What happens to a cell when placed in a hypotonic solution?
It shrinks
It swells
It remains the same
It dies immediately

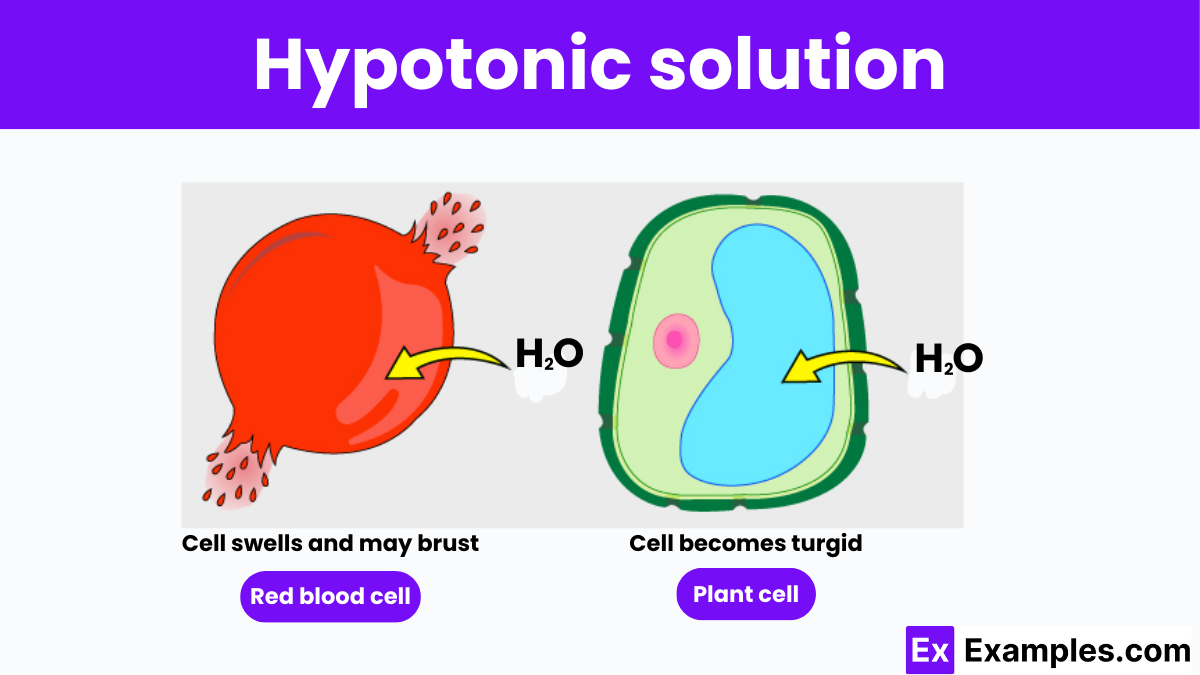
A hypotonic solution is defined by its lower concentration of solutes and higher concentration of water relative to the cytoplasm of a cell. This imbalance causes water to move into the cell through osmosis, striving to equalize solute concentrations across the cell membrane. In such conditions, cells absorb water, swell, and can potentially burst in a process known as cytolysis. The study of hypotonic solutions is crucial for comprehending how cells interact with their environment and maintain cellular health, particularly in medical and biological applications where fluid balance is key.
A hypotonic solution refers to a solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution. In the context of biology, this term is frequently discussed during the study of cell behavior in different environments.
Cells, the basic units of life, are surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, the external fluid has fewer solutes (like salt or sugar) and more water compared to the fluid inside the cell.
The key consequence of this imbalance is the movement of water into the cell through a process known as osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to one of higher solute concentration. In a hypotonic environment, water rushes into the cell because the cell’s interior is relatively saltier.
Results of Hypotonic Solutions on Cells:
A hypertonic cell refers to a cell that is placed in an environment where the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside. This results in water moving out of the cell via osmosis, causing the cell to shrink or crenate. This phenomenon is critical in various biological processes and can significantly impact cell function and health, particularly in the context of regulating cell volume and maintaining homeostasis in different environments.
When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, it is submerged in a fluid that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to the concentration inside the cell. This difference in solute concentration leads to a net movement of water into the cell through the process of osmosis.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. In the context of cells, the cell membrane acts as this semipermeable barrier.
The impact of a hypotonic solution can vary depending on whether the cell is an animal cell or a plant cell:
The turgidity achieved in plant cells is crucial for plant function. This state of turgor pressure helps maintain the plant’s rigidity and plays an essential role in the mechanical support of plants as well as in the opening and closing of stomata, which regulates gas exchange and transpiration in plants.
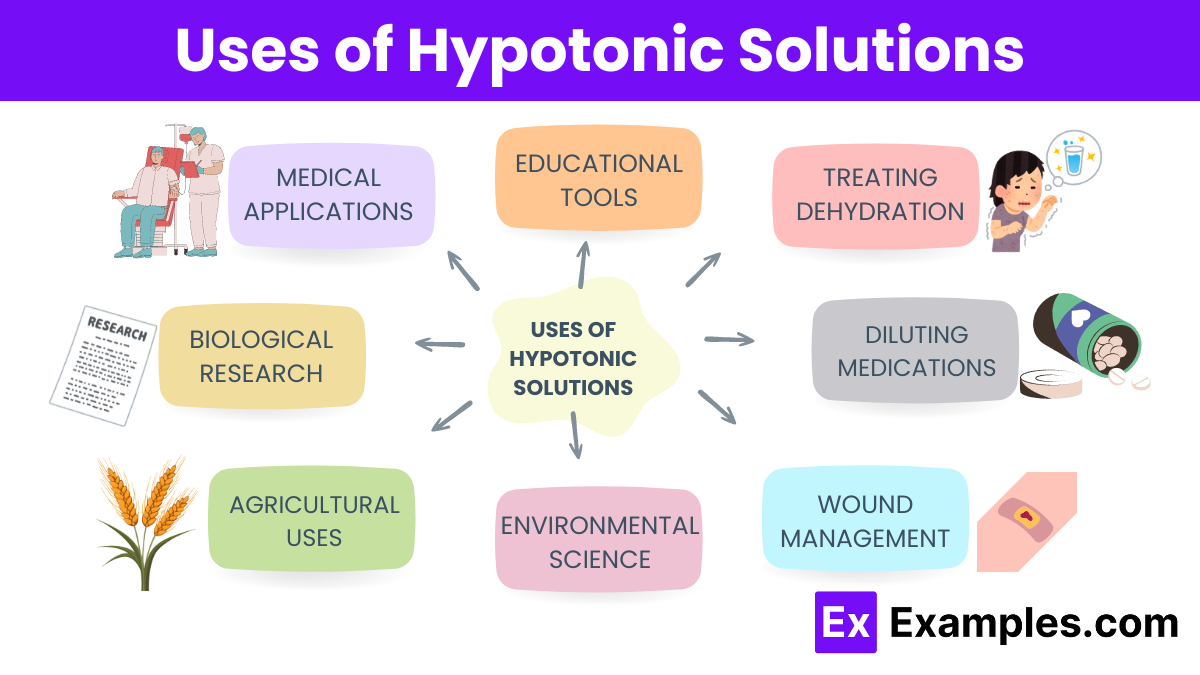
The formula for a hypotonic solution is not fixed like a chemical formula because it describes a condition relative to another environment. However, understanding its composition involves looking at the concentration of solutes it contains, which is crucial for determining its effects:
Hypotonic solutions have lower solute concentrations than the cell’s interior, causing water influx, while hypertonic solutions cause water to exit, shrinking the cell.
A common example of a hypertonic solution is sea water, which has a higher solute concentration compared to the cells of most organisms.
Examples of hypotonic IV fluids include 0.45% saline and 2.5% dextrose, which are used to hydrate cells by encouraging water intake.
0.9% NaCl (normal saline) is isotonic, meaning it has the same solute concentration as the blood and body fluids.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What happens to a cell when placed in a hypotonic solution?
It shrinks
It swells
It remains the same
It dies immediately
Which of the following best describes a hypotonic solution?
Lower concentration of solutes compared to the cell
Higher concentration of solutes compared to the cell
Equal concentration of solutes as the cell
No solutes present
In which environment will red blood cells undergo hemolysis?
Isotonic solution
Hypertonic solution
Hypotonic solution
Saturated solution
Which of the following would be an example of a hypotonic solution for a plant cell?
Distilled water
Saltwater
Sugar solution
Blood plasma
What is the primary movement of water in a hypotonic solution?
Out of the cell
Into the cell
Both in and out of the cell equally
No movement
What term describes the swelling and bursting of animal cells in a hypotonic solution?
Plasmolysis
Crenation
Hemolysis
Diffusion
What is the primary movement of water in a hypotonic solution?
Out of the cell
Into the cell
Both in and out of the cell equally
No movement
Which of the following solutions would be hypotonic to a human cell?
0.9% NaCl solution
10% NaCl solution
Pure water
5% glucose solution
What term describes the swelling and bursting of animal cells in a hypotonic solution?
Plasmolysis
Crenation
Hemolysis
Diffusion
How do plant cells respond differently than animal cells when placed in a hypotonic solution?
Both swell and burst
Plant cells burst, animal cells swell
Animal cells burst, plant cells become turgid
Both shrink
Which of the following solutions would be hypotonic to a human cell?
0.9% NaCl solution
10% NaCl solution
Pure water
5% glucose solution
What type of solution would cause a potato slice to gain weight?
Hypertonic solution
Hypotonic solution
Isotonic solution
No solution
How do plant cells respond differently than animal cells when placed in a hypotonic solution?
Both swell and burst
Plant cells burst, animal cells swell
Animal cells burst, plant cells become turgid
Both shrink
Which organelle helps plant cells maintain their structure in a hypotonic solution?
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Lysosome
What type of solution would cause a potato slice to gain weight?
Hypertonic solution
Hypotonic solution
Isotonic solution
No solution
Which organelle helps plant cells maintain their structure in a hypotonic solution?
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Lysosome
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

