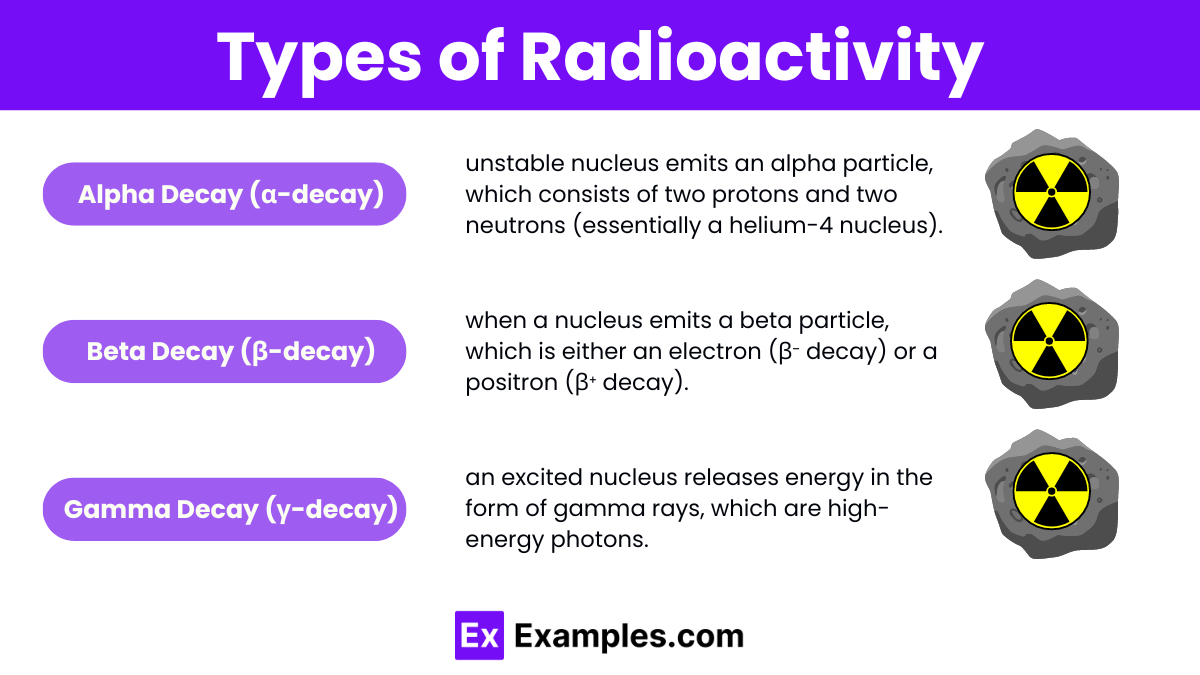
Radioactivity can be classified into four main types based on the nature of the emitted particles or radiation:
Radioactivity has a wide range of applications across various fields due to its unique properties. Here are some of the key uses:
It occurs when atomic nuclei are unstable and undergo decay to achieve a more stable state.
Alpha, beta, and gamma radiation are common types emitted during radioactive decay.
Exposure can damage cells and DNA, potentially leading to cancer or other health issues.
Rocks, soil, and cosmic rays contribute to natural background radiation.
Geiger counters and dosimeters measure radiation levels in counts per minute or sieverts.
It’s the time for half of a radioactive substance to decay into a stable form.
Splitting of atomic nuclei, releasing energy (e.g., in nuclear reactors and bombs).
Radiation is energy emitted from a source, while radioactivity involves the emission of particles or waves from atomic nuclei.
It can affect ecosystems and organisms, depending on exposure levels.
Yes, through processes like neutron bombardment or particle accelerators to create radioactive isotopes.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What type of radiation is most penetrating and requires heavy shielding to stop?
Alpha radiation
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
Neutron radiation
Which type of radioactive decay results in the emission of an electron from the nucleus?
Alpha decay
Beta-minus decay
Beta-plus decay
Gamma decay
What happens to the atomic number of an element during alpha decay?
It increases by 1
It decreases by 1
It increases by 2
It decreases by 2
Which radioactive decay process does not change the mass number of the element?
Alpha decay
Beta-minus decay
Beta-plus decay
Gamma decay
What is the typical range of alpha particles in air?
A few millimeters
A few centimeters
A few meters
A few kilometers
Which type of radioactive decay involves the emission of a positron?
Alpha decay
Beta-minus decay
Beta-plus decay
Gamma decay
In radioactive decay, what does the term "half-life" refer to?
The time taken for the radioactive element to disappear completely
The time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei to decay
The time taken for the radiation to become harmless
The time taken for the radiation to double in intensity
Which of the following particles is not involved in radioactive decay?
Neutron
Proton
Electron
Photon
Which type of radioactive radiation can be stopped by a sheet of paper?
Alpha radiation
Beta radiation
Gamma radiation
Neutron radiation
What does a Geiger counter measure?
Magnetic fields
Temperature
Radioactive radiation
Electrical current
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

