25+ Customer Journey Map Examples to Download
A Customer Journey Map is a strategic tool that visually maps the customer’s experience with a product or service across multiple touchpoints and interactions. It delineates the stages a customer progresses through, from initial awareness to post-purchase support, pinpointing pain points, opportunities for improvement, and instances of delight. Utilizing this management approach, businesses can pinpoint critical areas for optimization, improve customer satisfaction, and develop more personalized and seamless experiences. These enhancements are key to driving loyalty and retention, effectively aligning with broader business strategies for customer relationship management.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation illustrating the step-by-step experience a customer goes through when interacting with a product or service, highlighting key touchpoints and emotions.
Examples Of Customer Journey Map
- E-commerce Website: Journey from website visit to post-purchase feedback.
- Retail Store: Experience from entering the store to returning items.
- Mobile App: From download to regular use and updates.
- Subscription Services: From free trial through subscription upgrades to cancellation.
- Banking Services: Account opening, using online banking, and loan applications.
- Healthcare Services: Patient journey from appointment scheduling to follow-up.
- Travel and Tourism: Booking, traveling, and post-trip feedback.
- Insurance Claims: Claim filing to payment and post-claim service.
- Automotive Sales: Research, dealership visit, purchase, and after-sales.
- Real Estate: From house hunting to buying and moving in.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Free trial to subscription renewal and upsell.
- Education: Student enrollment, learning, graduation, and alumni involvement.
- Restaurant Dining: From reservation to dining and posting a review.
- Utility Services: Service connection to billing and service termination.
- Telecommunications: Plan selection, device purchase, and troubleshooting.
- Event Planning: Ticket purchase to post-event engagement.
- Public Transportation: Planning, ticketing, travel, and feedback.
- Fitness Club: Signing up, regular visits, and membership renewal.
- Pet Adoption: Adoption process and post-adoption support.
- Library Services: Membership, borrowing, event participation.
- Beauty Salon: Booking, service, product purchase, and rebooking.
- Home Improvement Projects: Research to project completion and follow-up.
- Legal Consultation Services: Initial inquiry to case resolution.
- Non-Profit Donor Engagement: Donation process to long-term support.
- Luxury Goods Shopping: Product discovery to after-sales care.
- Digital Marketing Campaigns: Targeting to campaign analysis and conversion.
Key Elements of Customer Journey Maps
- Persona: Profiles representing different customer segments.
- Touchpoints: Interactions between the customer and the business.
- Emotions: Feelings experienced at each touchpoint.
- Stages: Phases of the journey, from awareness to post-purchase.
- Channels: Communication mediums used by customers.
- Pain Points: Challenges or frustrations encountered.
- Opportunities: Moments for improvement or enhancement.
- Metrics: Data to measure success and identify areas for optimization.
Elements of a Customer Journey Map
- Customer Personas: Detailed profiles of the target customer that represent different segments of the user base.
- Stages of the Journey: The key phases a customer goes through in a nonprofit context, from becoming aware of the organization to post-donation activities. These stages can include awareness, consideration, decision, retention, and advocacy.
- Customer Touchpoints: Specific interactions the customer has with the business during their journey. This can include visits to a website, interactions with sales personnel, or usage of the product.
- Customer Emotions: The feelings and emotional states experienced by the customer at various points in the journey. Highlighting these can help identify areas needing improvement.
- Pain Points and Challenges: Difficulties or frustrations that customers face during their interaction with the brand, which might deter them from continuing the relationship.
- Opportunities: Potential areas for improvement or innovation that can enhance the customer experience.
- Channels and Resources: The various mediums through which interactions take place, such as in-store, online, mobile, or through customer service.
- Metrics: Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that measure the success of customer interactions at various stages.
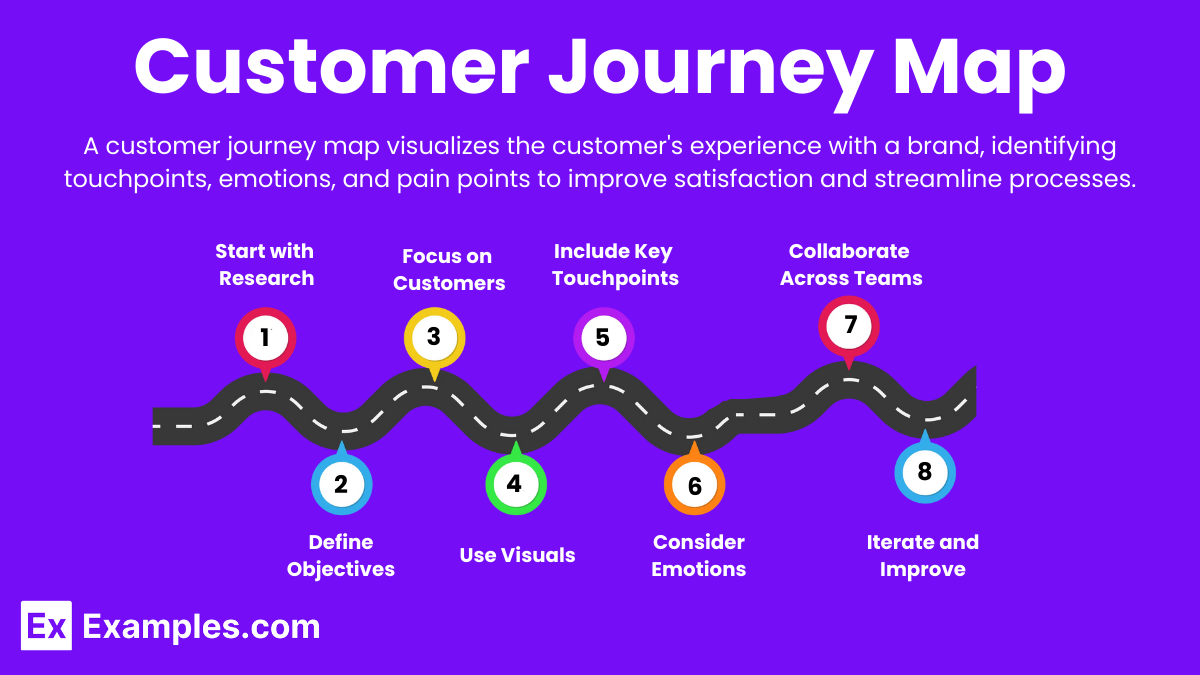
Rules for Creating Successful Journey Maps
- Start with Research: Gather data on customer behavior, preferences, and pain points.
- Define Objectives: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with the map.
- Focus on Customers: Keep the customer perspective central throughout the mapping process.
- Use Visuals: Create visual representations that are easy to understand and engage with.
- Include Key Touchpoints: Highlight critical interactions across the entire journey.
- Consider Emotions: Capture the emotional highs and lows experienced by customers.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Involve stakeholders from various departments to ensure comprehensive insights.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously update and refine journey maps based on feedback and evolving customer needs.
Customer Journey Stages
Awareness: Customers become aware of a product, service, or brand through various channels such as advertising, social media, or word-of-mouth.
Consideration: Customers research and evaluate different options, comparing features, prices, and reviews to make an informed decision.
Decision: Customers make a purchase decision, selecting the product or service that best meets their needs and preferences.
Purchase: Customers complete the transaction, whether online, in-store, or through other channels, to acquire the chosen product or service.
Post-Purchase Experience: After the purchase, customers experience the product or service, seeking support, using it, and forming opinions based on their experience.
Loyalty and Advocacy: Satisfied customers may become loyal to the brand, repurchasing products and advocating for it through positive reviews, referrals, or social media engagement.
Why is customer journey mapping important?
- Understanding Customer Needs: It helps businesses gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, pain points, and motivations throughout the entire journey.
- Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities: By visualizing the customer experience, businesses can pinpoint areas of friction, gaps in service, and opportunities for improvement.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Journey maps enable businesses to design and deliver more seamless, personalized, and satisfying experiences at every touchpoint, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Aligning Cross-Functional Teams: Journey mapping fosters collaboration across departments by providing a shared understanding of the customer journey, incorporating feedback, and encouraging teams to work together to address customer needs and deliver consistent experiences.
- Optimizing Marketing and Sales Efforts: It helps businesses tailor marketing messages, sales strategies, and product offerings to better align with customer needs and preferences at each stage of the journey, optimizing the budget allocation for maximum impact.
- Driving Business Growth:By enhancing the overall customer experience through journey mapping, businesses can achieve increased customer retention, higher conversion rates, and ultimately drive sales, business growth, and profitability.
Using a customer journey map to improve the customer experience
- Identify Pain Points: By mapping out the customer journey, you can clearly see where customers encounter problems or frustrations. These pain points can then be targeted for improvement, whether they’re related to service, product usability, or communication.
- Enhance Customer Touchpoints: Each touchpoint represents an opportunity to improve the customer’s impression of your brand. Analyzing these touchpoints through the journey map allows you to refine interactions to ensure they are as effective and pleasant as possible.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Understanding the critical stages of the customer journey helps businesses prioritize where to allocate resources for the greatest impact. For example, if many customers drop off at a specific stage, you can invest more in that area to improve retention.
- Personalize Customer Interactions: Customer journey maps often incorporate customer personas, which help in tailoring interactions to meet the specific needs and preferences of different customer segments. This personalization can lead to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Streamline Processes: A detailed map can reveal redundancies or inefficiencies in how customers are handled across different channels. Streamlining these processes can improve the overall customer experience and reduce operational costs.
What should be included in a customer journey map template?
- Define Objectives and Scope: Determine what you want to achieve and the focus of the journey map (product, service, or entire brand experience).
- Develop Customer Personas: Create profiles for your target customers, incorporating demographics, behaviors, and needs.
- Map the Journey Stages: Outline the key stages of the customer experience, from awareness to advocacy.
- Identify Touchpoints and Assess Interactions: Document where and how customers interact with your brand at each stage, analyzing actions, emotions, and pain points.
- Analyze and Optimize: Use the insights to propose actionable improvements, implement changes, and track their impact on customer satisfaction and other metrics.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
| Aspect | Customer Journey | Buyer Journey |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Encompasses the entire lifecycle of a customer with a brand. | Primarily focused on the process leading to a purchase. |
| Scope | Includes awareness, purchase, and post-purchase stages. | Mainly includes the stages before the purchase: awareness, consideration, and decision. |
| Objective | To enhance overall customer satisfaction and loyalty. | To drive sales and conversions. |
| Stages | Awareness, consideration, purchase, retention, and advocacy. | Awareness, consideration, and decision. |
| Key Concerns | Long-term relationship building, customer service, loyalty. | Product features, price comparison, and value proposition. |
| Metrics | Customer satisfaction, retention rates, lifetime value. | Conversion rates, cost per acquisition, sales metrics. |
| Interactions | Includes all touchpoints: pre-purchase, during purchase, and post-purchase. | Focuses on touchpoints that lead to purchasing decisions. |
Benefits of a Customer Journey Map
- Enhanced Customer Understanding: Gains insight into customer needs and experiences at various stages.
- Identification of Pain Points: Detects specific areas where customers encounter difficulties or frustrations.
- Improved Customer Engagement: Tailors communication strategies to meet customer needs effectively at different journey points.
- Streamlining of Operations: Identifies and eliminates inefficient processes that impact the customer experience.
- Higher Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Enhances overall satisfaction, increasing customer loyalty and promoting positive word-of-mouth.
What’s the first step in creating a customer journey map?
Define the scope and goals of the map.
How does a customer journey map help reduce churn?
By identifying and addressing critical pain points that lead to customer drop-offs.
Can a customer journey map impact revenue?
Yes, by enhancing customer experiences and improving conversions.
Should customer feedback be included in a customer journey map?
Absolutely, as it provides insight into customer satisfaction and pain points.
What is the role of metrics in a customer touchpoint?
Metrics help measure the success of interactions and guide improvements.
How does a customer journey map differ for B2B versus B2C?
B2B maps typically involve more decision-makers and longer cycles.
Is there a universal template for customer journey maps?
No, but many follow similar structures adapted to specific business needs.
How can a customer journey map facilitate cross-functional collaboration?
By aligning various departments around a common understanding of the customer experience.
What outcomes should you expect from a good customer journey map?
Improved customer engagement, satisfaction, and organizational efficiency.
How does technology affect the construction of a customer journey map?
Advances in analytics and digital tools enhance accuracy and insights.
What’s the ultimate goal of using a customer journey map?
To continuously improve the entire customer experience across all touchpoints.