10+ Incident Action Plan Examples to Download
Emergency incidents often cause panic and chaos, forcing us to act impulsively due to the rush of adrenaline that fills our system. But sometimes, making sudden decisions without thinking things through can lead to a series of consequences for the parties involved. Thus, without a proper action plan in place, a fire is bound to grow exponentially causing further damage to anything in its way.
Incidents vary greatly in their source, complexity, impact, and intensity, which is why the requirements for a detailed written plan would also depend on the type of incident at hand. But because most incidents happen at the most random circumstances, preparing for the worse case scenario is essential in the incident command system process. So in this article, let’s take a deeper look at how important incident action plans are along with how they are made.You may also see work action plans.
Incident Action Plan Example

Basic Incident Action Plan Example
Blank Incident Action Plan Template
Comprehensive Incident Action Plan Example
Defining an Incident Action Plan
An incident action plan (IAP) is a formal document that showcases an organized course of events that addresses the different phases of incident control within a given time period. This is necessary to bring about successful outcomes in an emergency operation, or any situation for that matter, in a timely manner. An IAP also facilitates in the dissemination of principal information regarding the current status of the basic response assets themselves. But because incident parameters gradually evolve over time, actions must be revised and updated on a regular basis to maintain consistent, well-founded guidance across the system.You may also see corrective action plans.
The writers behind an incident action plan are usually the incident command officers (or incident commanders) themselves. These are the people responsible for developing the action plan, successfully communicating their roles to each team member, and monitoring progress toward the completion of the plan.
Think of it this way. Some action plans cannot be developed until the commander can fully assess the situation in person. Upon arrival, the incident commander builds the action plan in their own mind. Since the other officers in the scene aren’t mind readers, it is essential that the commander articulates what’s in their mind to these responding officers so that they could take meaningful actions to accomplish a shared goal. This process serves as the foundation for administering the necessary operations in a safe and effective manner.You may also see one page action plan examples.
However, incident management is a lot more complicated when faced in real time. First-responders from different stations and precincts across the area are bound to gather altogether to resolve an incident before it escalates. But because there’s always a possibility of conflict regarding who’s in charge at the very moment—depending on the chain of command and situation at hand—having a proper management system is sure to encourage commitment and cooperation toward a common goal.
Hence, having a plan will enable commanders to accurately communicate the information necessary to transfer command to a later-arriving officer in the scene. This grants the current command officer the authority to make reasonable decisions to address the ongoing case.You may also see employee action plans.
But keep in mind that an incident action plan isn’t exclusive to fires, earthquakes, tornadoes, and other calamities or accidents, as some incident action plans are specially made to tackle certain matters within a company or organization.
Key Components
According to the National Incident Management System Consortium (NIMSC), there are four key components that are covered by an incident action plan, namely:
1. Command Options
A command officer should choose a command option based on their level of involvement. These command options include the investigation, the fast-attack, and the command-post.You may also see budget action plans.
2. Operational Priorities
Here, the command officer must decide what operational priorities should be obtained in the best interest of those at risk in the event. Life safety, incident stabilization, and property conservation are the three most recognized operational priorities that command officers must contemplate on.You may also see after action report examples.
3. Strategy
Once the first two components have been decided upon, the command officer must then formulate a strategy that will effectively manage the incident according to a risk/benefit profile. Though offensive and defensive action are two general options to choose from, some experts believe that a transitional strategy should also be considered. The concept of a transitional strategy simply depicts a change from an offensive strategy to a defensive strategy.
4. Supporting Tactics
It’s important for the command officer to assign tactics (tasks) to responders at the scene in support of their earlier decisions. Search, rescue, fire attack, and ventilation are just some examples of these tactics.You may also see smart action plans.
Out of the four components included in this list, the greatest consideration should be given to the operational priority. For starters, the decisions made in this step can greatly affect the outcome of the entire operation. And out of the three operational priorities given (life safety, incident stabilization and property conservation), the life of every individual involved is of utmost importance. This refers to the civilians who are in danger in the situation. The command officer must make a decision either to remove the threat from the citizens or to remove the citizens from harm’s way.
Even then, there are numerous factors that can put a citizen’s life at risk. If a command officer fails to stabilize a situation before it takes a turn for the worse, there may be further casualties involving both the civilians and the officers responding to the incident. This is why it’s important for a command officer to think critically before the crew can take action.You may also see restaurant action plans.
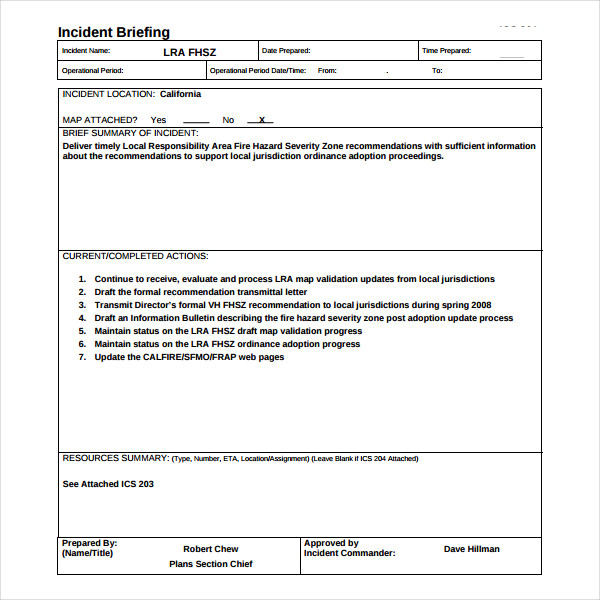
Editable Incident Action Plan Template
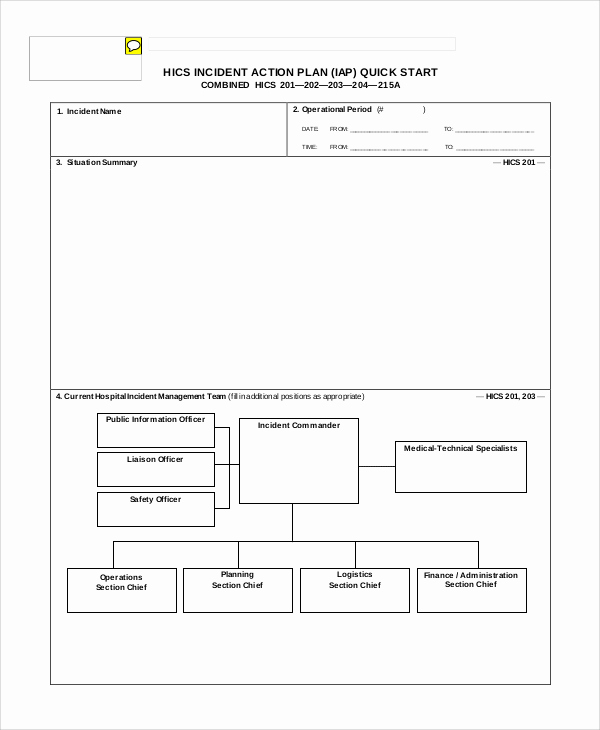
Incident Action Plan Quick Start Template
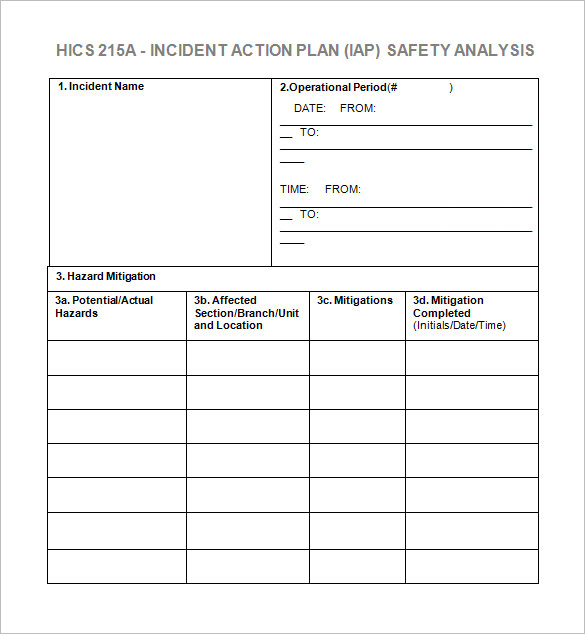
Incident Action Plan Safety Analysis Example
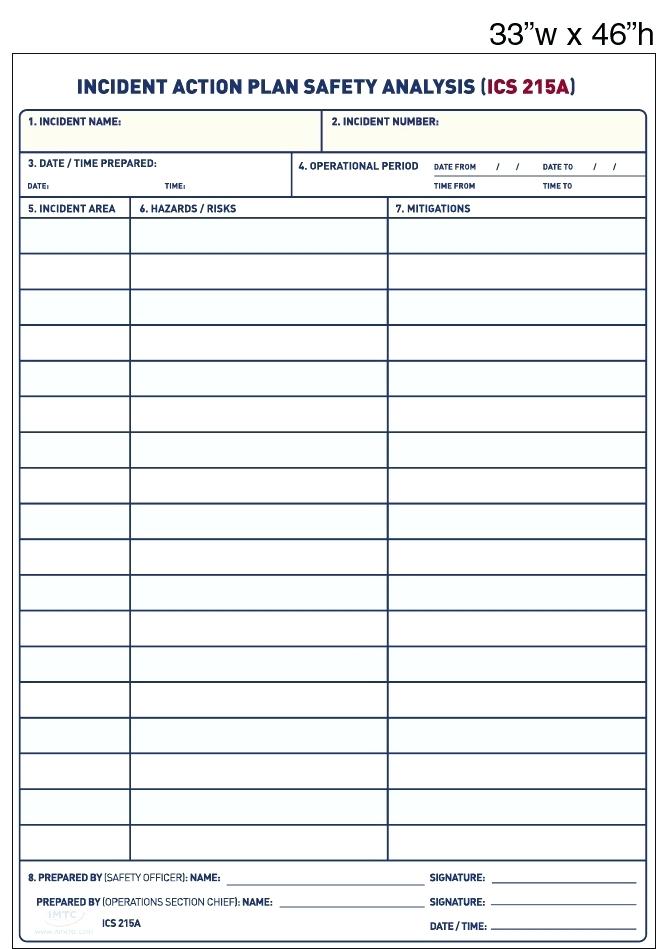
Incident Action Plan Template
The Importance of an Incident Action Plan
Despite how economic progress and development has undeniably changed our way of living for the better, opening doors to various job opportunities and whatnot, the infrastructures that make up our everyday lives pose many potential hazards to the establishments and tenants that surround them.
The September 11 attacks on the World Trade Center is one example of a devastating incident that has caused many casualties and damages on properties surrounding the area. Many people died that day and the months following the event, from being trapped inside the building, getting hit by falling debris, inhaling toxic dust at the scene, or from being exposed to various toxins in Ground Zero.You may also see operations management plan
But through it all, one thing that society (and history) would never forget is the sense of courage and bravery exhibited by our modern-day heroes who risked their own lives to save another. Firefighters, police officers, EMTs, and other first-responders rushed to the scene in spite of the danger no one ever thought would happen. According to witnesses and victims of the incident, you could see everyone working hand in hand to get civilians to safety.
Although we all know that the 9/11 attacks is one of the worst tragedies in U.S. history, just imagine if no one responded to the event accordingly? What if the commanding officers in the scene didn’t have a strategic action plan in place? How different would the outcomes be?
An incident action plan plays a significant role in the field of incident management. There are many variables that could affect how a situation may be handled, and the limited resources at a large-scale incident could make it extremely difficult for an on-scene supervisor to make well-balanced decisions. But with an incident action plan in place, a command officer can deliver clear instructions to other on-scene officers to ensure that everyone is on the same page. Tasks may be divided and delegated as planned, and decisions may be made based on a survey of the area, the situation being confronted, and the availability of resources. Though everything is uncertain, a well-developed plan increases the likelihood of a sound operation.You may also see research action plans.
Printable Incident Action Plan Example
Simple Incident Action Plan Example
Standard Incident Action Plan Example
A Guide to Incident Action Planning
Knowing how to construct an incident action plan and practicing it to proficiency is crucial for every first-responder. This includes firefighters, police officers, emergency medical technicians, paramedics, and rescuers. It’s important that all officers are knowledgeable on how to use a standardized process for developing an incident action plan. This standard process shall be applied for both training activities and actual emergency management to make sure that officers share a common expectation for how things will run.You may also see business action plans.
There are five essential elements for developing and communicating a command officer’s plans to fellow officers during an emergency incident. These are as follows:
1. Conduct a size-up.
Before anything else, an incident commander must conduct a 360-degree ground assessment on the situation at hand. The primary questions that a command officer should answer upon their arrival are:
1. What has happened prior to my arrival?
2. What is continuing to happen as time progresses?
3. What will continue to happen if we hadn’t intervened?
Next, the commander must quickly assess which interventions would be possible considering the assessed situation. Two factors must be considered during this process: the acceptability of risk and the risk assessment. In the concept of acceptability of risk, it is made clear that no building or property is worth the life of a responder; all interior actions involves an inherent risk; some risks are acceptable, in a measured and controlled manner; and that no level of risk is acceptable where there is no potential to save lives or property.You may also see project action plans.
In terms of risk assessment, the rules state that all feasible measures shall be taken to limit or prevent risks through risk assessment by a qualified officer; it is the responsibility of the command officer to evaluate the risk level in every situation; risk assessment is a continuous process for the entire duration of each incident; and if conditions are set to change, and risk increases, strategies and tactics should be improved.You may also see affirmative action plan examples
2. Identify your mode of operation.
This is where the operational priorities must be determined. The command officer may choose to rescue civilians through various efforts, administer an offense or defense to stabilize the situation, or choose to go on marginal mode, which is the most critical option available. In this mode of operation, the commander must closely monitor the situation to ensure that efficient progress is being made. If the situation only worsens, personnel must prepare to make a transition to the defensive mode.You may also see school operational plans.
3. Define your goals.
Similar to an emergency action plan, the command officer must establish a set of incident goals based on the three incident priorities: life safety, incident stabilization, and property conservation.
Naturally, the safety of civilians and responders in the scene should be of top priority in every decision made. The success of the operation may be measured according to how each step was completed.
4. Determine your tactical objectives to attain your incident goals.
What are the actions that must be taken in order for your team to accomplish the incident goals? Some common tactical objectives include removing occupants from an endangered area (like a burning building), conducting salvage work, or even extinguishing a fire. It’s important to track the completion of each objective to ensure that no tasks are overlooked. Continuous feedback or update from responding officers is critical to assess whether an objective has been completed or if another problem has arose.You may also see employee action plans
5. Set strategies to fulfill your incident objectives.
In the final step for developing your action plan, you need to evaluate the available resources with the tasks necessary to fulfill your tactical objectives. The roles and responsibilities of each responding officer should also be established for accountability reasons. This will help keep operations organized and in full control to limit or avoid fatalities and property damage.You may also see emergency action plans.
Developing an effective incident action plan is far from easy. It’s a skill that requires critical thinking and constant practice to develop proficiency. As a command officer, it is your duty to put the safety and welfare of civilians and your crew above all others, and make rational decisions based on what you have experienced or learned in your field. And with the specified guidelines and examples, you can increase the odds of a more successful outcome for every operation conducted.You may also see 90 day action plans.