30+ Nursing Case Study Examples
ScienceDirect posted a nursing ethics case study where an end-stage prostate cancer patient, Mr. Green, confided to nursing staff about his plan to commit suicide. The patient asked the nurse to keep it a secret. The ethical problem is whether the nurse should tell the health care team members about the patient’s thought without his permission. The best ethical decision for this nursing case study was to share this critical information with other health care professionals, which was the action the nurse took. The team adhered to the proper self-harm and suicide protocol. The appropriate team performed a palliative therapy. As a result, the patient didn’t harm himself and died peacefully a few months after he was discharged.
What Is a Nursing Case Study?
A nursing case study is a detailed study of an individual patient. Through this type of research, you can gain more information about the symptoms and the medical history of a patient. It will also allow you to provide the proper diagnoses of the patient’s illness based on the symptoms he or she experienced and other affecting factors. Nursing students usually perform this study as part of their practicum, making it an essential experience because, through this research methodology, they can apply the lessons they have learned from school. The situation mentioned above was an excellent example of a nursing case study.
Nursing Case Study Format
1. Introduction
- Purpose: Briefly introduces the case study, including the main health issue or condition being explored.
- Background: Provides context for the patient scenario, outlining the significance of the case in nursing practice.
- Objectives: Lists the learning objectives or goals that the case study aims to achieve.
2. Patient Information
- Demographics: Age, gender, ethnicity, and relevant personal information.
- Medical History: Past medical history, including any chronic conditions, surgeries, or significant health events.
- Current Health Assessment: Presents the patient’s current health status, including symptoms, vital signs, and results from initial examinations.
3. Case Description
- Clinical Presentation: Detailed description of the patient’s presentation, including physical examination findings and patient-reported symptoms.
- Diagnostic Findings: Summarizes diagnostic tests that were performed, including lab tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostic procedures, along with their results.
- Treatment Plan: Outlines the initial treatment provided to the patient, including medications, therapies, surgeries, or other interventions.
4. Nursing Care Plan
- Nursing Diagnoses: Identifies the nursing diagnoses based on the assessment data.
- Goals and Outcomes: Establishes short-term and long-term goals for the patient’s care, including expected outcomes.
- Interventions: Describes specific nursing interventions planned or implemented to address each nursing diagnosis and achieve the stated goals.
- Evaluation: Discusses the effectiveness of the nursing interventions, including patient progress and any adjustments made to the care plan.
5. Analysis
- Critical Analysis: Analyzes the case in depth, considering different aspects of patient care, decision-making processes, and the application of nursing theories and principles.
- Reflection: Reflects on the nursing practice, lessons learned, and how the case study has impacted the understanding and application of nursing knowledge.
6. Conclusion
- Summary: Provides a concise summary of the key points from the case study, including the patient outcome and the nursing care impact.
- Implications for Practice: Discusses the implications of the case for nursing practice, including any changes to practice or policy that could improve patient care.
- Recommendations: Offers recommendations for future care or areas for further study based on the case study findings.
Examples of Nursing Case Study
Free Download in Word Free Download in PDFManagement of Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI)
Introduction: A 58-year-old male with a history of hypertension and smoking presents to the emergency department with chest pain. This case study explores the nursing management for patients with AMI.
Patient Information:
- Demographics: 58-year-old male, smoker.
- Medical History: Hypertension, no previous diagnosis of heart disease.
- Current Health Assessment: Reports severe chest pain radiating to his left arm, sweating, and nausea.
Case Description:
- Clinical Presentation: Patient appeared in distress, clutching his chest.
- Diagnostic Findings: ECG showed ST-elevation in anterior leads. Troponin levels were elevated.
- Treatment Plan: Immediate administration of aspirin, nitroglycerin, and morphine for pain. Referred for emergency coronary angiography.
Nursing Care Plan:
- Nursing Diagnoses: Acute pain related to myocardial ischemia.
- Goals: Relieve pain and prevent further myocardial damage.
- Interventions: Monitoring vital signs, administering prescribed medications, and providing emotional support.
- Evaluation: Pain was managed effectively, and the patient was stabilized for angiography.
Analysis: The timely nursing interventions contributed to stabilizing the patient’s condition, showcasing the critical role nurses play in acute care settings.
Conclusion: This case highlights the importance of quick assessment and intervention in patients with AMI, emphasizing the nurse’s role in pain management and support.
Free Download in Word Free Download in PDFManaging Type 1 Diabetes in a Pediatric Patient
Introduction: A 10-year-old female diagnosed with type 1 diabetes presents for a routine check-up. This case study focuses on the nursing care plan for managing diabetes in pediatric patients.
Patient Information:
- Demographics: 10-year-old female.
- Medical History: Diagnosed with type 1 diabetes six months ago.
- Current Health Assessment: Well-controlled blood glucose levels, but expresses difficulty with frequent insulin injections.
Case Description:
- Clinical Presentation: Patient is active, engaging in school activities but struggles with diabetes management.
- Diagnostic Findings: HbA1c is 7.2%, indicating good control.
- Treatment Plan: Insulin therapy, carbohydrate counting, and regular blood glucose monitoring.
Nursing Care Plan:
- Nursing Diagnoses: Risk for unstable blood glucose levels.
- Goals: Maintain blood glucose within target range and increase patient comfort with diabetes management.
- Interventions: Education on insulin pump use, dietary advice, and coping strategies.
- Evaluation: Patient showed interest in using an insulin pump and understood dietary recommendations.
Analysis: This case emphasizes the importance of education and emotional support in managing chronic conditions in pediatric patients.
Conclusion: Effective management of type 1 diabetes in children requires a comprehensive approach that includes education, technological aids, and psychological support.
Free Download in Word Free Download in PDFElderly Care for Alzheimer’s Disease
Introduction: An 82-year-old female with Alzheimer’s disease presents with increased confusion and agitation. This case study examines the complexities of caring for elderly patients with Alzheimer’s.
Patient Information:
- Demographics: 82-year-old female.
- Medical History: Alzheimer’s disease, osteoarthritis.
- Current Health Assessment: Increased confusion, agitation, and occasional aggression.
Case Description:
- Clinical Presentation: Patient exhibits signs of advanced Alzheimer’s with memory loss and disorientation.
- Diagnostic Findings: Cognitive tests confirm the progression of Alzheimer’s.
- Treatment Plan: Non-pharmacological interventions for agitation, memory aids, and safety measures in the home.
Nursing Care Plan:
- Nursing Diagnoses: Impaired memory related to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Goals: Reduce agitation and prevent harm.
- Interventions: Use of calming techniques, establishing a routine, and environmental modifications.
- Evaluation: Agitation was reduced, and the patient’s safety was improved through environmental adjustments.
Analysis: The case underscores the need for tailored interventions to manage Alzheimer’s symptoms and improve the quality of life for the elderly.
Conclusion: Nursing care for Alzheimer’s patients requires a multifaceted approach focusing on safety, symptom management, and patient dignity.
Nursing Case Study Topics with Samples to Edit & Download
- Telehealth Nursing
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing
- Geriatric Nursing Care
- Palliative and End-of-Life Care
- Pediatric Nursing
- Emergency and Critical Care Nursing
- Chronic Disease Management
- Nursing Ethics and Patient Rights
- Infection Control and Prevention
- Oncology Nursing
- Nursing Leadership and Management
- Cultural Competence in Nursing
- Substance Abuse and Addiction Nursing
- Technological Innovations in Nursing
- Nursing Education and Training
Nursing Case Study Examples & Templates
1. Nursing Case Study Template
2. Free Nursing Student Care Plan Template
3. Nursing Action Case Study Example
4. Hospital Nursing Care Case Study Example
5. Printable Nursing Health Case Study Example
6. Fundamentals of Nursing Case Study Example
7. Sample Nursing Case Study Example
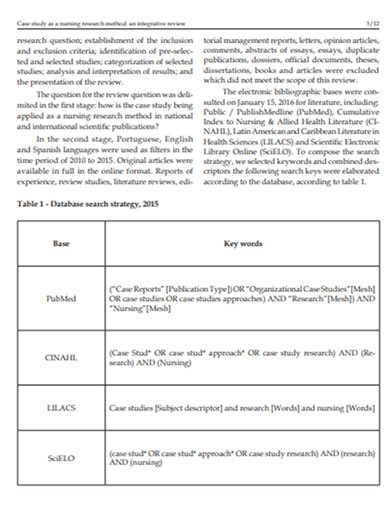
8. Nursing Research Case Study Example
9. Standard Nursing Case Study Example
10. Nursing Disability Case Study Example
11. Nursing care Patients Case Study Example
12. School of Nursing Case Study Example
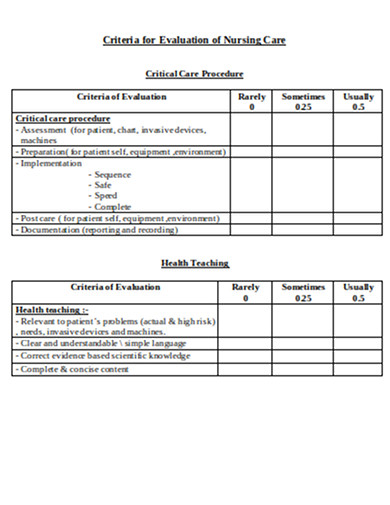
13. Evaluation of Nursing Care Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Segments
Typically, a nursing case study contains three main categories, such as the items below.
1. The Status of a Patient
In this section, you will provide the patient’s information, such as medical history, and give the current patient’s diagnosis, condition, and treatment. Always remember to write down all the relevant information about the patient. Other items that you can collect in this stage are the reasons for the patient to seek medical care and the initial symptoms that he or she is experiencing. After that, based on the gathered information, you will explain the nature and cause of the illness of the patient.
2. The Nursing Assessment of the Patient
In this stage, you will need to prepare your evaluation of the patient’s condition. You should explain each observation that you have collected based on the vital signs and test results. You will also explain each nursing diagnosis that you have identified and determine the proper nursing care plan for the patient.
3. The Current Care Plan and Recommendations
Describe the appropriate care plan that you can recommend to the patient based on the diagnosis, current status, and prognosis in detail, including how the care plan will affect his or her life quality. If needed, you can also evaluate the patient’s existing care plan and give recommendations to enhance it. It is also crucial to cite relevant authoritative sources that will support your recommendations.
Objectives of Nursing Case Study
Nursing case studies are integral educational tools that bridge theoretical knowledge with practical application in patient care. They serve several key objectives essential for the development of nursing students and professionals. Here are the primary objectives of nursing case studies:
1. Enhance Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning
Case studies encourage nurses to analyze complex patient scenarios, make informed decisions, and apply critical thinking skills to solve problems. They simulate real-life situations, requiring nurses to evaluate data, consider multiple outcomes, and choose the best course of action.
2. Improve Diagnostic Skills
Through the detailed analysis of patient information, symptoms, and diagnostic results, nursing case studies help improve diagnostic skills. They allow nurses to practice interpreting clinical data to identify patient conditions and understand the underlying causes of symptoms.
3. Facilitate Application of Theoretical Knowledge
Nursing case studies provide a direct bridge between classroom learning and clinical practice. They offer a practical venue for applying theoretical knowledge about anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and nursing theories to real-world patient care situations.
4. Promote Understanding of Comprehensive Patient Care
These studies emphasize the importance of holistic care, considering the physical, emotional, social, and psychological aspects of patient well-being. Nurses learn to develop comprehensive care plans that address all facets of a patient’s health.
5. Encourage Reflective Practice and Self-Assessment
Reflecting on case study outcomes enables nurses to evaluate their own decision-making processes, clinical judgments, and actions. This self-assessment promotes continuous learning and professional growth by identifying areas for improvement.
6. Foster Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Case studies often involve scenarios that require collaboration among healthcare professionals from various disciplines. They teach nurses the value of teamwork, communication, and the integration of different expertise to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
7. Enhance Patient Education and Advocacy Skills
By working through case studies, nurses improve their ability to educate patients and families about health conditions, treatment plans, and preventive measures. They also learn to advocate for their patients’ needs and preferences within the healthcare system.
8. Prepare for Real-Life Challenges
Nursing case studies prepare students and new nurses for the unpredictability and challenges of real-life clinical settings. They provide safe, controlled environments to practice responses to emergencies, ethical dilemmas, and complex patient needs without the risk of actual harm.
Steps in Nursing Process
Whether you are handling a patient with schizophrenia, pneumonia, diabetes, appendicitis, hypertension, COPD, etc, you will need to follow specific steps to ensure that you are executing the critical nursing process.
1. Assess the Patient
The first step of the nursing process requires critical thinking skills as it involves gathering both subjective and objective data. Subjective data includes verbal statements that you can collect from the patient or caregiver. In contrast, objective information refers to measurable and tangible data, such as vital signs, height, weight, etc. You can also use other sources of information, such as electronic health records, and friends that are in direct contact with the patient.
2. Diagnose the Patient
This critical step will help you in the next steps, such as planning and implementation of patient care. In this step, you will formulate a nursing diagnosis by applying clinical judgment. As a nurse, the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) will give you an up-to-date nursing diagnosis list, which will allow you to form a diagnosis based on the actual health problem.
3. Plan for a Proper Patient Care Plan
This part is where you will plan out the appropriate care plan for the patient. You will set this goal following the evidence-based practice (EDP) guidelines. The goal you will set should be specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely (SMART).
4. Implement the Plan
In this stage, you can execute the plan that you have developed in the previous step. The implementation may need interventions such as a cardiac monitor, medication administration, etc.
5. Evaluate the Results
It is crucial to remember that every time the team does an intervention, you must do a reassessment to ensure that the process will lead to a positive result. You may need to reassess the patient depending on his progress, and the care plan may be modified based on the reassessment result.
Where to find nursing case studies?
Nursing case studies can be found in a variety of academic, professional, and medical resources. Here are some key places to look for nursing case studies:
- Academic Journals: Many academic journals focus on nursing and healthcare and publish case studies regularly. Examples include the “Journal of Clinical Nursing,” “Nursing Case Studies,” and “American Journal of Nursing.”
- University and College Libraries: Many academic institutions provide access to databases and journals that contain nursing case studies. Libraries often have subscriptions to these resources.
- Online Medical Libraries: Websites like PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Wiley Online Library offer a vast collection of nursing and medical case studies.
- Professional Nursing Organizations: Organizations such as the American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National League for Nursing (NLN) often provide resources, including case studies, for their members.
- Nursing Education Websites: Websites dedicated to nursing education, such as Lippincott NursingCenter and Nurse.com, often feature case studies for educational purposes.
- Government Health Websites: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) sometimes publish case studies related to public health nursing and disease outbreaks.
- Nursing Textbooks and eBooks: Many nursing textbooks and eBooks include case studies to illustrate key concepts and scenarios encountered in practice.
- Online Nursing Forums and Communities: Forums and online communities for nursing professionals may share or discuss case studies as part of their content.
- Conference Proceedings: Nursing and healthcare conferences often include presentations of case studies. Many of these are published in the conference proceedings, which may be accessible online.
Carrying out a nursing case study can be a delicate task since it puts the life of a person at stake. Thus, it requires a thorough investigation. With that said, it is essential to gain intensive knowledge about this type of study. Today, we have discussed an overview of how to conduct a nursing case study. However, if you think that you are having problems with your writing skills, we recommend you to consider looking for an essay writing service from the experts in the nursing department to ensure that the output follows the appropriate writing style and terminology.