65+ Straw Man Fallacy Examples
In the realm of argumentation and debate, the ability to identify and counteract fallacies is a crucial skill. One such fallacy, known as the Straw Man Fallacy, is a common and deceptive tactic that can easily mislead an audience if not properly recognized. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Straw Man Fallacy, its identification, and its implications in various contexts.
What is a Straw Man Fallacy?
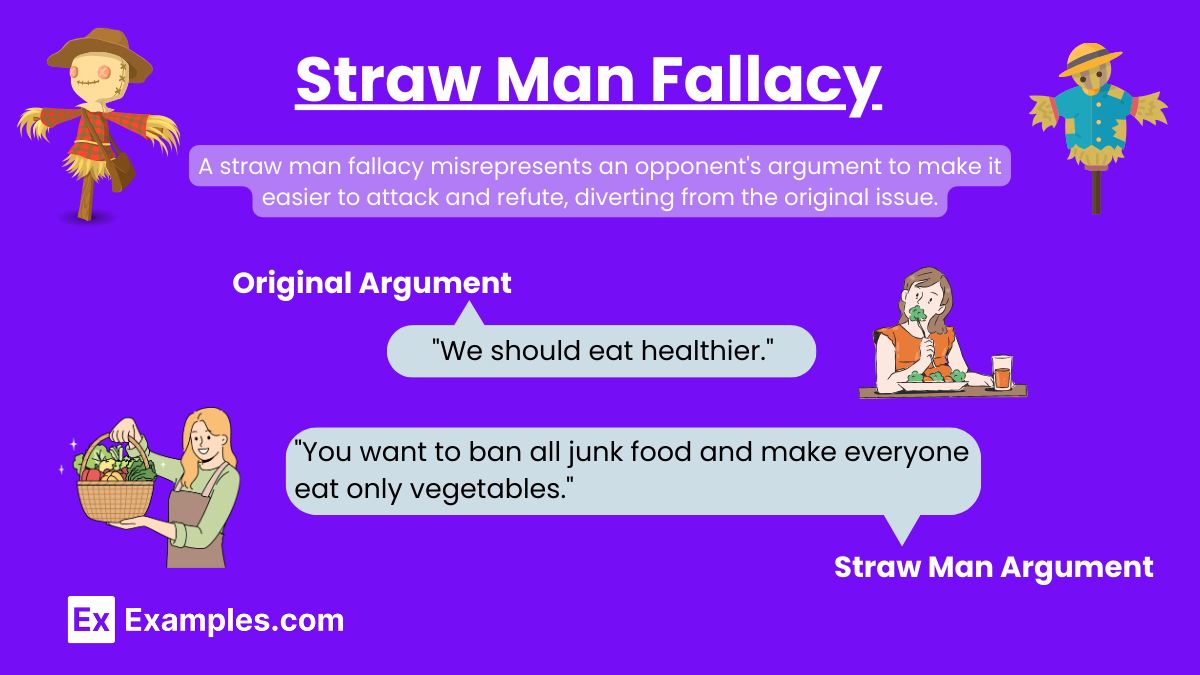
The Straw Man Fallacy, a type of Logical Fallacy, occurs when an individual distorts, exaggerates, or misrepresents an opponent’s argument, making it easier to attack and refute. This tactic is often used to divert attention from the actual issue at hand, creating a ‘straw man’ argument that is simpler to knock down. It’s a deceptive method that undermines the principles of fair debate and Deductive Reasoning.
History of the straw man fallacy
The straw man fallacy, a common rhetorical tactic, involves misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to attack. Its roots can be traced back to ancient Greece, where philosophers like Aristotle first identified and documented various logical fallacies, including forms of argument misrepresentation. Throughout the medieval and Renaissance periods, scholars continued to recognize and study this deceptive technique. The term “straw man” itself emerged in the modern era, metaphorically depicting a weak, easily defeatable version of an argument that is set up only to be knocked down. This fallacy remains prevalent in contemporary debates and discussions, highlighting the enduring relevance of logical scrutiny.
When and Why is the straw man fallacy used?
When is the Straw Man Fallacy Used?
The straw man fallacy is frequently employed in various contexts, including:
- Political Debates: Politicians often use straw man arguments to simplify and attack their opponents’ positions, making their own stance appear stronger.
- Public Discourse: In media and public discussions, individuals may use this fallacy to sway public opinion by presenting an exaggerated or distorted version of an opponent’s argument.
- Everyday Conversations: People use straw man arguments in personal disputes to deflect criticism or avoid addressing the actual points being made.
Why is the Straw Man Fallacy Used?
The straw man fallacy is used for several reasons:
- Easier to Refute: By creating a distorted or simplified version of the opponent’s argument, it becomes easier to refute. This can make the user appear more knowledgeable or persuasive.
- Deflection: It shifts the focus away from the actual issue, allowing the user to avoid engaging with the real argument and instead attack a weaker, more vulnerable position.
- Emotional Appeal: A straw man can provoke an emotional response, rallying support from those who may not scrutinize the argument closely.
- Misleading Persuasion: It can mislead an audience into believing that the opponent’s argument is fundamentally flawed, thereby strengthening the user’s own position.
What are different types of straw man fallacy?
1. Oversimplification
This type involves reducing a complex argument to a simple, flawed version, making it easier to attack. For example, if someone argues for nuanced climate change policies, an oversimplified straw man might be, “You just want to ban all cars.”
2. Extreme Exaggeration
In this form, the argument is exaggerated to an extreme level. For instance, if someone suggests regulations on gun ownership, an exaggerated straw man might be, “You want to take away everyone’s right to own a gun.”
3. Ignoring Context
This involves taking statements out of context to distort the opponent’s argument. For example, quoting someone out of context to make it seem like they hold a position they do not actually hold.
4. Attributing False Motives
Here, false intentions or motives are attributed to the opponent. For example, “You only want to increase taxes because you hate wealthy people,” when the actual argument might be about economic equity.
5. Refuting an Unstated Argument
This type involves attacking a point that the opponent never actually made. For instance, if someone argues for more renewable energy, a straw man response might be, “Renewable energy alone cannot power the world,” even if the original argument didn’t claim that.
6. Misquoting
Deliberately altering the opponent’s words to create a misrepresentation. For example, changing “We need to manage immigration better” to “We should close our borders completely.”
7. Attacking an Insubstantial Argument
This involves focusing on a minor or trivial part of the opponent’s argument and attacking it as if it represents the whole argument. For example, dismissing the entirety of climate change science by pointing out an error in a single study.
How to counter a straw man Fallacy
1. Identify the Misrepresentation
The first step is to clearly identify how your argument has been misrepresented. Point out the specific ways in which your original position has been distorted or simplified.
2. Restate Your Original Argument
Calmly and clearly restate your original argument. Emphasize the key points that were misrepresented and provide a concise summary of your actual stance.
3. Clarify Misunderstandings
Address any misunderstandings that may have led to the creation of the straw man. Explain any nuances or complexities that were overlooked in the misrepresentation.
4. Provide Evidence
Support your restated argument with evidence. This can include data, expert opinions, or logical reasoning that reinforces your original position and highlights the flaws in the straw man argument.
5. Ask for Acknowledgment
Politely ask your opponent to acknowledge the correct version of your argument. This encourages a more honest and constructive dialogue, as it invites them to engage with your actual points rather than the distorted version.
6. Redirect the Focus
Redirect the discussion back to the original issue. Remind your opponent and the audience of the main topic and emphasize the importance of addressing it directly.
7. Stay Calm and Composed
Maintain a calm and composed demeanor. Responding to a straw man fallacy with anger or frustration can undermine your credibility. A measured response demonstrates confidence in your position.
Straw man fallacy examples
1. Political Debate
Original Argument: “We should have stronger regulations on factory emissions to combat climate change.” Straw Man Argument: “My opponent wants to shut down all factories and destroy our economy.”
2. Public Health Discussion
Original Argument: “Vaccines are crucial for preventing the spread of infectious diseases.”
Straw Man Argument: “You think we should force everyone to get vaccinated regardless of their personal or religious beliefs.”
3. Educational Policy
Original Argument: “We need to improve our educational system by increasing funding for public schools.” Straw Man Argument: “You think throwing money at schools will solve all our problems.”
4. Economic Policy
Original Argument: “Raising the minimum wage can help reduce poverty and improve living standards.”
Straw Man Argument: “You want to double everyone’s wages overnight, which will cause massive inflation and job losses.”
5. Environmental Conservation
Original Argument: “We should protect endangered species by preserving their natural habitats.”
Straw Man Argument: “You care more about animals than about people’s livelihoods.”
6. Technology Use
Original Argument: “Social media platforms need better moderation to prevent the spread of misinformation.”
Straw Man Argument: “You want to censor the internet and control what people can say.”
7. Social Issues
Original Argument: “We need to address the systemic racism present in our criminal justice system.”
Straw Man Argument: “You think all police officers are racist and the entire system should be dismantled.”
8. Health and Nutrition
Original Argument: “Reducing sugar intake is important for improving public health.”
Straw Man Argument: “You want to ban all sugary foods and drinks.”
9. Workplace Policy
Original Argument: “Offering flexible work hours can improve employee productivity and satisfaction.”
Straw Man Argument: “You think everyone should just work whenever they feel like it and disregard business needs.”
10. Gun Control
Original Argument: “We need to implement stricter background checks for gun purchases to enhance public safety.”
Straw Man Argument: “You want to take away everyone’s guns and abolish the Second Amendment.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples Sentences
- “You want to ban all cars just because you think public transportation should be improved.”
- “You’re saying that if we implement a dress code, we’re living in a dictatorship.”
- “So you believe we should just give all our money to the poor and live in poverty ourselves?”
- “You think we should stop using plastic entirely and go back to the Stone Age.”
- “You’re suggesting we abolish exams, so you must want students to have no standards at all.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Real Life
- During a family discussion about eating healthier, someone says, “Oh, so you think we should just eat salads for every meal and starve?”
- In a workplace meeting, an employee suggests a flexible schedule, and another responds, “So you think everyone should just work whenever they want with no accountability?”
- In a debate about home-schooling, one person argues for its benefits, and the other responds, “You think traditional schools are worthless and harmful.”
- A friend says they prefer quiet weekends, and another replies, “So you want to become a hermit and never socialize again?”
- During a conversation about reducing screen time, someone says, “You think we should throw out all our electronics and live like it’s the 1800s.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Politics
- A politician advocating for environmental regulations is countered with, “You want to shut down all factories and ruin our economy.”
- During a healthcare debate, one side argues for universal healthcare, and the other responds, “You want to turn our country into a socialist state.”
- In discussions about tax reform, someone says, “You want to raise taxes so high that small businesses will go bankrupt.”
- When arguing for stricter gun control, a politician is met with, “You want to confiscate all guns and leave citizens defenseless.”
- During a debate on immigration, one side argues for reform, and the other responds, “You want to open the borders and let everyone in without any checks.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Advertising
- An ad promoting a new fitness program suggests, “Other programs make you work out for hours every day, but ours doesn’t.”
- A smartphone ad claims, “Our competitors’ phones are all bulky and outdated, but ours is sleek and modern.”
- A commercial for a dietary supplement states, “Other supplements don’t work and are full of chemicals, but ours is all-natural and effective.”
- An ad for a car boasts, “Other cars are unsafe and unreliable, but ours guarantees top-notch safety and performance.”
- A toothpaste brand advertises, “Other toothpastes don’t fight cavities effectively, but ours provides complete protection.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Movies
- In a superhero movie, a villain argues against the hero’s methods by saying, “You think you’re above the law and can do whatever you want without consequences.”
- In a romantic comedy, one character accuses another of being unromantic for saying they don’t like grand gestures: “So you think love shouldn’t be expressed at all?”
- In a drama about politics, a character suggests welfare reform and is countered with, “You want to abolish all social safety nets and leave people to fend for themselves.”
- In a sci-fi film, a scientist argues for cautious experimentation and is met with, “You think we should stop all progress and innovation.”
- In a courtroom drama, a lawyer argues for a client’s innocence, and the prosecutor responds, “So you think we should let all criminals go free?”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Media
- A news segment discussing climate change highlights a protester’s extreme view and portrays it as the mainstream environmental stance, saying, “Climate activists want to shut down all industries immediately.”
- A talk show host misrepresents a guest’s advocacy for police reform by saying, “You believe we should abolish the police entirely and let crime run rampant.”
- An article critiques a politician’s call for universal healthcare by stating, “They want to force everyone into government-run hospitals and eliminate private healthcare options.”
- A media outlet covers a debate on gun control by summarizing one side’s position as, “They want to take away all guns from law-abiding citizens.”
- A columnist mischaracterizes a push for renewable energy as, “They think we should abandon all fossil fuels overnight and risk economic collapse.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Social Media
- A tweet about the importance of animal rights gets misrepresented as, “You care more about animals than people.”
- A Facebook post advocating for veganism is countered with, “You want everyone to stop eating meat and starve.”
- An Instagram comment supporting body positivity is replied to with, “So you’re saying it’s okay to be unhealthy and ignore fitness altogether.”
- A LinkedIn discussion about remote work policies is met with, “You think people should just work from home and do nothing all day.”
- A TikTok video promoting mental health days is criticized with, “You think people should take a day off for every little problem and never work.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Literature
- In George Orwell’s “1984,” the Party misrepresents dissenters’ arguments as being entirely anti-society, suggesting they want total chaos and anarchy.
- In “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee, opponents of Atticus Finch misrepresent his defense of Tom Robinson as supporting all criminals, regardless of guilt.
- In “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen, Mr. Collins misrepresents Elizabeth Bennet’s rejection of his marriage proposal as her not understanding the importance of social status.
- In “The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger, Holden Caulfield’s critique of societal norms is often dismissed as adolescent rebellion without understanding his deeper issues.
- In “Frankenstein” by Mary Shelley, Victor Frankenstein’s fears about his creation are misrepresented by others as mere superstition.
Straw Man Fallacy Examples for Kids
- When a child says they don’t like broccoli, a parent responds, “So you think all vegetables are bad and want to eat candy all the time?”
- A student suggests shorter homework assignments, and the teacher says, “You think we should just stop giving homework and not learn anything.”
- A child asks for more playtime, and an adult replies, “So you think school is pointless and you shouldn’t learn anything?”
- When a kid prefers reading over sports, someone says, “You think exercise is useless and everyone should just sit around.”
- A child wants to go to bed later on weekends, and a parent says, “You think you should stay up all night and never sleep.”
Straw Man Fallacy Examples in Pop Culture
- In superhero movies, a hero advocating for a cautious approach is often countered with, “You think we should do nothing and let villains win.”
- In sitcoms, a character’s desire to save money is exaggerated by another character as, “You want to live like a miser and never have any fun.”
- In reality TV, a contestant’s strategy to form alliances is misrepresented as, “You’re here just to manipulate and deceive everyone.”
- In dystopian films, a character arguing for security measures is misrepresented as wanting to create a totalitarian state.
- In music lyrics, a song advocating for independence is mischaracterized as promoting isolation and anti-social behavior.
Sample Straw Man Fallacy Example
helpfulprofessor.com
Common Straw Man Fallacy Example

francais.unibe.ch
Straw Man Fallacy Activity Example

sites.isdschools.org
Politics Straw Man Fallacy Example

capitalideasonline.com
Straw Man Fallacy Visual Example

pure.uva.n
Straw Man Fallacy Example
weightology.net
Commercial Straw Man Fallacy Example

arg.tech
The Straw Man Fallacy Example

dwc.knaw.nl
How to determine Straw Man Fallacy
Recognizing a Straw Man Fallacy is not always straightforward, especially when it’s skillfully woven into the fabric of an argument. However, by following a systematic approach, one can learn to identify and counteract this fallacy. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process.
Understand the Original Argument
The first step in identifying a Straw Man Fallacy is to fully comprehend the original argument. This may involve asking Open Ended Questions to clarify any ambiguities and ensure you have a clear understanding of the points being made.
Identify Distortions or Misrepresentations
Next, look for any distortions or misrepresentations of the original argument. These could be exaggerations, oversimplifications, or complete misinterpretations. If the counter-argument seems to be addressing a point that wasn’t made or significantly distorts the original argument, it could be a Straw Man Fallacy.
Check for Relevance
The third step is to check the relevance of the counter-argument. A Straw Man Fallacy often involves diverting the discussion to a different, easier-to-refute argument. If the counter-argument seems unrelated or only tangentially related to the original argument, it might be a Straw Man.
Evaluate the Argument’s Impact
Finally, evaluate the impact of the argument. If the counter-argument seems to have unfairly ‘won’ the debate by knocking down the misrepresented argument, it’s likely a Straw Man Fallacy. This step requires critical thinking and an understanding of the broader context of the argument.
How is a Straw Man Fallacy different from an Ad Hominem fallacy?
While both are types of logical fallacies, they differ in their approach. A Straw Man Fallacy misrepresents an opponent’s argument to make it easier to attack, while an Ad Hominem fallacy attacks the person making the argument rather than the argument itself.
Can a Straw Man Fallacy be unintentional?
Yes, a Straw Man Fallacy can be unintentional. It often occurs when someone misunderstands or oversimplifies an argument. This is why it’s important to ask open-ended questions and ensure clear communication in a debate.
How can I avoid using a Straw Man Fallacy in my College Essay or Article Writing?
To avoid using a Straw Man Fallacy, ensure you fully understand the argument you’re addressing. Avoid oversimplifications and ensure your counter-arguments are relevant and directly address the points raised. Using a Fallacy Template can help you structure your arguments and avoid fallacies.
Why do people use straw man fallacies?
People use straw man fallacies to simplify complex arguments, divert attention, or make their own position seem stronger by attacking a weaker, distorted version of the opponent’s stance.
How can you counter a straw man fallacy?
Counter a straw man fallacy by clarifying and restating your original argument, highlighting the misrepresentation, and redirecting the discussion back to the actual points made.
Are straw man fallacies always intentional?
Straw man fallacies can be both intentional, as a deliberate tactic to mislead, or unintentional, resulting from misunderstanding or oversimplifying the original argument.
Can straw man fallacies occur in written arguments?
Yes, straw man fallacies can occur in written arguments, articles, and social media posts, where an author’s position is misrepresented and then attacked based on the distorted version.
How does a straw man fallacy differ from other fallacies?
A straw man fallacy specifically involves misrepresenting an opponent’s argument, while other fallacies, like ad hominem, attack the person instead of the argument, or appeal to emotion over logic.
Can you provide an example of a straw man fallacy?
If someone argues for better public transport and is countered with, “You want to ban all cars,” this misrepresentation simplifies the original argument into something easier to attack.
Why is it important to recognize straw man fallacies?
Recognizing straw man fallacies is crucial for maintaining honest and productive debates, ensuring arguments are addressed accurately, and preventing misleading or deceptive tactics in discussions.
The Straw Man Fallacy, while common, can be identified and avoided with careful attention and critical thinking. By understanding the original argument, identifying distortions, checking relevance, and evaluating the argument’s impact, one can effectively spot this fallacy. Whether in a debate, a college essay, or article writing, avoiding such fallacies and promoting fair argumentation is crucial. Remember, the goal of any argument should be to seek truth and understanding, not merely to ‘win’ by any means necessary.