Which of the following is a characteristic feature of monocotyledons?
Two seed leaves
Parallel venation in leaves
Vascular bundles in a ring
Taproot system

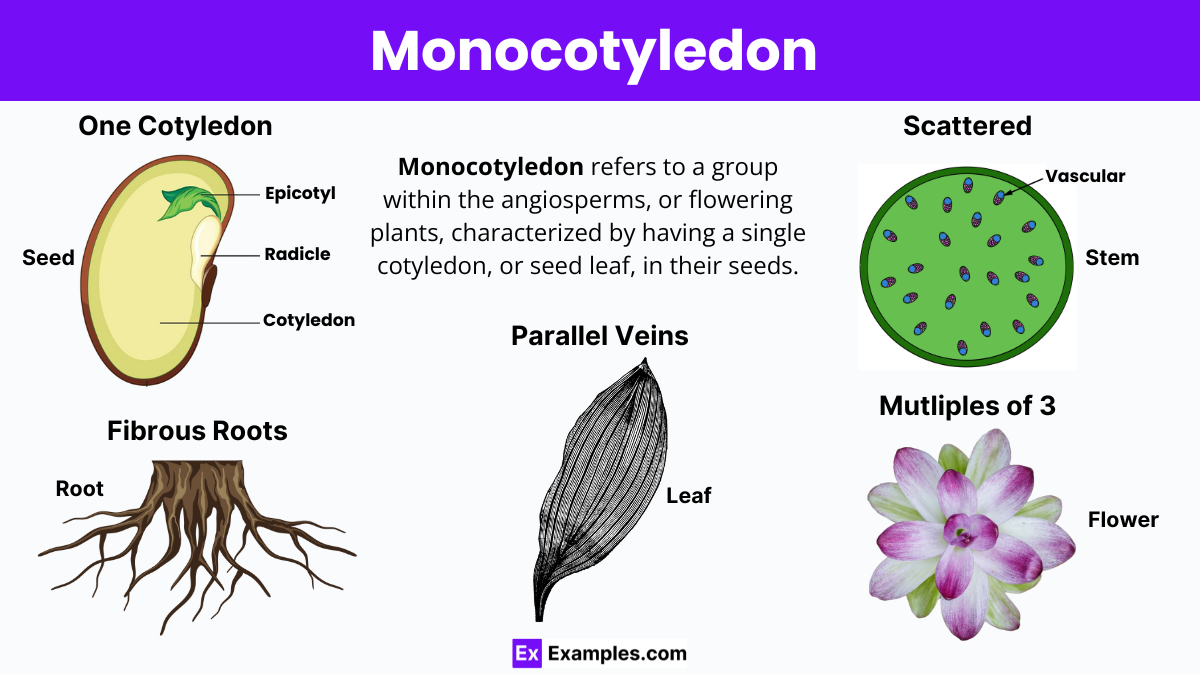
Monocotyledons, or monocots, represent one of the two major divisions of flowering plants known as angiosperms, alongside eudicotyledons (eudicots). Characterized by a single seed leaf, or cotyledon, monocots encompass approximately 60,000 species. This group includes some of the most economically significant plant families, such as Poaceae (true grasses) and Orchidaceae (orchids), the latter being the largest plant family in terms of species count. Monocots are crucial in agriculture, contributing the majority of plant biomass used globally, from cereals like rice, wheat, and maize to sugar cane and bamboo.
A monocotyledon, commonly referred to as a monocot, is a type of flowering plant (angiosperm) distinguished by having one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon, in its seed. Monocots are notable for their parallel leaf veins and floral structures typically arranged in multiples of three, encompassing a diverse array of plants including grains, palms, and orchids.
Identifying monocotyledons, or monocots, involves observing several distinct botanical characteristics. These traits help distinguish monocots from dicots, the other major group of flowering plants. Here’s how to identify a monocot based on key features:
1. Single Cotyledon:
2. Leaf Veins:
3. Floral Structure:
4. Root System:
5. Stem Structure:
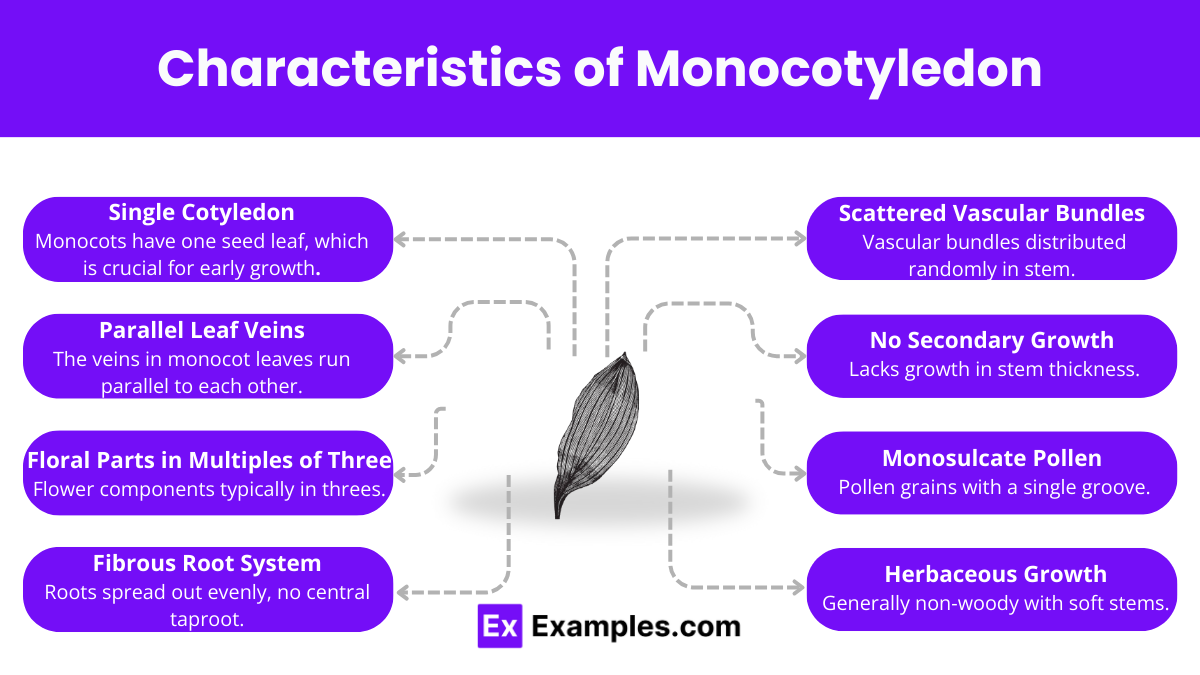
Monocotyledons have one cotyledon, parallel leaf veins, and floral parts in multiples of three, while dicotyledons typically feature two cotyledons, netted veins, and floral parts in fours or fives.
A monocotyledon, or monocot, is a type of flowering plant characterized by one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon, parallel leaf veins, and floral structures in multiples of three.
Identify monocots by their single cotyledon, parallel leaf veins, fibrous root systems, floral parts in multiples of three, and scattered vascular bundles in the stem.
Ten examples of monocots include wheat, corn, rice, bamboo, palm trees, lilies, orchids, tulips, bananas, and garlic.
Five common monocots are wheat, corn, rice, bamboo, and orchids, each significant in agriculture, horticulture, and ecological systems.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of monocotyledons?
Two seed leaves
Parallel venation in leaves
Vascular bundles in a ring
Taproot system
Which plant is an example of a monocotyledon?
Rose
Maple
Corn
Sunflower
Monocotyledons usually have flower parts in multiples of:
Two
Three
Four
Five
What type of root system is commonly found in monocotyledons?
Taproot system
Fibrous root system
Adventitious root system
None of the above
Which of the following is NOT a monocotyledon?
Lily
Wheat
Orchid
Oak
In monocotyledons, the arrangement of vascular bundles in the stem is:
In a ring
Scattered throughout the stem
Only in the center
In concentric circles
Which of these grains is a monocotyledon?
Rice
Barley
Oat
All of the above
Monocotyledons are part of which plant class?
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Bryophytes
Pteridophytes
Which feature distinguishes monocotyledons from dicotyledons?
Presence of seeds
Number of cotyledons
Type of chlorophyll
Mode of reproduction
Which monocotyledon is widely used as a staple food crop?
Potato
Maize
Bean
Tomato
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

