What information does an area chart typically represent?
Relationships between two variables
Proportions of different categories over time
Individual data points at a specific time
The distribution of a single variable
Step into the engaging world of Area Charts, an essential guide designed for educators keen on simplifying data interpretation for their students. This guide introduces the basics of area charts through easy-to-understand examples, enriching the teaching and learning experience. Ideal for presenting accumulated data over time, it helps in making comparisons and spotting trends effortlessly. Tailored for teachers and students, this guide enhances English communication skills by breaking down complex data insights into manageable lessons, promoting a more interactive and insightful educational journey.
Area charts are a graphical representation that showcases quantitative data over a period. Similar to line charts, but with the area below the line filled in, they provide a vivid picture of volume or magnitude changes over time. This fill helps to highlight the extent of change, making it easier for students to grasp the concept of trends and data fluctuations. Simple, yet powerful, area charts are a fantastic tool for teachers aiming to illustrate complex data in a more accessible way, fostering an environment where students can visually connect with the material presented.
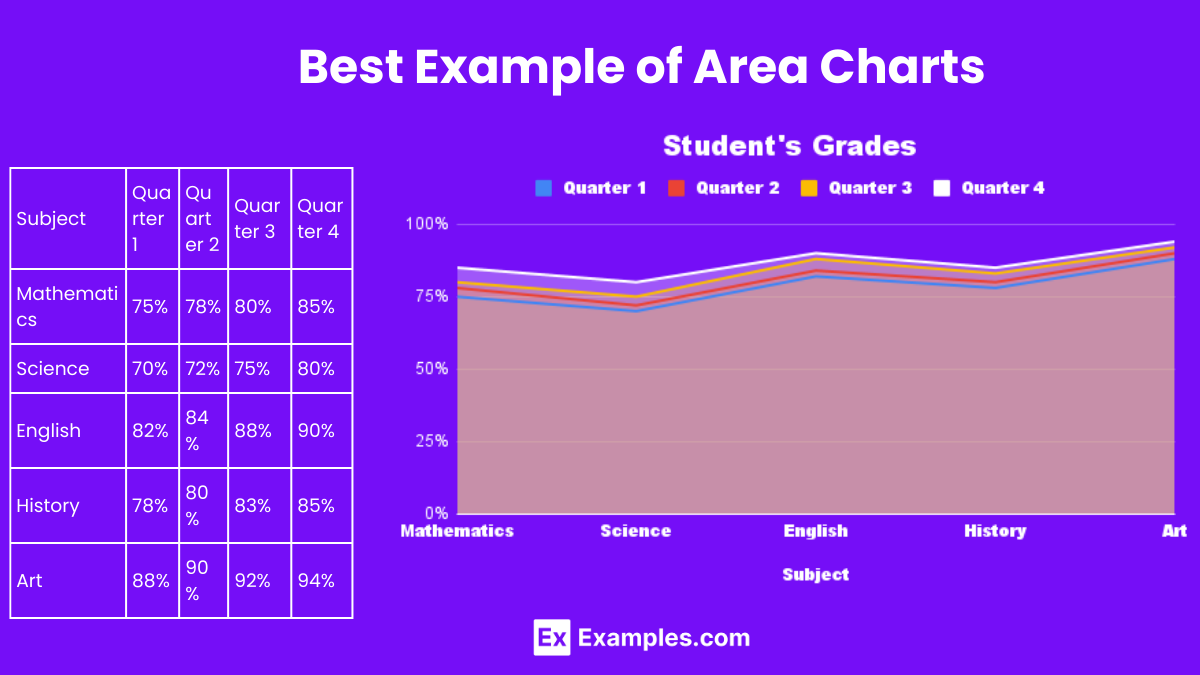
An exemplary use of area charts can be found in tracking the progress of a student’s grades throughout the academic year. By plotting time on the horizontal axis and grades on the vertical axis, the chart fills the area under the line, showcasing how grades have improved or declined over time. This visual tool not only aids teachers in explaining the importance of consistent study habits but also enables students to visually assess their performance. Through such practical applications, area charts become an invaluable resource in education, turning abstract numbers into meaningful narratives that encourage student engagement and understanding.
Area charts are versatile tools in data visualization, effectively illustrating changes over time and comparing different categories. They excel in displaying cumulative totals using color-filled areas beneath lines, making it easier to understand volume changes or trends within datasets. Ideal for educators, students, and professionals, area charts facilitate a clearer comprehension of complex information through visual representation.
An area chart can display the total rainfall each month over a year, with the vertical axis representing rainfall amount and the horizontal axis the months. This visualizes seasonal weather patterns effectively.
This example uses an area chart to show the proportion of website traffic coming from different channels (e.g., direct, referral, social) over time, highlighting trends in how viewers discover the site.
Compare yearly sales data across different product lines. An area chart can help in visualizing which products are leading sales and how sales trends are evolving over the years.
An area chart can track the fluctuating value of stocks over time, offering investors a clear view of market trends and helping in making informed decisions.
This chart can illustrate the hourly energy consumption in a building, showing peaks during daytime and lower usage at night, aiding in energy management and planning.
| Feature | Area Chart | Line Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization | Uses color-filled areas below the lines to show volume. | Uses lines to represent changes in values over time. |
| Best Used For | Displaying cumulative totals and trends over time. | Highlighting changes and trends without focusing on volume. |
| Data Interpretation | Easier to visualize the magnitude of changes over time. | Better for precise value comparisons at specific points. |
| Complexity | Best for single categories or stacked for multiple layers. | Suitable for comparing multiple datasets simultaneously. |
| Visual Impact | The filled area emphasizes the volume and cumulative effect. | Focuses attention on the direction and rate of data changes. |
Area charts come in various forms, each suited for different analytical purposes, enhancing data storytelling with visual depth and clarity.
1. Stacked Area Chart
Stacked area charts are perfect for comparing the composition of multiple data groups over time, showing how each category contributes to the total volume.
2. Percent Stacked Area Chart
This variation shows how each category’s proportion of the total changes over time, ideal for understanding relative distribution within a whole.
3. 3D Area Chart
Adds a three-dimensional aspect to the visualization, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and making the data presentation more engaging, although sometimes at the cost of clarity.
4. Streamgraph
A modern take on the traditional area chart, streamgraphs display data in a flowing, organic shape, often used for more artistic data visualization.
5. Range Area Chart
Highlights the range between two data series for each point in time, effectively visualizing the variance and trends within the dataset, such as temperature highs and lows over a year.
Area charts excel in visualizing how a quantity evolves over time, making them ideal for displaying accumulated values, trends, and volumes. They are particularly useful in educational settings to teach students about data analysis, emphasizing changes within datasets over periods. Area charts facilitate the comparison of multiple categories visually, helping to highlight growth patterns, declines, or cyclical movements in a clear, intuitive manner. Their application ranges from comparing sales figures, website traffic, to analyzing economic data, offering a versatile tool for educators to integrate into lessons.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Visually Intuitive: Easily display trends and volumes over time. | Can Be Overwhelming: Multiple overlapping areas can complicate the chart. |
| Effective for Comparison: Highlight differences between datasets. | Limited Detail: Not ideal for conveying specific data points. |
| Highlight Growth or Decline: Clearly show how quantities change. | Obscures Data: In stacked charts, lower layers may be hidden. |
| Versatile Application: Useful in various educational contexts. | Requires Context: Best understood with prior explanation. |
| Engages Students: Visuals can make abstract data more accessible. | Color Dependency: Relies heavily on color to differentiate data, which can be an issue for color-blind viewers. |
| Feature | Area Chart | Bubble Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used to display the quantitative data over time and highlight the magnitude of change. | Illustrates the relationships between three variables on a two-dimensional plot. |
| Visualization | Shows trends by filling the area under the line connecting different data points. | Displays data points as bubbles, where the size of the bubble represents the third dimension. |
| Use Case | Ideal for tracking changes in one or more related groups over the same time period. | Best for comparing and contrasting the magnitude and relation of data points in a dataset. |
| Complexity | Relatively simple and straightforward, focusing on time series data. | More complex, providing a multi-dimensional analysis of data. |
| Interpretation | Easy to interpret for trends and volume change over time. | Requires understanding of bubble size in addition to X and Y axes positions to analyze data. |
1. X-Axis (Horizontal Axis): Represents the time period or the categories being compared.
2. Y-Axis (Vertical Axis): Indicates the quantitative value that each point on the X-axis represents.
3. Data Points: Specific values plotted on the chart that represent the intersection of X and Y values.
4. Trend Line (or Line Graph): Connects the data points, showing the change over time or categories.
5. Fill Area: The area between the trend line and the X-axis, typically shaded or colored.
1. Financial Analysis: Tracking Stock Market Trends
2. Environmental Studies: Monitoring Temperature Changes
3. Marketing Analysis: Website Traffic Over Time
4. Health Sector: Patient Admission Rates
5. Education: Analyzing Test Scores
Area charts offer a visually impactful way to display data trends over time, making them ideal for educational and analytical purposes. They highlight volume change, enabling educators and students to grasp complex concepts quickly. With their ability to compare multiple datasets on the same graph, area charts simplify data analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of statistical information. This makes them an invaluable tool in both classroom settings and professional data analysis.
Interpreting patterns in area charts allows for a nuanced understanding of data trends, enabling educators to teach critical thinking and analytical skills. This analysis is crucial in identifying correlations, understanding market trends, or assessing environmental changes, thereby enriching educational content with real-world applications and insights.
In summary, area charts are a powerful visual tool for both teaching and learning, offering clear insights into data trends and comparisons over time. They enhance the educational process by simplifying complex data interpretation, fostering critical thinking, and improving communication skills. Whether in economics, environmental studies, or market analysis, area charts facilitate a deeper understanding of subjects, making them indispensable in the classroom and beyond.
Text prompt
Add Tone
Area Chart vs. Bubble Chart
Types Of Area Charts
What information does an area chart typically represent?
Relationships between two variables
Proportions of different categories over time
Individual data points at a specific time
The distribution of a single variable
In an area chart, if the area of one section increases, what does it indicate?
The value of that category is decreasing
The value of that category is increasing
The category is becoming irrelevant
The total value is decreasing
How can you differentiate between multiple data series in an area chart?
By the different colors or patterns used for each series
By the size of the chart
By the height of the chart
By the legends only
What does the vertical axis of an area chart usually represent?
The time period
The categories
The values or measurements
The total count of all categories
When is it most appropriate to use an area chart?
When you want to compare parts of a whole over time
When you need to show a single data point
When comparing two variables without time
When displaying categorical data
In an area chart with overlapping areas, what does the overlap indicate?
An error in data representation
A direct comparison between categories
A relative proportion of categories
A change in data scale
What would be the impact on the area chart if the values for one category drop significantly?
The area for that category would increase
The area for that category would decrease
The area for that category would remain the same
The chart would display an error
What type of data is best suited for an area chart?
Data that changes over time
Data that is static
Categorical data with no numerical values
Data with very few points
If two areas on an area chart are the same size but different colors, what does that imply?
The two categories have the same value
One category is larger than the other
There is a discrepancy in the data
The chart is incorrectly labeled
How can you interpret the trend of a single category in an area chart?
By comparing it to the overall total
By looking at the changes in its area over time
By examining the color intensity
By checking the horizontal axis
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

