Which of the following best describes diffusion?
Movement of water across a membrane
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Active transport of ions
Movement of molecules against their concentration gradient
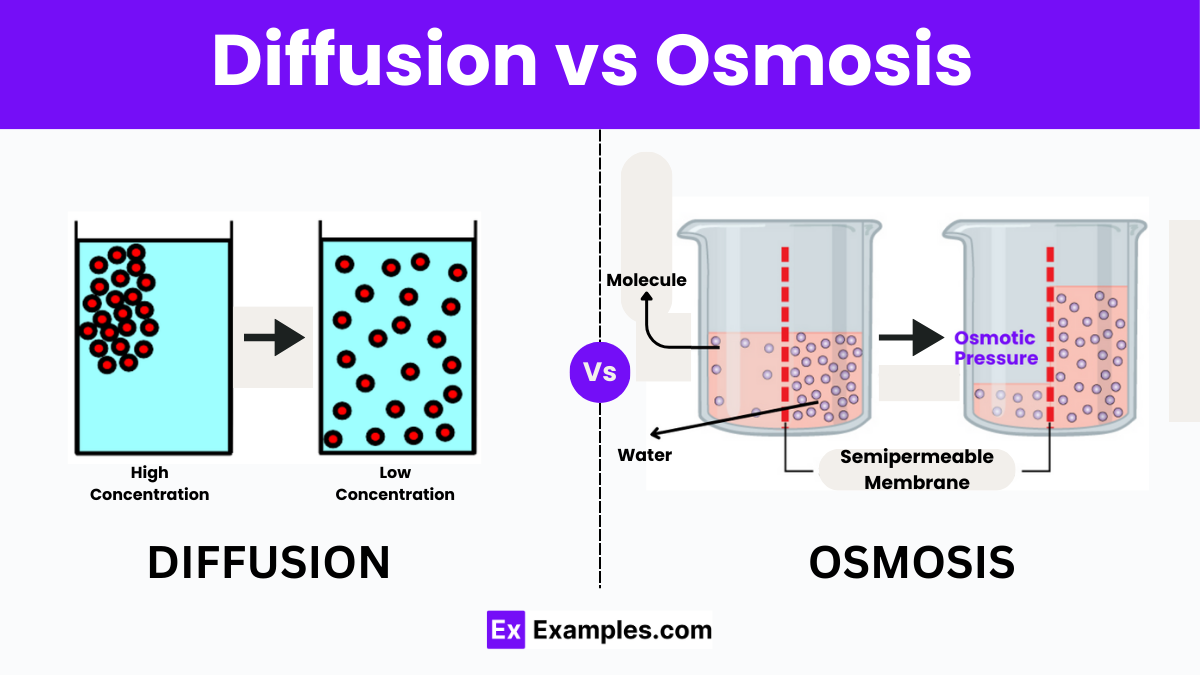
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental processes that facilitate the movement of particles in biological systems, playing crucial roles in maintaining the homeostasis of cells and organisms. Despite their similar nature in facilitating the transport of substances, they have distinct characteristics and functions. Understanding the differences between diffusion and osmosis is vital for comprehending how substances navigate through different environments, from the cellular level to whole organisms.
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium is achieved. It does not require energy and can occur in gases, liquids, and solids. Diffusion is responsible for various phenomena in nature, such as the scent of a flower spreading in the air or the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs.
Osmosis, on the other hand, is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration. Osmosis is crucial for maintaining the proper hydration and nutrient balance within cells and is fundamental to processes such as plant nutrient absorption and kidney filtration.
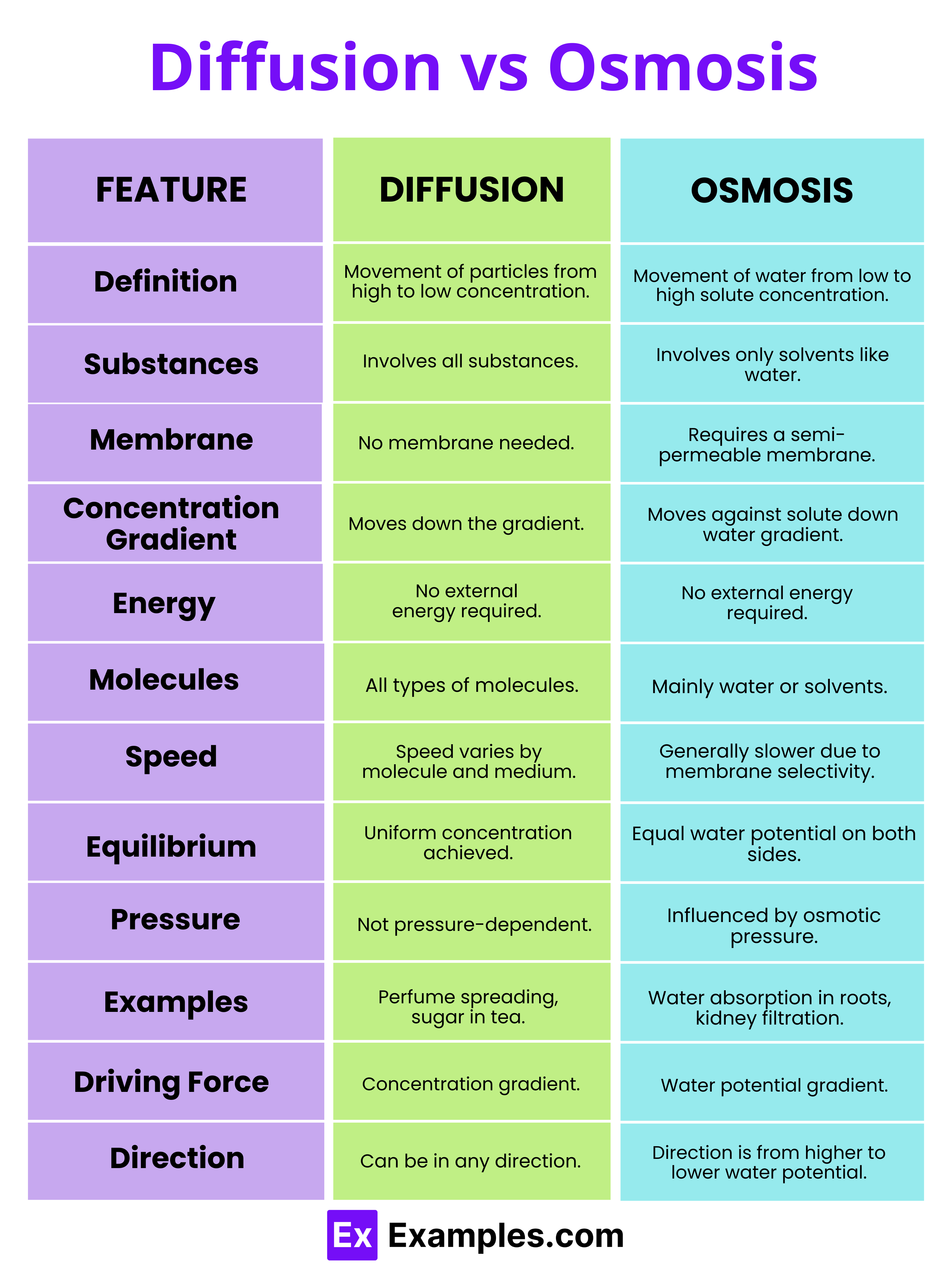
| Feature | Diffusion | Osmosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. | The movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. |
| Substances Involved | Can involve any type of substances, including gases, liquids, and solids. | Involves only water or other solvents moving through a membrane. |
| Requirement of Membrane | Does not require a membrane; can occur in free space. | Requires a semi-permeable membrane to occur. |
| Concentration Gradient | Occurs down the concentration gradient. | Occurs against the solute concentration gradient, but down the solvent (water) concentration gradient. |
| Energy Requirement | Does not require external energy; driven by the inherent kinetic energy of particles. | Does not require external energy but is influenced by the potential energy of water molecules. |
| Types of Molecules | Involves all types of molecules and ions. | Primarily involves water molecules or other solvent molecules. |
| Process Speed | Speed can vary based on the type of molecules and the medium. | Generally slower than diffusion due to the selective permeability of the membrane. |
| Equilibrium | Achieved when the concentrations become uniform throughout, without any net movement of molecules. | Achieved when the water potential on both sides of the membrane is equal, leading to no net movement of water. |
| Pressure Influence | Not directly influenced by pressure. | Osmotic pressure can influence the direction and rate of osmosis. |
| Examples | Perfume aroma spreading in a room, sugar dissolving in tea. | Absorption of water by plant roots, kidney filtration. |
Diffusion involves the spread of all substances, while osmosis specifically refers to water movement through a semi-permeable membrane.
The key difference is that osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane, whereas diffusion involves any substance spreading out.
Yes, osmosis exclusively describes the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane.
Osmosis occurs when water moves across a semi-permeable membrane to balance solute concentrations, differing from diffusion’s solute or solvent spread.
Osmosis requires a semi-permeable membrane, only involves water, and balances solute concentrations, unlike diffusion’s broader substance movement.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following best describes diffusion?
Movement of water across a membrane
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Active transport of ions
Movement of molecules against their concentration gradient
Osmosis specifically refers to the movement of:
Solutes
Solvents
Water
Gases
Which of the following is true about osmosis but not diffusion?
Involves solute molecules
Requires a semipermeable membrane
Occurs in liquids and gases
Does not require energy
During diffusion, molecules move:
Randomly
With the help of energy
Against the concentration gradient
Through protein channels only
Which process involves the movement of water molecules through aquaporins in the cell membrane?
Diffusion
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
Which of the following does not affect the rate of diffusion?
Temperature
Concentration gradient
Surface area
Light intensity
In which direction does water move during osmosis?
From high water concentration to low water concentration
From low solute concentration to high solute concentration
From high solute concentration to low solute concentration
From high to low pressure
Diffusion is crucial for which of the following processes in the human body?
Digestion
Muscle contraction
Gas exchange in the lungs
Bone growth
Which statement is true about both diffusion and osmosis?
Both require energy
Both move substances against their concentration gradient
Both require transport proteins
Both involve passive movement of molecules
What happens to a red blood cell placed in a hypertonic solution?
It swells
It shrinks
It remains the same
It bursts
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

