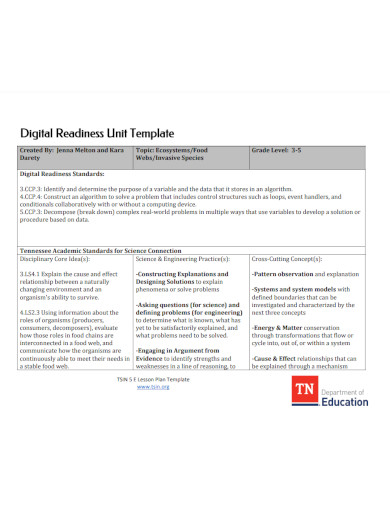
What is a food web?
A single chain of organisms eating each other
A complex network of interconnected food chains
A list of all herbivores in an ecosystem
A diagram showing only producers and consumers
All the organisms in a given area follow a hidden hierarchy of predators and prey that would normally be very hard to envision. Scientists and researchers use food webs and food chains to create and envision said hierarchy.









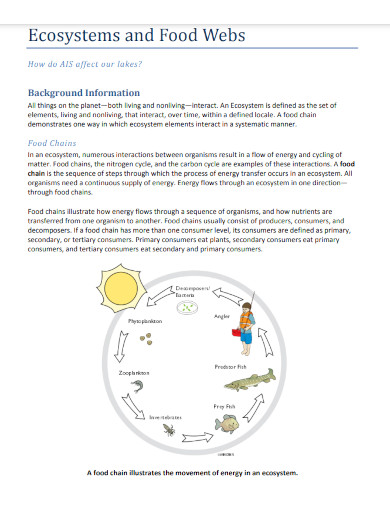
















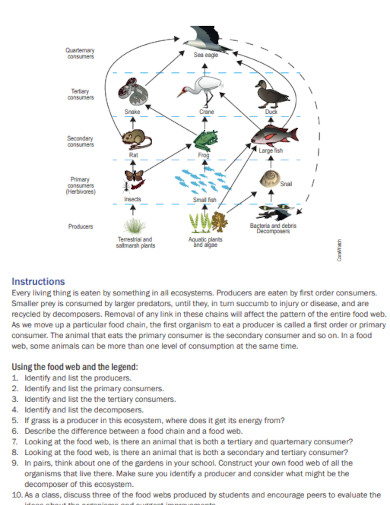



A food web illustrates the complex relationships between all the organisms in a specific ecosystem and biome. The food web denotes the cycle of energy by classifying the organisms in a variety of trophic levels and shows how each organism is interdependent with one another.
A food web illustrates the complex relationships between all the organisms in a specific ecosystem and biome. The food web denotes the cycle of energy by classifying the organisms in a variety of trophic levels and shows how each organism is interdependent with one another.which could lead to the ecological restoration of said ecosystem. Creating a food web will take some time; you may refer to the food web templates on the links above.
Begin by researching all the organisms in a given ecosystem or biome. The research should include all the terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial organisms, as the food web is a more comprehensive illustration.
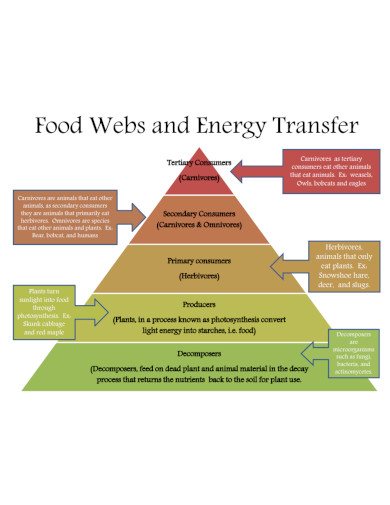
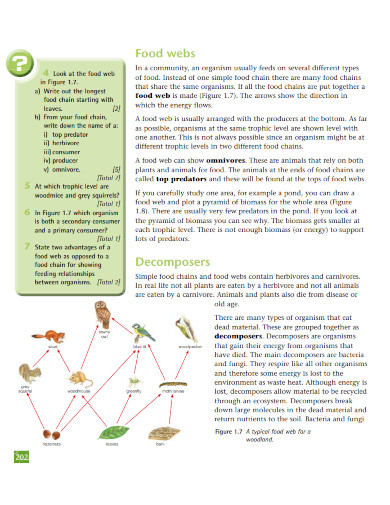
After you have researched all of the organisms, you will now classify each of these organisms by their trophic level. The trophic level will indicate their position in the food web. The lower the organism’s trophic level, the more predators it will have the opposite is also true.
When you have finished classifying the organisms, you must arrange said organisms based on their trophic levels. The higher the trophic level, the more central the organism is concerning the food web.
You will then connect these organisms based on their prey/predatory relationships. The connections will illustrate the primary food and energy source of the organism and will complete the food web.
[/ns_row]
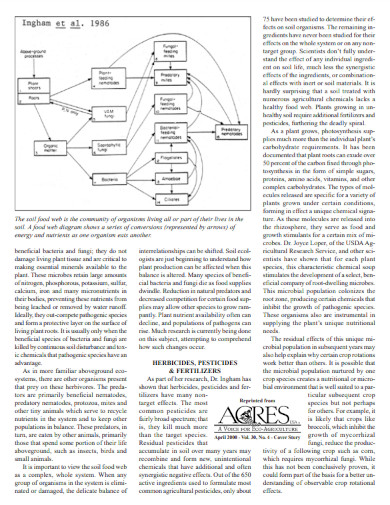
A food web is a collection of various food chains that illustrates the energy cycle of a specific ecosystem. The food chain, on the other hand, focuses on a specific biome’s cycle of energy but is limited in its scope. A food web has a larger range than a food chain; therefore an organism central to the food web is disturbed, then an ecosystem collapse will occur. But this does not mean that a disturbance in the food chain has a lower environmental impact than that of the food chain. This wholly depends on the position of the organism concerning its placement in the food web and the food chain.
The ocean’s food web begins with the producers at the lowest tropic level of the oceanic food web. These producers consist of the base-level microorganisms and the oceanic plant life on the ocean floor; the producers of the ocean’s food web are the plankton, ocean bacteria, and algae. The consumers then follow the producers, as these predators will consume the microorganisms for energy. The consumers will consist of most organisms in the food web, which will centralize to the apex predator in the food web. Smaller consumers are the guppies, baby fishes, and shrimps, while larger consumers consist of octopi, sharks, and whales. Afterward, the food web will then have scavengers, which will consume the dead bodies and use their bodies to recycle the potential energy back to the producers. These scavengers include crabs, janitor fishes, and lobsters.
Yes, the soil in a specific ecosystem or biome will have its own intricate and complex food web. The soil food web includes five trophic levels that begin with the plants that will use the energy from the sun to create food. The consumers in the second trophic level will eat the food created by the plants; said consumers consist of various insects, fungi, and parasites. The third trophic level is composed of various insect and fungi-eating organisms like arthropods and bacteria-eating worms. The predators of said arthropods and worms will compose the fourth trophic level; these include mantis, locusts, and other large insects and worms. At the top of the food web are the larger predators like birds and beavers.
The food web is a web that connects and illustrates the various food chains that will be at play in a specific ecosystem or biome. Illustrating or creating a food web requires the person to conduct various painstaking research on the relationships between all the organisms in a given setting.
A food web depicts how different organisms in an ecosystem interact through food consumption, showing interconnectedness and energy flow.
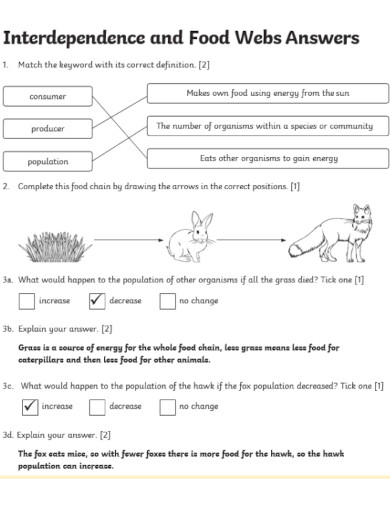
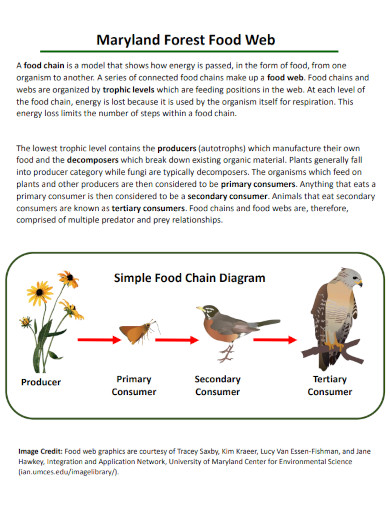
In a forest, a food chain might be: Sun → Grass → Rabbit → Fox. In the same ecosystem, a food web would include multiple interconnected chains.
A food chain shows a linear sequence of organisms where each serves as food for the next, illustrating energy transfer in an ecosystem.
A food web is like a big food map showing who eats whom in nature. It includes all plants and animals and how they depend on each other for food.
A food chain is a lineup of who eats whom in nature. It’s like a dinner line, starting from plants and ending with animals.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is a food web?
A single chain of organisms eating each other
A complex network of interconnected food chains
A list of all herbivores in an ecosystem
A diagram showing only producers and consumers
Which of the following best describes the role of a producer in a food web?
Decomposes dead organisms
Consumes other organisms for energy
Converts sunlight into energy through photosynthesis
Preys on other animals
In a food web, what is the primary role of decomposers?
To create energy from sunlight
To eat producers
To break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients
To compete with herbivores
Which of these organisms would most likely be at the top of a food web?
Grass
Rabbit
Lion
Insect
If a primary consumer is removed from a food web, what is the likely impact on the ecosystem?
Increase in producer population
Decrease in decomposer activity
Increase in top predators
No significant impact
Which statement is true about food webs compared to food chains?
Food webs are less complex than food chains
Food webs show a single pathway of energy flow
Food webs are more realistic representations of energy flow in ecosystems
Food webs only include herbivores and carnivores
In a marine food web, which organism is most likely a producer?
Shark
Algae
Crab
Fish
How do omnivores fit into a food web?
They only consume producers
They only consume decomposers
They consume both producers and other consumers
They are at the top of the food web
What effect would an increase in the population of a top predator have on a food web?
Increase in herbivores
Decrease in producers
Decrease in the population of prey species
No effect
In a forest ecosystem, which of the following organisms might serve as a secondary consumer?
Oak tree
Deer
Wolf
Grasshopper
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

