What number should be multiplied with 6 to get 54?
7
8
9
10

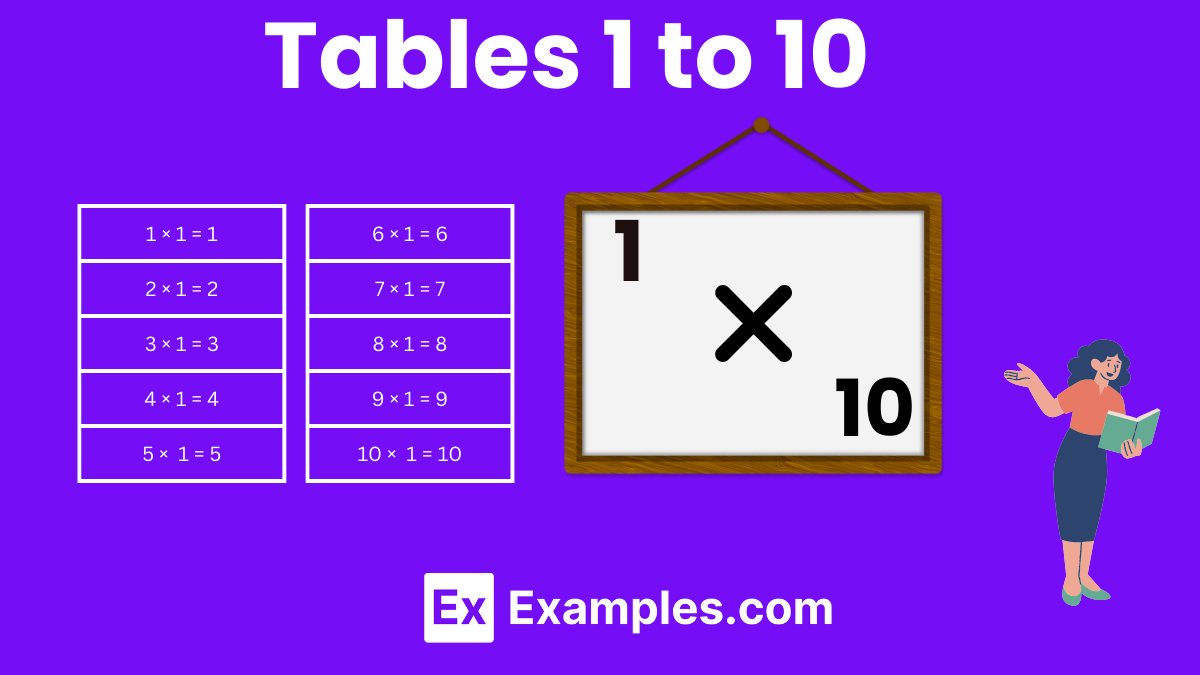
The multiplication tables from 1 to 10 are foundational elements of basic mathematics education, crucial for young learners to grasp early on. These tables cover the products of numbers 1 through 10, each multiplied by numbers from 1 to 10, forming a core part of arithmetic that supports further mathematical learning and understanding. Mastery of these tables significantly enhances a student’s ability to quickly perform calculations, helping with more complex operations such as division, fractions, and problem-solving in everyday situations.
Download Tables From 1 to 10 Pdf
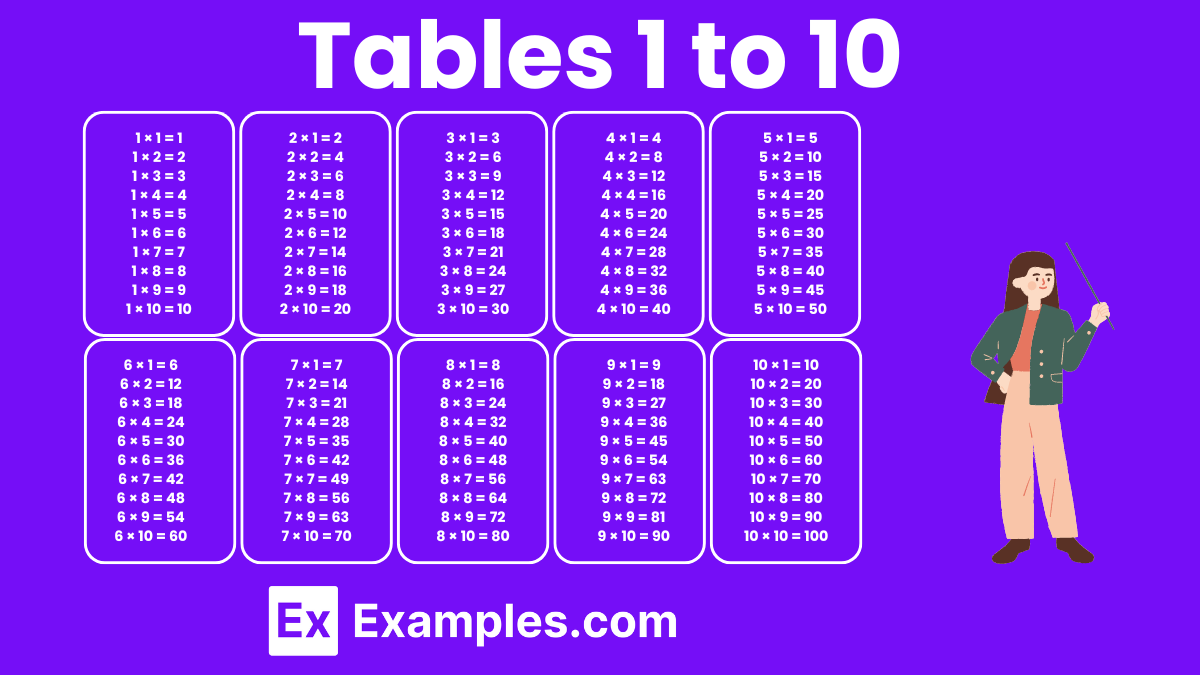
A multiplication chart for tables 1 to 10 forms a 10×10 grid, where each row and column is labeled from 1 to 10. The intersections of these rows and columns display the products, providing a clear visual representation of basic multiplication. This chart is fundamental in teaching young learners the building blocks of arithmetic, aiding in quick calculations and enhancing numerical understanding.
A multiplication chart for tables from 1 to 10 is a clear and organized visual aid that showcases the products of numbers ranging from 1 to 10 with each other. It features a grid format where each column and each row are headed by numbers 1 through 10. The intersection of each row and column within this grid shows the product of the two numbers, facilitating quick and easy access to multiplication facts. This chart is particularly helpful for young students who are just beginning to learn their multiplication tables, providing them with a simple method to look up answers and reinforce their learning through repetition and visualization.
Download Tables From 1 to 10 Pdf
| 1 x 1 = 1 | 2 x 1 = 2 | 3 x 1 = 3 | 4 x 1 = 4 | 5 x 1 = 5 |
| 1 x 2 = 2 | 2 x 2 = 4 | 3 x 2 = 6 | 4 x 2 = 8 | 5 x 2 = 10 |
| 1 x 3 = 3 | 2 x 3 = 6 | 3 x 3 = 9 | 4 x 3 = 12 | 5 x 3 = 15 |
| 1 x 4 = 4 | 2 x 4 = 8 | 3 x 4 = 12 | 4 x 4 = 16 | 5 x 4 = 20 |
| 1 x 5 = 5 | 2 x 5 = 10 | 3 x 5 = 15 | 4 x 5 = 20 | 5 x 5 = 25 |
| 1 x 6 = 6 | 2 x 6 = 12 | 3 x 6 = 18 | 4 x 6 = 24 | 5 x 6 = 30 |
| 1 x 7 = 7 | 2 x 7 = 14 | 3 x 7 = 21 | 4 x 7 = 28 | 5 x 7 = 35 |
| 1 x 8 = 8 | 2 x 8 = 16 | 3 x 8 = 24 | 4 x 8 = 32 | 5 x 8 = 40 |
| 1 x 9 = 9 | 2 x 9 = 18 | 3 x 9 = 27 | 4 x 9 = 36 | 5 x 9 = 45 |
| 1 x 10 = 10 | 2 x 10 = 20 | 3 x 10 = 30 | 4 x 10 = 40 | 5 x 10 = 50 |
| 6 x 1 = 6 | 7 x 1 = 7 | 8 x 1 = 8 | 9 x 1 = 9 | 10 x 1 = 10 |
| 6 x 2 = 12 | 7 x 2 = 14 | 8 x 2 = 16 | 9 x 2 = 18 | 10 x 2 = 20 |
| 6 x 3 = 18 | 7 x 3 = 21 | 8 x 3 = 24 | 9 x 3 = 27 | 10 x 3 = 30 |
| 6 x 4 = 24 | 7 x 4 = 28 | 8 x 4 = 32 | 9 x 4 = 36 | 10 x 4 = 40 |
| 6 x 5 = 30 | 7 x 5 = 35 | 8 x 5 = 40 | 9 x 5 = 45 | 10 x 5 = 50 |
| 6 x 6 = 36 | 7 x 6 = 42 | 8 x 6 = 48 | 9 x 6 = 54 | 10 x 6 = 60 |
| 6 x 7 = 42 | 7 x 7 = 49 | 8 x 7 = 56 | 9 x 7 = 63 | 10 x 7 = 70 |
| 6 x 8 = 48 | 7 x 8 = 56 | 8 x 8 = 64 | 9 x 8 = 72 | 10 x 8 = 80 |
| 6 x 9 = 54 | 7 x 9 = 63 | 8 x 9 = 72 | 9 x 9 = 81 | 10 x 9 = 90 |
| 6 x 10 = 60 | 7 x 10 = 70 | 8 x 10 = 80 | 9 x 10 = 90 | 10 x 10 = 100 |
Problem:
1 x 9 = ?
Solution:
1 x 9 = 9
(Multiplying any number by 1 yields the number itself.)
Problem:
2 x 5 = ?
Solution:
2 x 5 = 10
(Two times five equals ten.)
Problem:
3 x 7 = ?
Solution:
3 x 7 = 21
(Three times seven results in twenty-one.)
Problem:
4 x 8 = ?
Solution:
4 x 8 = 32
(Four times eight equals thirty-two.)
Problem:
5 x 10 = ?
Solution:
5 x 10 = 50
(Five multiplied by ten results in fifty.)
Problem:
6 x 6 = ?
Solution:
6 x 6 = 36
(Six times six equals thirty-six.)
Problem:
7 x 4 = ?
Solution:
7 x 4 = 28
(Seven times four yields twenty-eight.)
Problem:
8 x 9 = ?
Solution:
8 x 9 = 72
(Eight multiplied by nine results in seventy-two.)
Problem:
9 x 3 = ?
Solution:
9 x 3 = 27
(Nine times three equals twenty-seven.)
Problem:
10 x 7 = ?
Solution:
10 x 7 = 70
(Ten times seven results in seventy.)
Learning multiplication tables 1 to 10 is essential as it forms the foundation for various mathematical concepts and calculations. It helps in developing strong arithmetic skills and facilitates quicker problem-solving.
Some strategies include practicing regularly, using mnemonic devices, breaking down larger numbers into smaller factors, identifying patterns, and using visual aids like charts and diagrams.
Yes, there are several tricks and patterns such as skip counting, recognizing multiples, identifying symmetry, and using known facts to derive unknown ones that can aid in memorization.
Encourage your child to practice regularly, offer praise and positive reinforcement for their efforts, provide additional support through tutoring or educational resources, and break down multiplication problems into smaller, more manageable steps.
dults can improve their multiplication skills for tables 1 to 10 by revisiting basic multiplication concepts, practicing regularly, using mnemonic devices, and seeking out educational resources or courses designed for adult learners.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What number should be multiplied with 6 to get 54?
7
8
9
10
If 5 is multiplied by which number, the result is 35?
6
7
8
9
Which of the following is not a multiple of 4?
16
20
24
26
What is the missing number: 9 × _ = 81?
7
8
9
10
If 8 times a number equals 64, what is the number?
7
8
9
10
What is the product of 3 and the sum of 5 and 6?
30
33
35
36
How many times does 7 fit into 56?
7
8
9
10
If 3 times a number equals 27, what is the number?
7
8
9
10
What is the missing number: 4 × _ = 32?
6
9
8
7
What is the missing number: 5×_=455 \times \_ = 455×_=45?
4
7
9
6
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

