What is the unit of electric potential in the SI system?
Volt
Coulomb
Ohm
Ampere

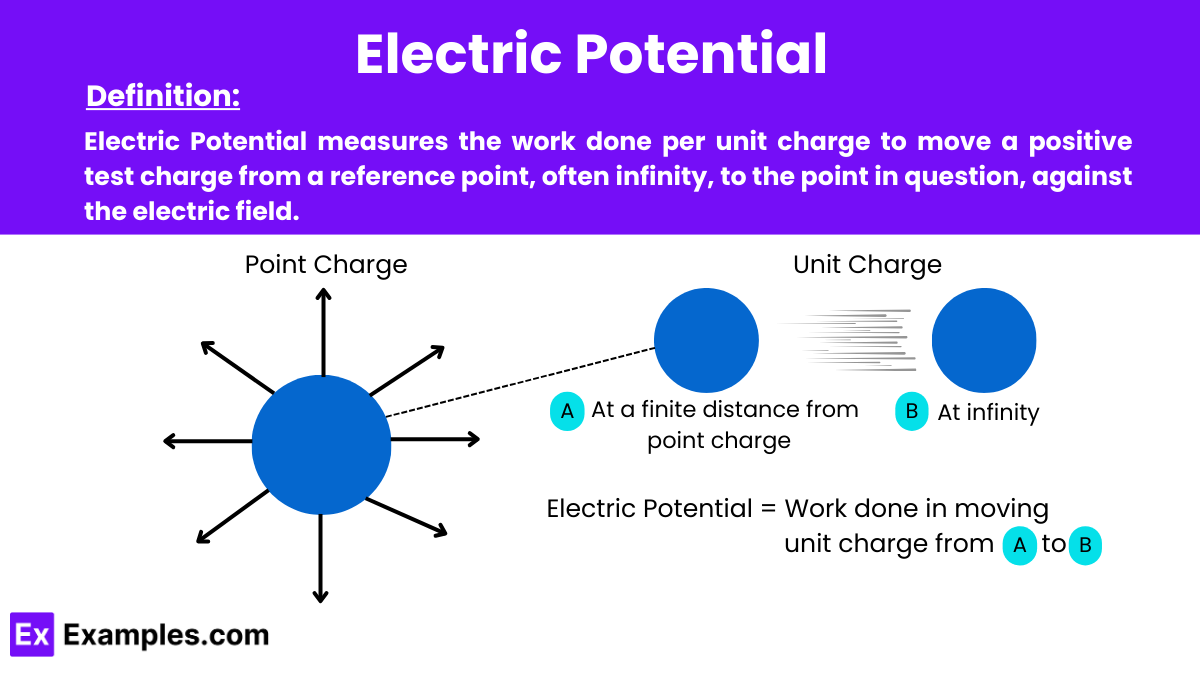
Electric Potential is a concept in physics that quantifies the amount of potential energy a unit charge would have at a specific point in an electric field. It measures the work done per unit charge to move a positive test charge from a reference point, often infinity, to the point in question, against the electric field.
The formula for Electric Potential (V) at a point in an units of electric field is given by:
For the electric potential due to a point charge, the formula is:
Electric potential is energy per unit charge, while potential energy is the total energy of a charged object due to its position in an electric field.
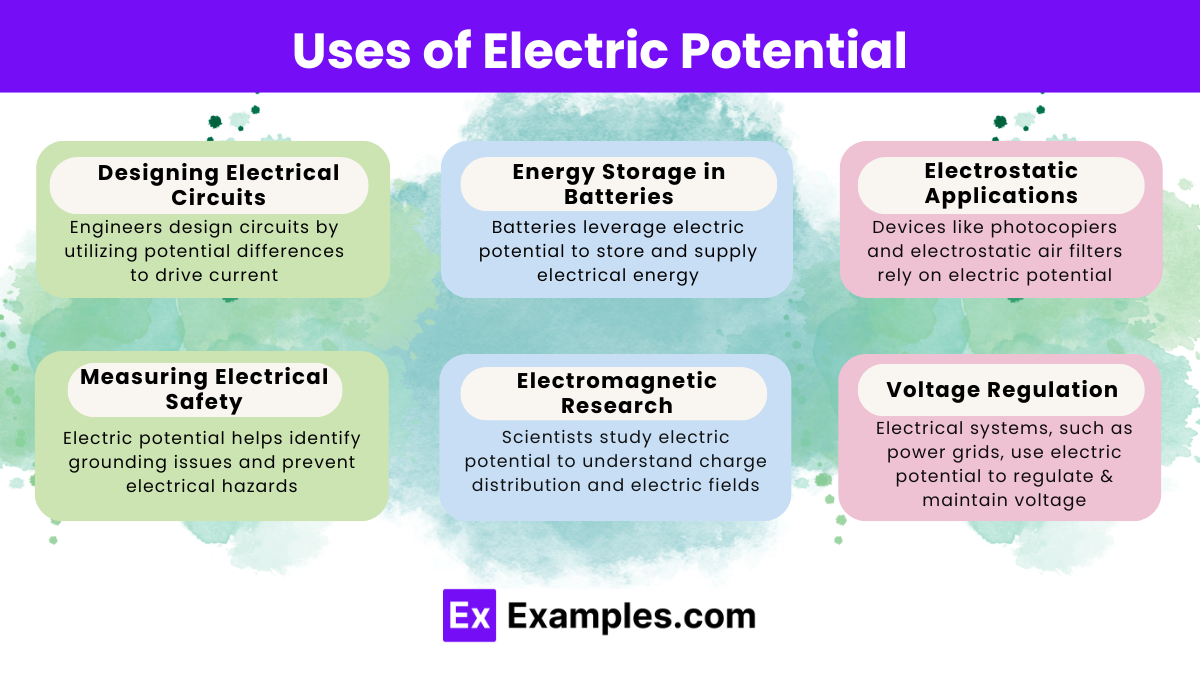
The unit for electric potential is the volt (V), which represents one joule per coulomb. It’s commonly used to indicate voltage in circuits.
Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points. It shows the amount of work required to move a unit charge between those points.
Use the formula 𝑉=KQ/r, where k is Coulomb’s constant, Q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge.
Batteries use electric potential to create voltage differences, providing energy that powers electrical devices and enables current flow through circuits.
It drives the current by providing a potential difference across circuit components, enabling devices like resistors and capacitors to function correctly.
The charge’s magnitude and distribution, distance from the charge, and the surrounding medium’s permittivity impact the electric potential at a given point.
In a uniform field, electric potential decreases linearly along the field’s direction. The greater the distance, the higher the potential difference.
Yes, electric potential can be negative if work is required to move a charge in opposition to the direction of the electric field.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the unit of electric potential in the SI system?
Volt
Coulomb
Ohm
Ampere
Which formula represents the relationship between electric potential (V), work (W), and charge (Q)?
V = W/Q
V = W*Q
V = Q/W
V = W-Q
If the electric potential at a point is 10 V and the charge is 2 C, what is the work done?
5 J
20 J
10 J
2 J
If the potential difference between two points is 12 V and the charge is 3 C, what is the work done in moving the charge?
36 J
4 J
15 J
12 J
What is the relationship between electric potential (V) and electric field (E) over a distance (d)?
V = Ed
V = E/d
V = E*d²
V = E/d²
If the electric field is 5 V/m and the distance is 2 m, what is the electric potential difference?
10 V
15 V
20 V
25 V
What is the potential energy of a 2 C charge at a point with an electric potential of 5 V?
2.5 J
10 J
1 J
7 J
How does the electric potential change as the distance from a point charge increases?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It depends on the medium
If the work done in moving a charge of 1 C between two points is 5 J, what is the potential difference between the points?
5 V
1 V
10 V
2 V
Which point has higher electric potential, closer to a positive charge or farther away?
Closer
Farther
Both are equal
Depends on the magnitude of the charge
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

