5+ 504 Plan Examples to Download
Every student deserves a fair and inclusive education, and for students with disabilities, a 504 Plan can be instrumental in ensuring equal opportunities. In this article, we will explore over 20 real-life 504 Plan examples, providing valuable insights into the documentation process, goals and objectives, legal considerations, and more. Whether you are an educator, parent, or advocate, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to effectively support students with disabilities in their educational journey.
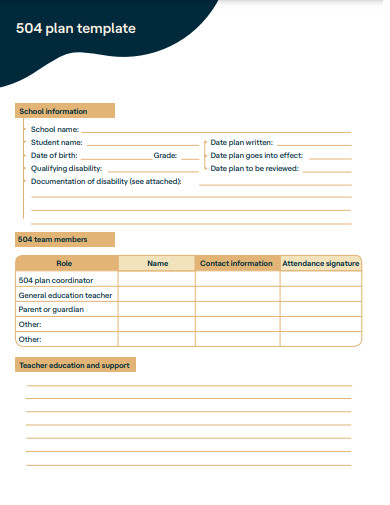
1. 504 Plan Template

2. Sample 504 Plan Template

3. Medical 504 Plan Template

4. Preschool 504 Plan Template

5. College 504 Plan Template

6. Section 504 Plan Manual
7. 504 Plan
8. 504 Plan Development
9. Sample 504 Plan
10. Parent and Educator 504 Plan
11. 504 Accumulation Plan
12. 504 Plan Example
13. 504 Plan Teams
14. 504 Plan Outline
15. 504 Plan Referral Checklist
16. 504 Plan Format
17. Simple 504 Plan
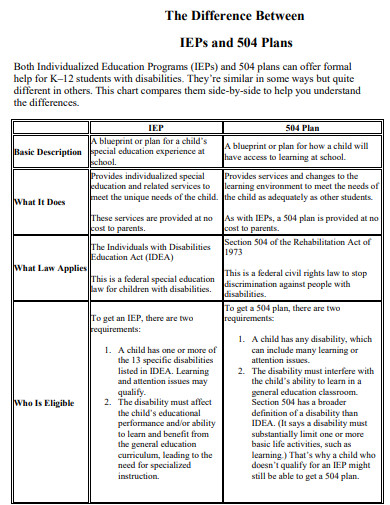
18. IEPs and 504 Plans
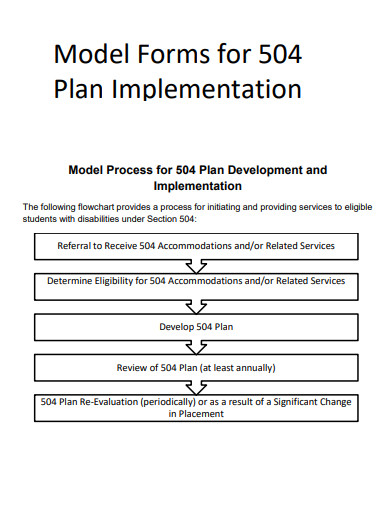
19. 504 Plan Implementation
20. Standard 504 Plan
21. Printable 504 Plan
What is a 504 Plan?
A 504 Plan is a legally binding document designed to remove barriers that may impede a student’s ability to fully participate in their education due to a disability. Unlike an Individualized Education Program (IEP), which is reserved for students who require specialized instruction, a 504 Plan provides reasonable accommodations, modifications, and support services that allow students with disabilities to access educational opportunities on an equal basis with their peers. The plan is tailored to meet the specific needs of each student and is a collaborative effort between parents or guardians, educators, and other relevant professionals.
How to Create a 504 Plan
Crafting a well-designed and effective 504 Plan requires careful consideration and collaboration among all stakeholders involved. This step-by-step guide will provide you with a structured approach to writing a comprehensive 504 Plan that addresses the unique needs of each student, ensuring they receive the support necessary to thrive in their educational environment.
Step 1: Initial Assessment and Documentation:
The first step in creating a 504 Plan is to conduct a thorough assessment of the student’s disability, its impact on their educational performance, and the accommodations or modifications they may require. Check out 10+ documentation procedure examples here to gain insights into the assessment and documentation process, ensuring accurate and comprehensive records.
Step 2: Establish Goals and Objectives
Once the assessment is complete, the next step is to define clear and measurable goals and objectives for the student. These goals should be realistic, specific, and aligned with the student’s individual needs. By setting achievable objectives, educators can track progress and ensure the student receives the necessary support. Explore examples of 10+ legal documents here to learn how to effectively establish goals and objectives in a 504 Plan.
Step 3: Determining Accommodations and Support Services:
In this stage, the focus shifts to determining the appropriate accommodations and support services that will help the student access their education effectively. Each student’s needs will vary, and it is essential to consider their specific requirements while maintaining a level playing field with their peers. To aid in this process, check out 10+ documentation plan examples and templates here, providing valuable insights into various accommodation strategies.
FAQs
Can a 504 Plan be modified or changed over time?
Yes, a 504 Plan can and should be modified as necessary to address the changing needs of the student. Regular reviews and updates should be conducted to ensure the plan remains relevant and effective in supporting the student’s educational progress.
How does a 504 Plan differ from an Individualized Education Program (IEP)?
While both a 504 Plan and an IEP are designed to support students with disabilities, there are key differences between the two. An IEP is for students who require specialized instruction, whereas a 504 Plan provides accommodations and support services to ensure equal access to education without specialized instruction.
What legal considerations should be taken into account when creating a 504 Plan?
When creating a 504 Plan, it is crucial to be aware of legal requirements and ensure compliance. Familiarize yourself with 10+ legal document examples here, which provide insights into important considerations and legal aspects associated with the development and implementation of a 504 Plan.
In conclusion, A well-crafted 504 Plan is a powerful tool that empowers students with disabilities, ensuring they receive the necessary support and accommodations to thrive in their educational journey. By following the step-by-step guide outlined above and exploring the diverse range of examples and resources available, you can foster an inclusive learning environment that celebrates the unique strengths and abilities of all students. Remember, addressing the individual needs of students is a collaborative effort, and together, we can make a significant impact in their educational success.