Which characteristic of a wave describes the distance between two consecutive crests?
Frequency
Amplitude
Wavelength
Speed

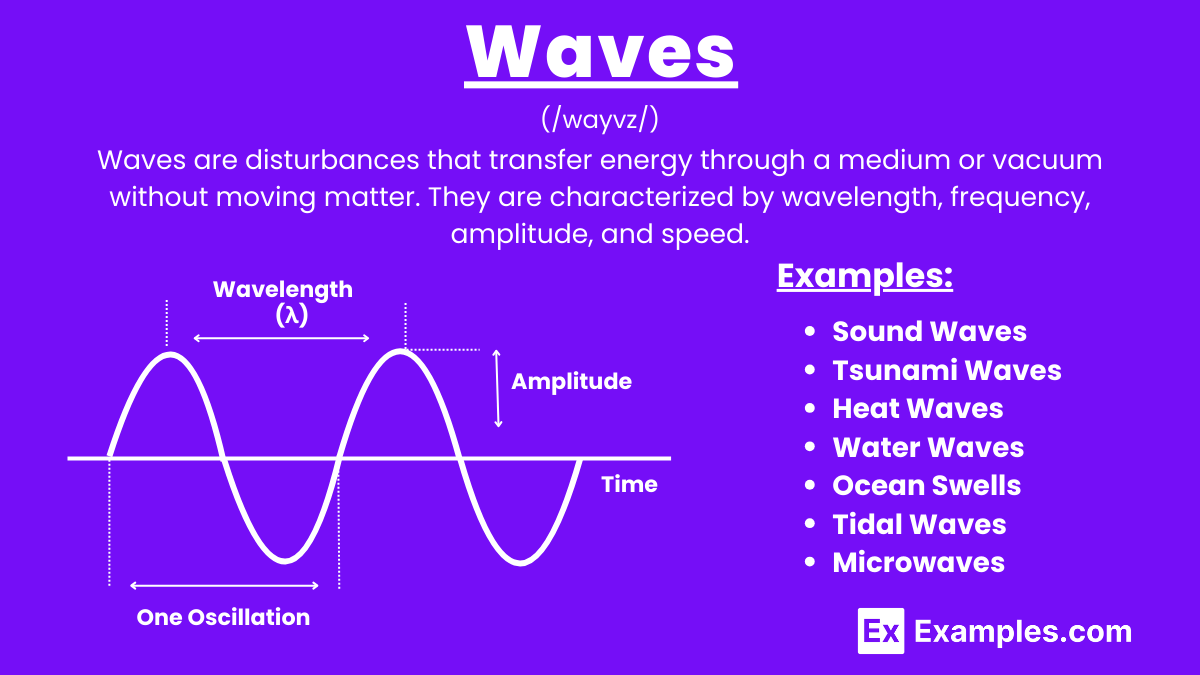
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another without the permanent displacement of the medium through which they travel. They can propagate through various mediums such as solids, liquids, and gases, and can also travel through a vacuum in the case of electromagnetic waves. Waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed. There are different types of waves, including mechanical waves like sound waves and water waves, and electromagnetic waves like light and radio waves. Waves play a crucial role in various natural phenomena and technological applications, making them fundamental concepts in physics.
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium or vacuum without moving matter. They are characterized by wavelength, frequency, amplitude, and speed. Waves can be mechanical, like sound, or electromagnetic, like light, and are essential in physics and technology.
Waves are everywhere around us, playing a crucial role in various physical phenomena and technological applications. Here are some examples of different types of waves:

Waves can be broadly categorized into several types based on their properties and the mediums through which they travel. Here are the main types of waves:
Mechanical waves require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel through.The energy is transferred from one particle to the next, allowing the wave to move through the medium. Mechanical waves are further classified into three main types: longitudinal waves, transverse waves, and surface waves.
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum. They are generated by the acceleration of charged particles and include a wide spectrum of different types of waves, each with unique properties and uses.
Matter waves, also known as de Broglie waves, refer to the wave-like behavior of particles. This concept is central to quantum mechanics and was proposed by Louis de Broglie in 1924. The fundamental idea is that all particles exhibit both particle and wave characteristics, a principle known as wave-particle duality.
Examples: Electron waves in an atom, neutron diffraction.
| Aspect | Mechanical Waves | Non-Mechanical Waves |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Waves that require a medium to travel through. | Waves that do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum. |
| Examples | Sound waves, water waves, seismic waves | Light waves, radio waves, X-rays |
| Medium Requirement | Need a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to propagate | Do not need a medium; can propagate through a vacuum |
| Type of Energy Transfer | Transfer mechanical energy through the medium | Transfer electromagnetic energy |
| Speed | Generally slower, speed depends on the medium | Generally faster, speed is the same in a vacuum (speed of light) |
| Nature of Propagation | Longitudinal or transverse | Always transverse |
| Dependence on Medium | Speed and behavior depend on the properties of the medium | Speed and behavior are independent of the medium |
| Application | Used in fields like acoustics, oceanography, and seismology | Used in fields like optics, telecommunications, and medical imaging |
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another without transferring matter. They are characterized by several fundamental properties:
In transverse waves, particle displacement is perpendicular to wave direction, while in longitudinal waves, particle displacement is parallel.
Amplitude is the maximum displacement of particles from their equilibrium position, indicating the wave’s energy.
Waves transfer energy through particle vibrations in the medium or through electromagnetic fields in a vacuum.
Reflection occurs when a wave bounces back after hitting a barrier, changing direction but staying in the same medium.
Refraction is the bending of waves as they pass from one medium to another, changing speed and direction.
Diffraction is the spreading out of waves when they pass through a small opening or around an obstacle.
Interference is the interaction of two or more waves, resulting in a new wave pattern, which can be constructive or destructive.
A standing wave is a wave that remains stationary, characterized by nodes (no movement) and antinodes (maximum movement), often formed by reflection and interference.
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves overlap, the resulting wave displacement is the sum of individual wave displacements.
Wave attenuation is the gradual loss of wave energy as it travels through a medium, resulting in a decrease in amplitude and intensity.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which characteristic of a wave describes the distance between two consecutive crests?
Frequency
Amplitude
Wavelength
Speed
What happens to the frequency of a wave if the wavelength increases while the speed remains constant?
Frequency increases
Frequency decreases
Frequency remains the same
Frequency becomes zero
Which of the following is a measure of the energy carried by a wave?
Frequency
Speed
Amplitude
Wavelength
What is the term for the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit time?
Wavelength
Amplitude
Frequency
Speed
What determines the pitch of a sound wave?
Speed
Amplitude
Wavelength
Frequency
Which type of wave requires a medium to travel through?
Electromagnetic waves
Radio waves
Sound waves
Light waves
In which medium does sound travel fastest?
Air
Water
Solid
Vacuum
Which of the following describes a wave that travels in a direction parallel to its oscillation?
Transverse wave
Longitudinal wave
Standing wave
Electromagnetic wave
In which situation would you observe constructive interference?
When two waves are out of phase
When two waves meet and cancel each other out
When two waves meet and their amplitudes add up
When a wave bounces back from a surface
What is the primary factor that affects the speed of a wave traveling through a medium?
Wavelength
Frequency
Medium's properties
Amplitude
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

