14+ Financial Performance Analysis Report Examples
Financial Performance Analysis Reports in PDF are valuable tools used by organizations to assess their financial health and make informed decisions. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of an organization’s financial performance, highlighting key metrics and trends. By analyzing financial data and presenting it in a clear and concise format, these reports enable stakeholders to gain insights into the company’s financial standing and make informed decisions. In this article, we will delve into the definition of a Financial Performance Analysis Report and provide a step-by-step guide on how to create one. Additionally, we will address some frequently asked questions and explore the importance of financial performance analysis in today’s business landscape.
1. Financial Analysis Report Template

2. Performance Analysis Report Template

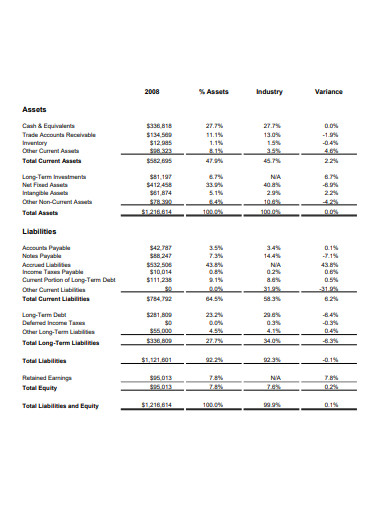
3. Financial Performance Analysis Report
4. Financial Performance Evaluation Analysis Report
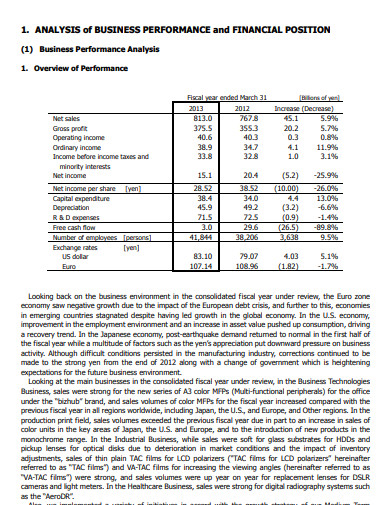
5. Business Performance Analysis Report
6. Financial Performance Analysis Report Example
7. Financial Performance Analysis Report Template
8. Significance of Financial Performance Analysis Report
9. Sample Financial Performance Analysis Report
10. Financial Performance Ratio Analysis Report
11. Financial Performance Analysis Annual Report
12. Simple Financial Performance Analysis Report
13. Financial Performance And Management Analysis Report
14. Financial Performance Overview Analysis Report
15. Study On Financial Performance Analysis Report
What is Financial Performance Analysis Report?
A Financial Performance Analysis Report is a document that provides an in-depth evaluation of an organization’s financial performance. It encompasses the analysis of various financial statements, such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, to assess the company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health. This report is crucial for stakeholders, including investors, shareholders, lenders, and management, as it helps them understand the organization’s financial position and make strategic decisions. By examining key financial ratios, trends, and benchmarks, a Financial Performance Analysis Report enables stakeholders to identify areas of strength and weakness, assess performance against industry standards, and evaluate the effectiveness of financial strategies and management practices.
How to Create a Financial Performance Analysis Report
Creating a Financial Performance Analysis Report involves several key steps to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness. Follow this step-by-step guide to create an effective report:
Step 1: Determine the Scope and Goals
Determine the Scope and Goals
Step 2: Gather Financial Data
Collect the necessary financial statements and data, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, for the designated period. Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data to obtain reliable analysis results.
Step 3: Calculate Financial Ratios
Calculate key financial ratios, such as profitability ratios (e.g., gross profit margin, net profit margin), liquidity ratios (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio), and solvency ratios (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio). These ratios provide valuable insights into the organization’s financial performance and help compare it with industry benchmarks.
Step 4: Analyze Trends and Variances
Identify trends and variances in financial performance by comparing current and historical data. Look for significant changes or patterns that may impact the organization’s financial health and operational efficiency.
Step 5: Interpret Findings
Analyze the calculated ratios, trends, and variances to interpret the organization’s financial performance. Identify strengths and weaknesses, potential risks, and areas for improvement. Provide clear explanations and supporting evidence for your analysis.
Step 6: Prepare Visual Presentations
Present the findings in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format. Utilize charts, graphs, and tables to highlight key metrics, trends, and comparisons. Use concise and informative captions to enhance the understanding of the data.
Step 7: Summarize and Provide Recommendations
Summarize the key findings of the analysis, highlighting the organization’s financial strengths and weaknesses. Provide actionable recommendations to improve financial performance based on the analysis results and goals set at the beginning of the report.
FAQs
What is the difference between an Annual Financial Report and a Financial Performance Analysis Report?
An Annual Financial Report is a comprehensive document that provides a detailed overview of a company’s financial activities and results over a fiscal year. It includes financial statements, notes, and other disclosures required by accounting standards. On the other hand, a Financial Performance Analysis Report focuses specifically on analyzing the financial performance of an organization, providing insights into profitability, liquidity, and solvency.
How does Financial Performance Analysis contribute to effective performance management?
Financial Performance Analysis is a crucial component of performance management. By evaluating financial metrics and trends, organizations can assess their performance against goals, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions. It helps align financial strategies with organizational goals and supports the evaluation of the effectiveness of financial management practices.
Why is financial health analysis important for stakeholders?
Financial health analysis provides stakeholders, such as investors, shareholders, and lenders, with critical information about the organization’s financial well-being. It enables stakeholders to evaluate the organization’s ability to generate profits, meet its financial obligations, and sustain long-term growth. This analysis helps stakeholders make informed investment decisions and assess the overall financial risk associated with the organization.
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations must prioritize financial performance analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health. In conclusion, by creating and analyzing Financial Performance Analysis Reports, organizations can assess their profitability, liquidity, and solvency, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning. These reports provide valuable insights for stakeholders, facilitating effective performance management and supporting the achievement of organizational goals. In an era where financial stability and growth are paramount, harnessing the power of financial performance analysis is key to success.