30+ Deductive Reasoning Examples
Deductive reasoning stands as a powerful logical process that starts with a general theory and moves toward a specific conclusion. It relies on the structure and validity of the premises to ensure that the conclusion is true if the premises are true. This method forms the backbone of many scientific and mathematical theories, offering a clear and predictable path from hypothesis to verification. Deductive reasoning helps us navigate complex information by providing a systematic way to draw conclusions from given facts, making it an indispensable tool in many academic fields and everyday decision-making processes.
What is Deductive Reasoning?
Deductive Reasoning Examples

- All birds have feathers, and a robin is a bird. Therefore, a robin has feathers.
- All mammals breathe air. A dolphin is a mammal. Therefore, a dolphin breathes air.
- If all cars have wheels and a Tesla is a car, then a Tesla has wheels.
- Water boils at 100°C. The temperature of the kettle’s water is at 100°C. Therefore, the water in the kettle is boiling.
- All humans are mortal. Socrates is human. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.
- No reptiles have fur. A lizard is a reptile. Therefore, a lizard does not have fur.
- All squares have four sides. This shape is a square. Therefore, this shape has four sides.
- If someone is a teacher, they must have a teaching degree. Maria is a teacher. Therefore, Maria has a teaching degree.
- To legally drive a car, one must have a driver’s license. John is driving a car. Therefore, John has a driver’s license.
- All roses need sunlight to grow. This plant is a rose. Therefore, it needs sunlight to grow.
- All planets orbit a star. Earth is a planet. Therefore, Earth orbits a star.
- Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. A ball is thrown against a wall. Therefore, the ball will bounce back.
- If you save money, your bank balance increases. Alice saves money every month. Therefore, Alice’s bank balance increases every month.
- All bachelors are unmarried men. Tom is a bachelor. Therefore, Tom is an unmarried man.
- All Olympic sprinters run fast. Usain Bolt is an Olympic sprinter. Therefore, Usain Bolt runs fast.
- If the light switch is off, the light will not be on. The light switch is off. Therefore, the light is not on.
- All iPhones use iOS as their operating system. My phone is an iPhone. Therefore, my phone uses iOS.
- Vegetarians do not eat meat. Sarah is a vegetarian. Therefore, Sarah does not eat meat.
- All prime numbers greater than 2 are odd. 17 is a prime number greater than 2. Therefore, 17 is odd.
- If it is raining, the ground is wet. It is raining. Therefore, the ground is wet.
- All chefs can cook. Lisa is a chef. Therefore, Lisa can cook.
- All fish live in water. A salmon is a fish. Therefore, a salmon lives in water.
- If the sun rises, it is day. The sun has risen. Therefore, it is day.
- All psychologists study behavior. Dr. Lee is a psychologist. Therefore, Dr. Lee studies behavior.
- Only students can borrow books from the school library. Jake has borrowed a book from the school library. Therefore, Jake is a student.
- All citizens of a country have the right to vote there. Emily is a citizen of Canada. Therefore, Emily has the right to vote in Canada.
- Every square is a rectangle with equal sides. This rectangle has equal sides. Therefore, this rectangle is a square.
- If an animal is a bird, it lays eggs. An eagle is a bird. Therefore, an eagle lays eggs.
- All governments have laws. The government of France exists. Therefore, the government of France has laws.
- If a number is divisible by two, it is even. 8 is divisible by two. Therefore, 8 is even.
Deductive Reasoning Examples in Everyday Life
- Solving Puzzles: When you’re working on a puzzle, such as a Sudoku or a logic grid puzzle, you use deductive reasoning to eliminate possibilities and narrow down the potential solutions until you find the correct one.
- Making Decisions: Imagine you’re trying to decide what to wear based on the weather forecast. If the forecast predicts rain, you deduce that you should bring an umbrella or wear waterproof clothing to stay dry.
- Cooking: When following a recipe, you often use deductive reasoning to understand how ingredients and cooking methods interact. For example, if a recipe calls for baking soda and you know that it reacts with acidic ingredients to produce carbon dioxide, you deduce that there must be an acidic component in the recipe to activate the baking soda.
- Navigation: When driving or navigating a new area, you might use deductive reasoning to determine the correct route. If you know that your destination is south of your current location, you deduce that you need to travel in a southerly direction.
- Problem-Solving: In troubleshooting situations, deductive reasoning helps identify the root cause of a problem by systematically eliminating potential causes based on evidence and logical analysis.
- Shopping: When comparing prices or evaluating product features, you might use deductive reasoning to determine which option offers the best value for your money. For example, if two similar products have different prices, you might deduce that the cheaper one offers better value unless there are significant differences in quality.
- Legal Reasoning: Lawyers use deductive reasoning to build arguments and make cases based on existing laws, precedents, and evidence. They systematically analyze the facts of a case to draw logical conclusions and support their arguments.
- Scientific Inquiry: Scientists use deductive reasoning to formulate hypotheses and design experiments. They make predictions based on existing theories and evidence, then test those predictions to either support or refute the hypothesis.
Examples in Literature
- Detective Fiction: In addition to Sherlock Holmes, Agatha Christie’s Hercule Poirot and Miss Marple series also heavily rely on deductive reasoning. These detectives systematically analyze clues, question suspects, and use logical deduction to unravel complex mysteries.
- Literary Analysis: Scholars and students of literature often use deductive reasoning to analyze texts and interpret their meaning. They gather evidence from the text, such as character actions and dialogue, narrative structure, and thematic elements, then draw logical conclusions about the author’s intended message or symbolism.
Examples in Education
- Mathematics: In advanced mathematics, deductive reasoning is used to prove complex theorems and conjectures. Mathematicians construct rigorous logical arguments, starting from basic axioms and definitions, to establish the validity of mathematical statements.
- Problem-Based Learning: Educators employ deductive reasoning in problem-based learning approaches, where students are presented with real-world problems and tasked with identifying solutions through logical analysis and inquiry. Students develop critical thinking skills by systematically evaluating information, identifying patterns, and formulating solutions based on deductive reasoning.
Examples in Healthcare
- Diagnosis: Healthcare professionals not only rely on deductive reasoning but also use differential diagnosis, a systematic method to identify the most likely cause of a patient’s symptoms by considering all possible explanations and eliminating unlikely ones through deductive logic.
- Treatment Planning: In addition to deductive reasoning, healthcare providers also consider evidence-based practice when developing treatment plans. They integrate clinical expertise with the best available research evidence and patient preferences to make informed decisions about the most effective treatments for individual patients.
Examples in Science
- Hypothesis Testing: Scientists use deductive reasoning not only in experimental research but also in theoretical modeling. Theoretical physicists, for example, use deductive logic to derive mathematical equations that describe physical phenomena, allowing them to make predictions that can be tested experimentally.
- Data Analysis: In scientific fields such as biology and psychology, deductive reasoning is used to analyze research data and draw conclusions. Researchers apply statistical methods and logical reasoning to interpret data, identify patterns, and draw inferences about the underlying mechanisms or relationships being studied.
Types of Deductive Reasoning
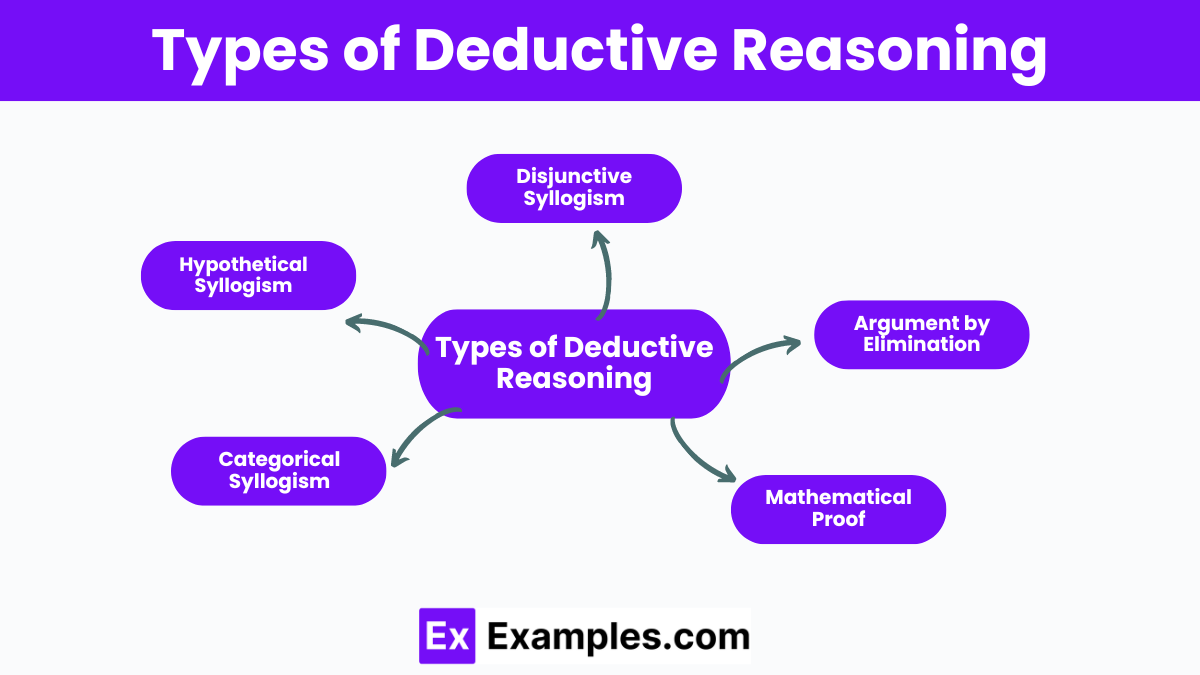
Deductive reasoning is a logical process where one draws a conclusion based on premises that are generally assumed to be true. There are several types of deductive reasoning:
- Categorical Syllogism: This type of deductive reasoning involves drawing conclusions about categorical propositions. These propositions typically use statements like “all,” “some,” or “none” to describe relationships between categories. For example, if all humans are mortal and Socrates is human, then it follows deductively that Socrates is mortal.
- Hypothetical Syllogism: In hypothetical syllogism, the reasoning involves conditional statements. If “if-then” statements are true, then the conclusion can be drawn deductively. For instance, if A implies B, and B implies C, then A implies C.
- Disjunctive Syllogism: This type of deductive reasoning involves a disjunction, which means a logical “or” statement. If one of the options is eliminated, then the conclusion can be drawn based on the remaining options. For example, if it’s either raining or sunny, and it’s not raining, then it must be sunny.
- Argument by Elimination: In this type, potential explanations or options are systematically eliminated until only one possibility remains, which is then concluded to be true. For instance, if a detective eliminates all suspects but one, then that remaining suspect must be the culprit.
- Mathematical Proof: Mathematical proofs are a form of deductive reasoning where conclusions are derived from axioms and previously proven theorems using logical steps. Each step follows from the previous ones with certainty, leading to a final conclusion.
These types of deductive reasoning are essential tools in various fields such as mathematics, philosophy, science, and everyday problem-solving. They help ensure logical consistency and validity in arguments and conclusions.
When to Use
Deductive reasoning is particularly useful in situations where you need to draw specific conclusions from general principles or premises. Here are some scenarios where deductive reasoning is commonly applied
- Formal Logic: Deductive reasoning forms the backbone of formal logic systems. It’s used in mathematical proofs, computer programming, and philosophical arguments where precise, step-by-step reasoning is required.
- Problem-Solving: When faced with a problem that can be broken down into a series of logical steps, deductive reasoning helps in systematically arriving at a solution. This is common in fields like mathematics, engineering, and scientific research.
- Decision Making: Deductive reasoning can aid decision-making processes by allowing individuals to assess the logical implications of various choices. For example, in business strategy, deductive reasoning might be used to predict the outcomes of different courses of action.
- Legal Reasoning: Deductive reasoning is crucial in legal contexts, where lawyers and judges must analyze laws and precedents to reach logical conclusions about guilt, innocence, liability, and other legal matters.
- Education: In education, deductive reasoning is often used to teach students critical thinking skills. By presenting them with general principles and guiding them through logical deductions, educators help students understand how to draw conclusions based on evidence and reasoning.
- Scientific Method: Deductive reasoning plays a role in the scientific method, where hypotheses are formulated based on existing theories and then tested through experimentation. Scientists use deductive reasoning to make predictions about the outcomes of experiments and observations.
- Policy Making: Policymakers often use deductive reasoning to assess the potential effects of proposed policies. By analyzing how these policies align with broader principles or objectives, policymakers can anticipate their likely impact on society.
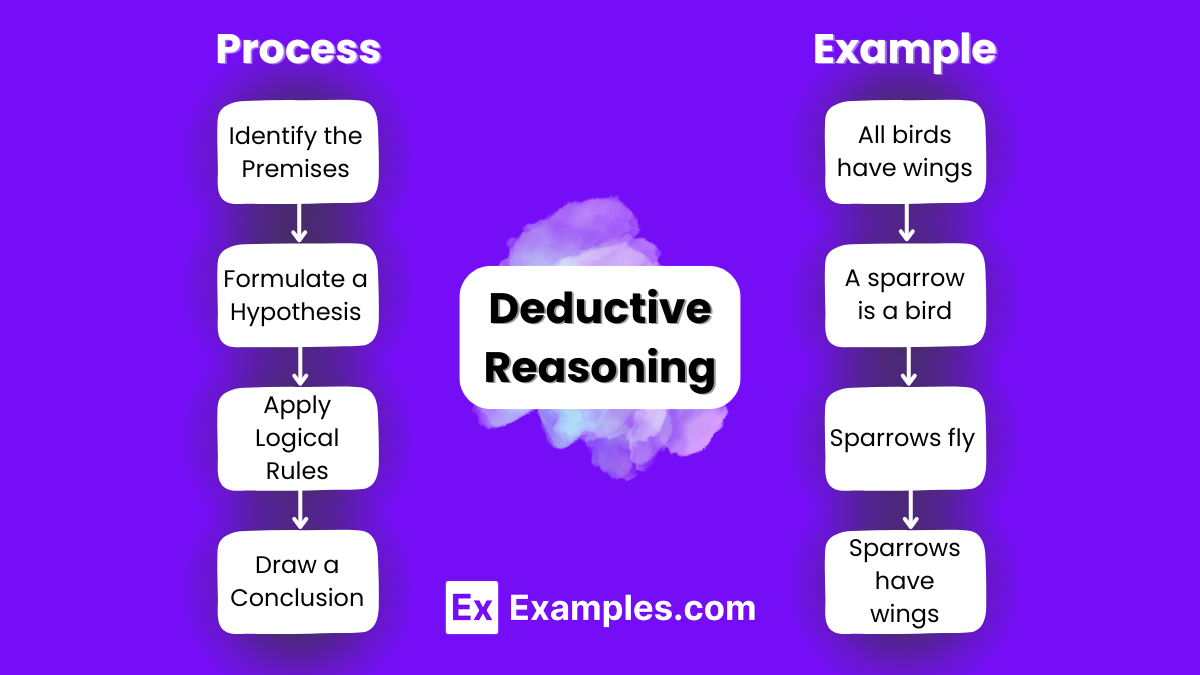
How does Deductive Reasoning work? – Process
Deductive reasoning follows a structured process to draw logical conclusions from given premises. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how deductive reasoning works
- Establish Premises: Deductive reasoning begins with the identification of one or more premises, which are statements or assertions assumed to be true. These premises serve as the starting point for the logical deduction process.
- Identify Relevant Principles or Rules: Next, the reasoner identifies any relevant principles, rules, or generalizations that apply to the premises. These principles provide the logical framework for deriving conclusions.
- Formulate Hypothesis or Prediction: Based on the premises and relevant principles, the reasoner formulates a hypothesis or prediction about a specific outcome or scenario. This hypothesis represents the conclusion that the reasoning process aims to validate.
- Apply Logical Rules: Deductive reasoning relies on the application of logical rules to draw conclusions. These rules include principles of inference such as modus ponens (if A implies B, and A is true, then B must be true) and modus tollens (if A implies B, and B is false, then A must be false).
- Make Deductive Inferences: Using the premises and logical rules, the reasoner makes deductive inferences to determine whether the hypothesis logically follows from the premises. This involves systematically deriving intermediate conclusions based on the premises and principles.
- Evaluate Validity: The reasoner evaluates the validity of the deductive inferences to ensure that each step in the reasoning process follows logically from the previous steps. This involves checking for logical consistency and coherence throughout the deduction.
- Draw Conclusion: If the deductive inferences lead to a logically valid conclusion that aligns with the hypothesis, the reasoner accepts the conclusion as true. This conclusion represents the logical consequence of the premises and principles involved in the reasoning process.
- Assess Certainty: Finally, the reasoner assesses the certainty or confidence level associated with the conclusion. While deductive reasoning aims to derive conclusions with certainty, the strength of the conclusion may vary depending on the clarity and reliability of the premises and principles.
Tips and Techniques
- Understand the Structure: Recognize the structure of deductive arguments, including premises and conclusions. Being able to identify and analyze these elements will help you evaluate the validity of arguments.
- Clarify Assumptions: Identify any assumptions underlying the premises of an argument. Questioning these assumptions can help uncover potential flaws in reasoning.
- Practice with Examples: Work through examples of deductive reasoning problems to become more familiar with different types of arguments and how to approach them.
- Use Visual Tools: Diagrams, charts, and visual representations can sometimes clarify complex deductive arguments, especially in fields like logic and mathematics.
- Master Logical Connectives: Understand how words like “if-then,” “and,” “or,” and “not” affect the logical structure of arguments. Practice translating statements into logical forms.
- Be Systematic: Approach deductive reasoning systematically, breaking down arguments into smaller components and evaluating each part individually.
- Check for Validity: Assess the validity of deductive arguments by determining whether the conclusion necessarily follows from the premises. Look for logical fallacies or errors in reasoning.
- Practice Critical Thinking: Develop critical thinking skills by questioning assumptions, considering alternative explanations, and evaluating evidence objectively.
- Study Logic: Familiarize yourself with basic principles of logic, such as modus ponens, modus tollens, and other logical rules and fallacies.
- Seek Feedback: Discussing deductive reasoning problems with others or seeking feedback on your solutions can help you refine your skills and identify areas for improvement.
Deductive Reasoning vs Inductive Reasoning
| Aspect | Deductive Reasoning | Inductive Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Definition | Moves from general principles to specific instances. | Moves from specific instances to general principles. |
| Logic | Follows a top-down approach. | Follows a bottom-up approach. |
| Validity of Conclusion | If premises are true, the conclusion must be true. | Conclusion is probable based on premises. |
| Certainty | Provides certainty in conclusions. | Provides probability in conclusions. |
| Examples | All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal. | Every swan I have seen is white. Therefore, all swans are white (which might not be true). |
| Nature of Reasoning | Starts with general principles, then applies them to specific cases. | Starts with specific observations, then forms general principles. |
| Used in | Mathematics, logic, philosophy, etc. | Scientific research, everyday observations, data analysis, etc. |
Inductive Reasoning
- Definition: Inductive reasoning is a logical process where one makes generalizations based on specific observations or evidence. It involves moving from specific instances to broader generalizations or theories.
- Structure: Inductive reasoning follows a bottom-up approach. It begins with specific observations or evidence and then draws broader conclusions or generalizations based on patterns observed in the data. Unlike deductive reasoning, the conclusions of inductive reasoning are not guaranteed to be true.
- Certainty: Inductive reasoning provides probabilistic conclusions. The conclusions are based on observed patterns or evidence, but there’s always a degree of uncertainty. Inductive conclusions may be strong or weak depending on the quality and quantity of evidence available.
- Examples:
- Every observed raven is black. (Observation)
- Therefore, all ravens are black. (Inductive generalization)
Deductive Reasoning In Various Fields
- Mathematics: In mathematics, deductive reasoning is used extensively in proofs. Mathematicians start with axioms and then use logical arguments to derive theorems and corollaries. Each step in a mathematical proof must follow logically from the previous steps, based on established rules of inference.
- Logic and Philosophy: Deductive reasoning is central to both logic and philosophy. Philosophers use deductive reasoning to construct arguments and evaluate the validity of conclusions. Logical syllogisms, such as “All humans are mortal, Socrates is a human, therefore Socrates is mortal,” illustrate deductive reasoning in action.
- Science: In science, deductive reasoning is used to formulate hypotheses and predictions based on existing theories or observations. Scientists develop hypotheses deductively and then conduct experiments or make observations to test them. If the observations match the predictions, it provides support for the hypothesis.
- Law and Legal Reasoning: Deductive reasoning plays a crucial role in legal reasoning and argumentation. Legal professionals construct arguments based on statutes, precedents, and legal principles to arrive at conclusions about a case. Judges apply deductive reasoning to interpret laws and make decisions in court.
- Computer Science and Programming: Deductive reasoning is employed in programming and software development to design algorithms and solve problems. Programmers use logical reasoning to develop code that follows a series of steps to achieve a specific outcome. Debugging involves deductive reasoning to identify and correct logical errors in code.
- Education and Pedagogy: Educators use deductive reasoning to structure lesson plans and teaching materials. They often present concepts in a logical sequence, starting with general principles and moving to specific examples. This approach helps students understand complex topics by building upon foundational knowledge.
What is the main idea of deductive reasoning?
Deductive reasoning starts with a general premise and uses it to reach a specific conclusion, ensuring logical validity within structured arguments.
What is deductive logic in simple words?
Deductive logic involves drawing specific conclusions from general principles, ensuring logical consistency and validity within a structured argument or reasoning process.
What is an example of inductive reasoning?
Observing past occurrences to infer future outcomes, like assuming all observed swans are white, concluding all swans are white.
How do you explain inductive reasoning?
Observing past occurrences to infer future outcomes, like assuming all observed swans are white, concluding all swans are white.
Which passage is the best example of deductive reasoning?
A passage establishing that “All mammals are warm-blooded. Whales are mammals. Therefore, whales are warm-blooded” exemplifies deductive reasoning.
What is the most common form of deductive reasoning?
Categorical syllogism, where conclusions are drawn from two premises containing categories, is the most common form of deductive reasoning.
What is an example of deductive reasoning in the workplace?
“If all employees who meet sales targets receive bonuses, and Jane met her sales targets, then Jane will receive a bonus.” This is deductive reasoning in the workplace.
Is deductive reasoning always true?
Deductive reasoning ensures logical validity within its structure, but conclusions rely on the truth of premises. Thus, validity does not guarantee truth.
What is deductive logic in child development?
In child development, deductive logic fosters critical thinking by teaching children to draw conclusions based on given premises, aiding problem-solving skills.
What is an example of deductive logic in psychology?
Assuming “All humans are mortal. Socrates is a human. Therefore, Socrates is mortal” showcases deductive logic in psychological reasoning, aiding hypothesis testing and analysis.