60+ Text Structure Examples
In order to properly grasp the information offered in a piece of writing, text structure is crucial. Writers may aid their readers in understanding the material by arranging the information in a way that is logical and cohesive, allowing them to see the relationships between different concepts, follow the progression of the argument, and grasp the key points being made.
What is Text Structure?
Text Structure Example Sentences
- Chronological Order: “In the morning, she woke up, brushed her teeth, and then went for a run.”
- Compare and Contrast: “Dogs are loyal and affectionate, while cats are independent and curious.”
- Cause and Effect: “The heavy rainfall caused the river to overflow, resulting in widespread flooding.”
- Problem and Solution: “The school faced a shortage of supplies, so they organized a fundraiser to purchase more.”
- Description: “The library is a quiet, serene space filled with rows of books and comfortable reading nooks.”
- Sequence/Process: “To make a cup of tea, first boil water, then steep the tea bag, and finally add sugar or honey to taste.”
- Classification: “Mammals, such as lions and whales, give birth to live young, whereas birds and reptiles lay eggs.”
- List: “Her favorite hobbies include painting, hiking, reading, and playing the piano.”
- Spatial/Descriptive: “The cozy cabin is nestled in the mountains, surrounded by tall pine trees and a sparkling lake nearby.”
- Generalization and Example: “Many fruits are nutritious. For example, oranges are high in vitamin C and apples are a good source of fiber.”
Narrative Text Structure Examples
- Beginning: “Once upon a time, in a small village, there lived a young girl named Lily who dreamed of exploring the world.”
- Rising Action: “One day, Lily found an old map hidden in her attic. She decided to follow the map’s trail, which led her through dense forests and across raging rivers.”
- Climax: “After facing numerous challenges, including a fierce storm and a pack of wild animals, Lily finally reached the hidden treasure marked on the map.”
- Falling Action: “With the treasure in hand, Lily began her journey back home, reflecting on the bravery and resourcefulness she had discovered within herself.”
- Conclusion: “Lily returned to her village as a hero, sharing her newfound wealth and stories of adventure with her friends and family. Her journey had changed her forever, and she knew she was capable of anything.”
- Setting: “In the heart of the bustling city, a small, cozy bakery stood out with its warm, inviting aroma of freshly baked bread and pastries.”
- Characters: “John, a retired detective with a keen eye for detail, found himself drawn back into the world of mystery when a young woman named Sarah asked for his help.”
- Conflict: “Sarah’s brother had gone missing under mysterious circumstances, and despite the police’s best efforts, no leads had been found.”
- Resolution: “With John’s expertise, they uncovered a trail of clues leading to an old warehouse, where they found Sarah’s brother unharmed, caught up in a case of mistaken identity.”
- Dialogue: “As they sat in the dimly lit café, Sarah whispered, ‘Thank you, John. I don’t know what I would have done without you.’ John smiled and replied, ‘Sometimes, the past calls us back for a reason.'”
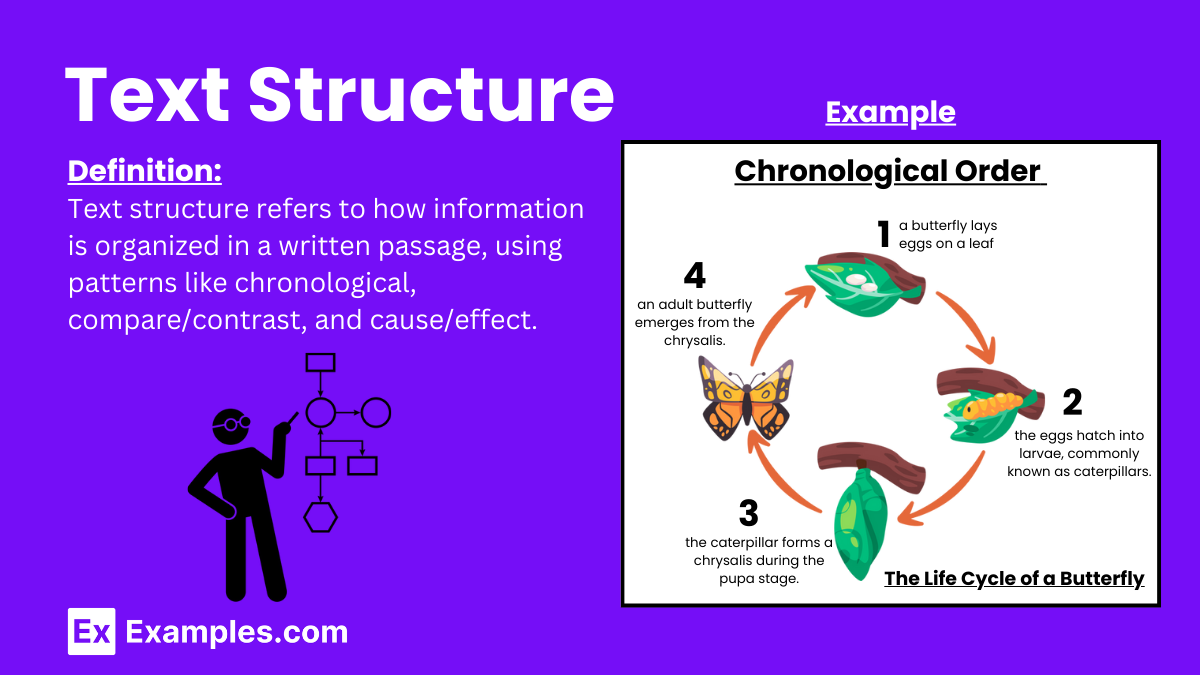
Chronological Text Structure Examples
- First Day at School:
“On her first day of school, Emma woke up early, dressed in her new uniform, and ate a quick breakfast. She then walked to the bus stop, boarded the bus, and found a seat. At school, she met her teacher and classmates, explored the playground during recess, and learned about the classroom rules.” - Historical Event:
“In 1492, Christopher Columbus set sail from Spain on August 3rd. After a long journey across the Atlantic, he and his crew sighted land on October 12th. They landed on an island in the Bahamas, marking the beginning of European exploration in the Americas.” - Daily Routine:
“Every morning, John wakes up at 6:00 AM. He then brushes his teeth, takes a shower, and gets dressed. After breakfast, he leaves for work at 7:30 AM. At noon, he takes a lunch break, and by 5:00 PM, he finishes his workday and heads home. In the evening, he has dinner, watches TV, and goes to bed by 10:00 PM.” - Cooking Recipe:
“To make a simple pasta dish, first boil water in a large pot. Add the pasta to the boiling water and cook for 8-10 minutes. While the pasta is cooking, heat olive oil in a pan and sauté garlic and onions. Add tomatoes and cook until soft. Drain the pasta, mix it with the sauce, and serve hot.” - Travel Itinerary:
“On the first day of their vacation, the family arrived in Paris and checked into their hotel. The next day, they visited the Eiffel Tower in the morning and took a boat tour on the Seine River in the afternoon. On the third day, they explored the Louvre Museum and enjoyed a leisurely dinner at a local restaurant.” - Scientific Process:
“To conduct the experiment, first gather all necessary materials, including a beaker, water, and a thermometer. Next, fill the beaker with water and place it on a heat source. Gradually increase the temperature and observe the water as it starts to boil. Record the temperature at which the water boils.” - Life Cycle of a Butterfly:
“The life cycle of a butterfly begins when an egg is laid on a leaf. The egg hatches into a caterpillar, which eats leaves and grows rapidly. After reaching a certain size, the caterpillar forms a chrysalis. Inside the chrysalis, it undergoes metamorphosis and eventually emerges as a butterfly.” - Event Timeline:
“The wedding ceremony started at 3:00 PM with the bride walking down the aisle. By 3:30 PM, the couple exchanged vows and rings. At 4:00 PM, guests moved to the reception area for cocktails and appetizers. Dinner was served at 6:00 PM, followed by dancing and festivities until midnight.” - Historical Biography:
“Abraham Lincoln was born on February 12, 1809. He grew up in a log cabin in Kentucky and later moved to Illinois. In 1830, he began his political career and was elected as the 16th President of the United States in 1860. He led the country through the Civil War and issued the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863. Lincoln was assassinated on April 14, 1865.” - Building Construction:
“The construction of the new library began with clearing the land in January. By March, the foundation was laid, and the framework was erected in April. Throughout the summer, workers installed plumbing, electrical systems, and interior walls. By September, the exterior was completed, and the interior was finished in November. The library opened to the public in December.”
Persuasive Text Structure Examples
- Introduction: “Every student should have access to free school meals because it ensures they receive the nutrition they need to succeed academically.”
- Thesis Statement: “Banning plastic bags will significantly reduce environmental pollution and protect marine life.”
- Supporting Argument 1: “Regular exercise improves mental health by reducing anxiety, depression, and negative mood while improving self-esteem and cognitive function.”
- Supporting Argument 2: “Implementing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can decrease our reliance on fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.”
- Counterargument and Rebuttal: “Some argue that electric cars are too expensive. However, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, along with government incentives, make them a cost-effective choice.”
- Supporting Argument 3: “A longer school day provides students with more time for learning and extracurricular activities, leading to better academic performance and well-rounded development.”
- Call to Action: “To combat climate change effectively, we must all adopt sustainable practices such as recycling, conserving water, and reducing energy consumption.”
- Conclusion: “In conclusion, adopting a vegetarian diet not only benefits personal health but also reduces the environmental impact of meat production. It’s time to make a change for the betterment of our planet and our future.”
- Ethical Appeal: “It’s our moral responsibility to provide shelter and support for the homeless, ensuring everyone has the basic necessities of life.”
- Emotional Appeal: “Imagine a world where no child goes to bed hungry. By supporting local food banks, we can make this vision a reality and bring hope to countless families in need.”
Description Text Structure Examples
- Describing a Place: “The tropical beach stretched for miles, its white sand glistening under the bright sun. Palm trees swayed gently in the warm breeze, and the crystal-clear turquoise water lapped softly at the shore.”
- Describing a Person: “Maria is a tall woman with long, curly brown hair that cascades down her back. Her hazel eyes are always full of warmth and kindness, and her smile can light up any room.”
- Describing an Object: “The antique clock, made of polished mahogany, stood majestically on the mantelpiece. Its golden hands moved gracefully over the Roman numerals, and the pendulum swung silently back and forth.”
- Describing an Event: “The carnival was a riot of colors and sounds. Brightly lit rides spun in dizzying circles, while children laughed and screamed with delight. The smell of cotton candy and popcorn filled the air, mingling with the cheerful music from the carousel.”
- Describing a Scene: “In the heart of the forest, a small clearing opened up, bathed in dappled sunlight. Wildflowers in shades of purple, yellow, and white carpeted the ground, and a gentle brook trickled through, its water sparkling in the light.”
- Describing a Feeling: “After receiving the good news, a wave of relief washed over him. His heart felt light, and a broad smile spread across his face as he realized the hard work had finally paid off.”
- Describing a Weather Condition: “The storm raged outside, with thunder booming and lightning flashing across the dark sky. Heavy rain pounded against the windows, and the wind howled through the trees, bending them almost to the ground.”
- Describing a Meal: “The gourmet dinner was a feast for the senses. The steak was perfectly cooked to a juicy medium-rare, accompanied by creamy mashed potatoes and crisp, tender asparagus. A rich, velvety red wine sauce completed the dish, enhancing its flavors.”
- Describing a Pet: “Max, the golden retriever, has a shiny, golden coat and expressive brown eyes. His playful nature and boundless energy make him a favorite among children, and he loves nothing more than a good game of fetch.”
- Describing a Room: “The living room was cozy and inviting, with a plush sofa covered in soft, patterned cushions. A thick, woolen rug lay in front of the fireplace, where a fire crackled warmly. Shelves lined with books and trinkets added a personal touch to the space.”
Text Structure Examples for Kids
- Chronological Order: “First, Jack woke up and had breakfast. Then he went to school. After school, he played soccer with his friends. Finally, he went home and had dinner.”
- Compare and Contrast: “Cats are quiet and like to be alone, while dogs are loud and love to be with people. Cats use a litter box, but dogs need to be taken outside.”
- Cause and Effect: “Because it rained, the picnic was canceled. The grass was too wet to sit on, and the playground was slippery.”
- Problem and Solution: “Tommy couldn’t find his homework. He looked everywhere but still couldn’t find it. So, he asked his teacher for another copy and promised to be more careful next time.”
- Description: “The fluffy, white kitten had big, blue eyes and a tiny pink nose. Its fur was as soft as a cloud, and it made a cute meowing sound.”
- Sequence/Process: “To make a sandwich, first take two slices of bread. Then spread peanut butter on one slice and jelly on the other. Put the slices together and enjoy your sandwich.”
- Classification: “There are many types of fruits. Apples and oranges are juicy fruits. Bananas and grapes are soft fruits. Each fruit has its own unique taste and texture.”
- List: “In her backpack, Lily packed a notebook, a pencil case, a water bottle, and a snack. She made sure she had everything she needed for school.”
- Spatial/Descriptive: “In the center of the playground, there is a big slide. Next to the slide is a set of swings. Across from the swings, there is a sandbox filled with toys.”
- Generalization and Example: “Many animals live in the forest. For example, deer roam freely, squirrels climb trees, and birds build nests high up in the branches.”
More Samples of Text Structure in PDF
1. 20 Strategies to Teach Text Structure
2. Text Structure Signal Words
3. Introducing Text Structures in Writing-5th Grd
4. Teaching Text Structure
5. Understanding Text Structures
6. Text Structure Sort
7. Text Structure Overview
8. Informational Text Structures
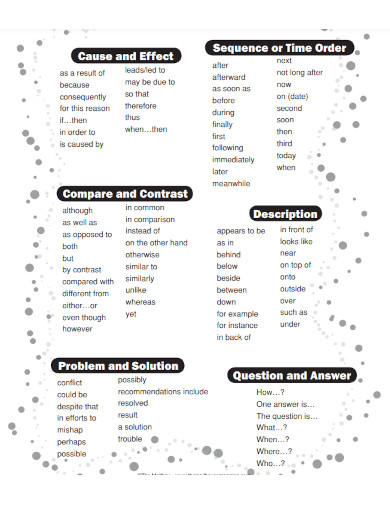
Types of Text Structures
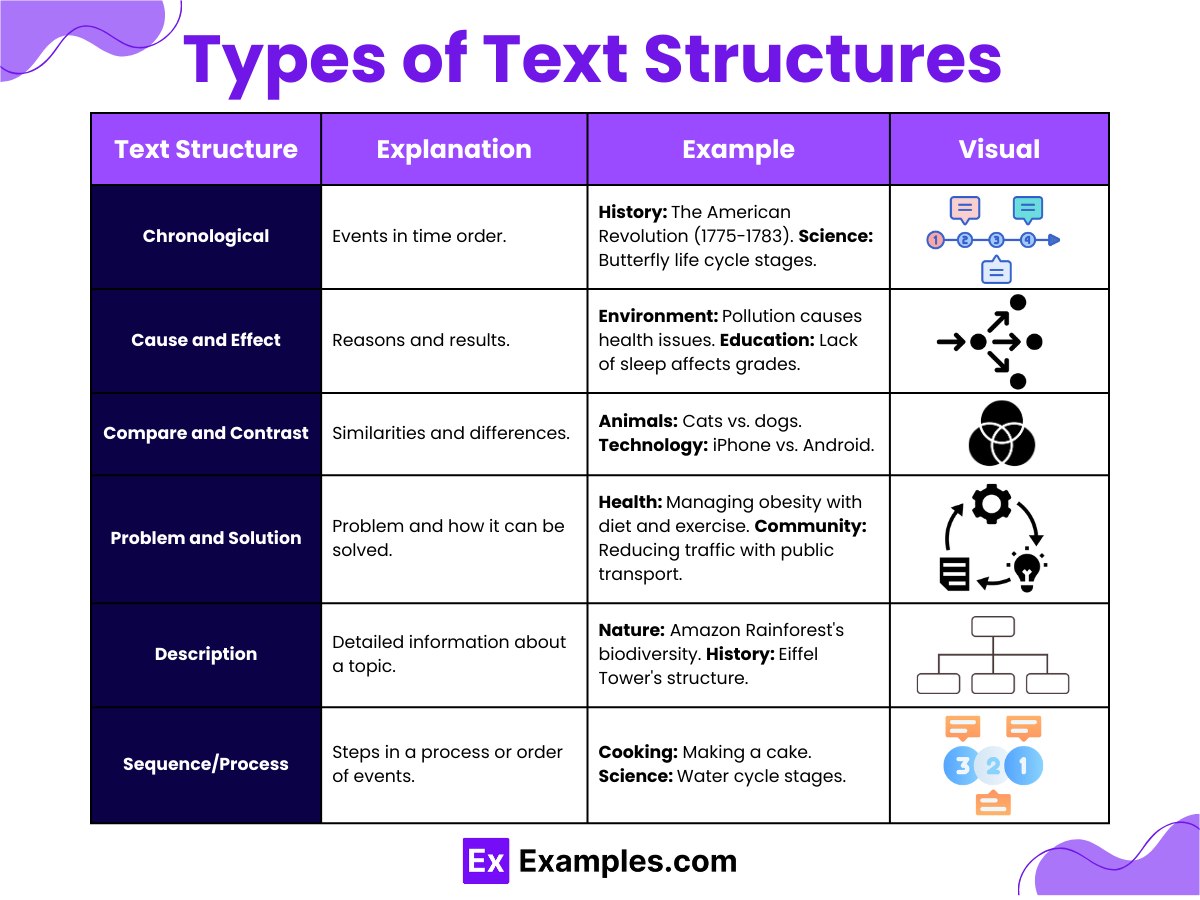
Text structure refers to how information is organized within a written text. Understanding different types of text structures can help in effectively communicating ideas and ensuring clarity for the reader. Here are the common types of text structures:
1. Chronological Order
- This structure presents events in the sequence they occurred. It is often used in narratives and historical texts.
- Example: Biographies, historical events.
2. Compare and Contrast
- This structure examines the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
- Example: Comparing the habitats of lions and tigers.
3. Cause and Effect
- This structure explains reasons why something happened and the resulting effects.
- Example: Discussing the causes of pollution and its effects on the environment.
4. Problem and Solution
- This structure identifies a problem and proposes one or more solutions.
- Example: Outlining a community issue and suggesting ways to address it.
5. Description
- This structure provides detailed information about a person, place, thing, or idea to give a clear picture.
- Example: Describing the features of a new technology.
6. Sequence/Process
- Similar to chronological order, this structure explains the steps in a process or how something works.
- Example: Instructions on how to build a model airplane.
7. Classification
- This structure categorizes items into different groups or types based on shared characteristics.
- Example: Classifying types of government systems.
8. List
- This structure presents a list of items, often organized by importance or another logical order.
- Example: Listing the top ten destinations to visit in a city.
Benifits of Text Structure
1. Improves Comprehension
- Understanding text structure helps readers grasp the main ideas and details of a text more effectively.
2. Enhances Retention
- Recognizing patterns in text organization aids in remembering information for longer periods.
3. Facilitates Analysis
- Identifying text structures allows readers to analyze and interpret content more critically and accurately.
4. Supports Writing Skills
- Knowledge of different text structures assists writers in organizing their thoughts clearly and logically.
5. Boosts Reading Speed
- Familiarity with text structures helps readers predict what will come next, increasing their reading efficiency.
6. Aids in Summarization
- Recognizing the structure of a text makes it easier to summarize its key points succinctly.
7. Enhances Engagement
- Well-structured texts are often more engaging, making reading a more enjoyable experience.
8. Assists in Test Preparation
- Understanding text structures can help students tackle standardized test questions more effectively.
How to Explain Text Structure?
Explaining text structure involves breaking down the ways information is organized within a text. Here’s how you can explain text structure effectively:
1. Define Text Structure
- Begin by explaining that text structure refers to how information is organized in a written passage. This helps set the foundation for understanding different types of structures.
2. Introduce Common Types
- Chronological Order: Events are presented in the sequence they occur.
- Compare and Contrast: Examines similarities and differences between subjects.
- Cause and Effect: Explains reasons and resulting effects.
- Problem and Solution: Identifies a problem and proposes solutions.
- Description: Provides detailed information to create a clear picture.
3. Use Examples
- Provide clear, relatable examples for each type of text structure to illustrate how they are used in writing.
- Chronological Order: “First, gather ingredients. Next, mix them. Finally, bake.”
- Compare and Contrast: “While apples are sweet, lemons are sour.”
- Cause and Effect: “It rained, so the streets flooded.”
- Problem and Solution: “Traffic congestion is an issue. Improved public transport can help.”
- Description: “The Grand Canyon is vast with layered red rocks.”
4. Visual Aids
- Use diagrams, charts, or graphic organizers to visually represent each text structure. This helps in better understanding and retention.
5. Interactive Activities
- Engage students with activities like sorting sentences into different text structures, or identifying text structures in reading passages.
6. Highlight Importance
- Explain the benefits of understanding text structures, such as improved comprehension, retention, and analytical skills.
7. Practice and Review
- Provide practice exercises where students identify and use different text structures in writing. Regular review sessions help reinforce their understanding.
How to Properly Structure Text
Structuring text properly involves organizing ideas, information, and events in a way that makes sense and is easy to follow. Here are some general tips for properly structuring text:
Step 1: Identify the main idea or thesis statement
The main idea of the text should be stated clearly and early on, preferably in the introduction or first paragraph. The gist of the thesis statement can also be restated in the conclusion paragraph.
Step 2: Use headings and subheadings
Headings and subheadings can help to organize the text into sections and make it easier to follow. They should be descriptive and accurately reflect the content of each section. Citations, whether in Chicago style, MLA format, or APA format, should be properly written as well.
Step 3: Use topic sentences
Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence that states the main point or idea of the paragraph. This helps to keep the text focused and on-topic.
Step 4: Use transitions
Transitions are words or phrases that connect one idea to another and help to create a smooth and logical flow of information. Examples of transitions include “however,” “therefore,” “meanwhile,” and “in conclusion.”
Step 5: Consider the audience and purpose
The structure of the text should be appropriate for the intended audience and purpose. For example, a scientific paper will have a different structure than a personal narrative.
Step 6: Revise and edit
After writing the initial draft, revise and edit the text to ensure that the structure is clear and logical. This may involve moving paragraphs around, rephrasing sentences, or adding or removing information.
Why is text structure important?
Text structure helps readers understand and organize information, improving comprehension and retention of the material.
What are the main types of text structures?
The main types include chronological order, compare and contrast, cause and effect, problem and solution, and description.
How does recognizing text structure improve reading?
Recognizing text structure allows readers to better predict and understand the flow of information, making reading more efficient and enjoyable.
Can text structures be combined in a single text?
Yes, authors often use multiple text structures within a single piece to convey information more effectively and comprehensively.
How can I identify text structure in a passage?
Look for signal words and phrases such as “first,” “similarly,” “because,” “problem,” and “describes” to identify the text structure.
What is the chronological order structure?
Chronological order presents events in the sequence they occurred, often used in narratives and historical texts.
How does compare and contrast structure work?
Compare and contrast structure examines similarities and differences between two or more subjects to highlight their unique features.
What is the purpose of a cause and effect structure?
Cause and effect structure explains reasons why something happened (cause) and the resulting outcomes (effect).
When is a problem and solution structure used?
Problem and solution structure is used to identify a problem and propose one or more solutions to address it.
What is a descriptive text structure?
Descriptive text structure provides detailed information about a person, place, thing, or idea to give readers a clear picture.