What is the primary function of insulin in the body?
To break down proteins
To regulate blood sugar levels
To store fats
To produce enzymes

Insulin is a vital organic compound and hormone that plays a crucial role in the chemistry of the human body. Produced in the pancreas, insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels by enabling cells to absorb glucose, which is then used for energy. It is essential for maintaining the body’s overall health, as it ensures that glucose circulates properly and doesn’t reach harmful levels in the blood. Understanding insulin’s function is important, especially for those managing conditions like diabetes, where insulin production or response is impaired.
Rapid-acting insulin starts working within 15 minutes after injection and peaks in about 1 hour, providing an effective glucose management for approximately 2 to 4 hours. It is used primarily to control blood sugar levels during meals, commonly known as bolus insulin. Examples include insulin lispro (Humalog), insulin aspart (NovoLog), and insulin glulisine (Apidra).
Short-acting insulin, or regular insulin, takes effect within 30 minutes and lasts 5 to 8 hours. Its peak action is around 2 to 3 hours after injection. This type of insulin is typically used before meals to manage rise in blood sugar that follows eating. It is often combined with longer-acting insulin for comprehensive blood sugar control.
Intermediate-acting insulin starts working about 1 to 2 hours after injection and remains effective for 12 to 18 hours. Its peak activity ranges from 4 to 12 hours. Often used twice daily, this type helps control blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. NPH insulin (Humulin N, Novolin N) is a common example of this category.
Long-acting insulin shows a steady effect that starts within 1 to 2 hours and lasts up to 24 hours or more, with no pronounced peak. It mimics the insulin action seen in the body between meals and overnight. This type is crucial for maintaining baseline insulin levels and is usually administered once or twice a day. Examples include insulin glargine (Lantus) and insulin detemir (Levemir).
Ultra long-acting insulin, with the longest duration of action, lasts over 24 hours, often up to 36 hours, with a very stable, peakless profile. Designed for once-daily dosing, it ensures all-day and all-night coverage with a very steady rate. Insulin degludec (Tresiba) and insulin glargine U-300 (Toujeo) are prominent forms of this insulin type.
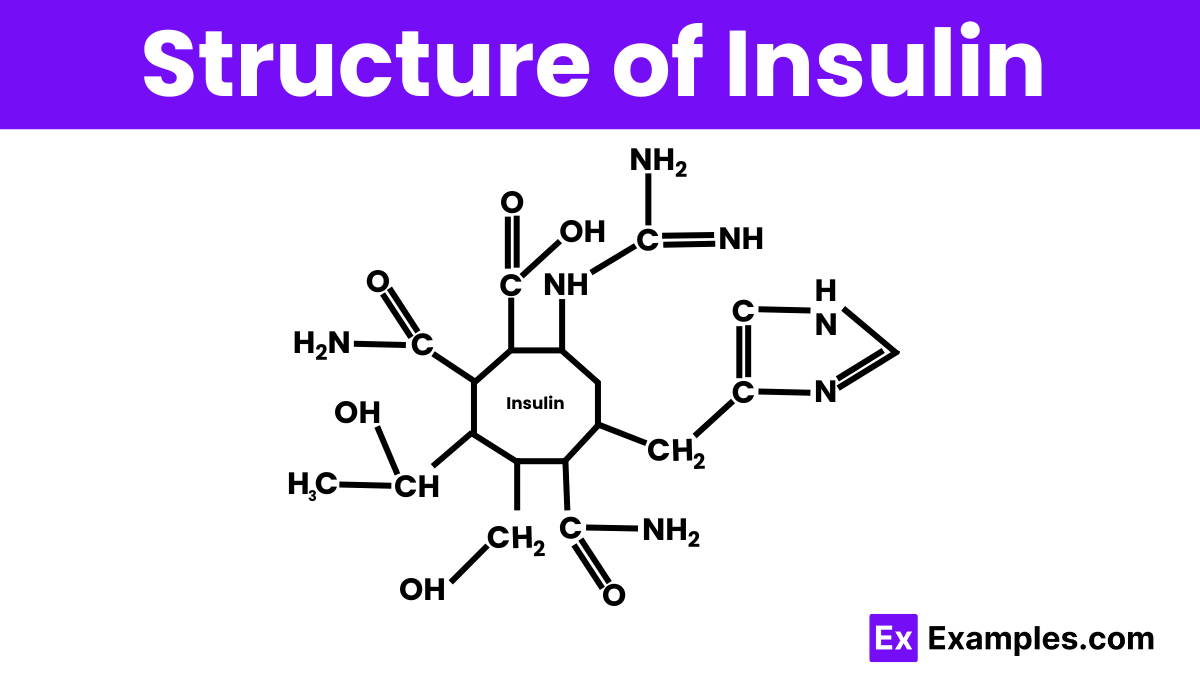
Insulin is a peptide hormone made up of two chains of amino acids, known as the A and B chains, linked together by disulfide bonds. The A chain consists of 21 amino acids, and the B chain is longer with 30 amino acids. These chains fold into a specific three-dimensional shape that is crucial for insulin’s function in regulating blood glucose levels. This structure allows insulin to bind to its receptor on the surfaces of cells, facilitating the uptake of glucose into the cells and helping to lower blood sugar levels in the body.
Insulin plays a crucial role in the body by regulating blood sugar levels. It acts as a key that allows glucose, the primary source of energy for cells, to enter various tissues in the body, including muscle and fat cells. When you eat, your blood sugar rises, prompting the pancreas to release insulin. This hormone helps cells absorb glucose, either to be used immediately for energy or to be stored for later use. By managing the level of glucose in the blood, insulin prevents it from becoming too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia), maintaining overall balance and supporting metabolic functions.
Insulin enables cells in muscle, fat, and liver tissues to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, which they use for energy or store for future use.
Insulin helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels by prompting cells to take in glucose, thereby preventing high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) after meals.
Insulin stimulates the liver and muscle cells to convert glucose into glycogen, a stored form of glucose, which the body can use during periods of fasting or increased energy demand.
Insulin signals the liver to stop producing glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, helping to keep blood sugar levels stable between meals and overnight.
Insulin facilitates the uptake of fatty acids and glycerol into fat cells, converting them into triglycerides that store as fat tissue, thus promoting fat storage.
Insulin aids in the absorption of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, into muscle cells, promoting protein synthesis and preventing protein breakdown.
The primary trigger for insulin release is the rise in blood glucose levels that occurs after eating. When you consume carbohydrates, they break down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream and signals the pancreas to secrete insulin. Additionally, the consumption of certain amino acids from proteins and hormones like incretins, released by the gut during food intake, can also stimulate insulin production. Other factors, such as the autonomic nervous system and some medications, can influence insulin release, ensuring the body maintains balanced blood sugar levels.
Rapid-acting insulin taken before meals, starts working in 15 minutes, peaks in about an hour, and lasts 2 to 4 hours.
Insulin aspart, another rapid-acting insulin similar to insulin lispro, takes effect within 15 minutes of injection, peaks around 1 to 3 hours, and lasts for 3 to 5 hours. It’s typically used to manage blood sugar spikes during meals.
It is a long-acting insulin that provides a steady level of insulin in the body for a full 24 hours. It begins working a few hours after injection and helps maintain a stable blood glucose level throughout the day and night without a peak.
Insulin detemir, a long-acting insulin, varies in duration from 18 to 23 hours depending on the dosage. It slowly releases insulin, lowering blood sugar levels and is typically administered once or twice daily.
Insulin degludec, an ultra long-acting insulin, offers over 42 hours of consistent insulin levels, maintaining stable, predictable blood sugar control, typically with once-daily administration.
Insulin is essential for glucose regulation and energy management, making it crucial for overall health, especially in diabetics.
Diabetics without insulin can experience life-threatening complications within hours or days, depending on their condition’s severity.
If a non-diabetic takes insulin, it can cause dangerously low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), which can be fatal without intervention.
Medical professionals use insulin, a peptide hormone naturally synthesized by the pancreas, to manage diabetes. It is not a chemical drug.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of insulin in the body?
To break down proteins
To regulate blood sugar levels
To store fats
To produce enzymes
Which organ produces insulin?
Liver
Kidneys
Pancreas
Stomach
Insulin is most important for regulating the levels of which of the following?
Protein
Glucose
Fat
Vitamins
What condition is most commonly associated with a lack of insulin production?
Hypertension
Diabetes mellitus
Cancer
Osteoporosis
Insulin resistance primarily leads to which type of diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes
Gestational diabetes
Juvenile diabetes
Which of the following is an effect of insulin on blood sugar?
Decreases blood sugar levels
Increases blood sugar levels
Has no effect on blood sugar levels
Maintains constant sugar levels without change
How does insulin help cells use glucose?
It blocks glucose entry into cells
It creates glucose inside the cells
It converts glucose to fat
It transports glucose from the bloodstream into cells
What happens to blood glucose levels when there is a deficiency of insulin?
Blood glucose levels decrease
Blood glucose levels remain constant
Blood glucose levels increase
No change in blood glucose levels
Which hormone works opposite to insulin to increase blood glucose levels?
Glucagon
Cortisol
Adrenaline
Thyroxine
What role does insulin play in fat storage?
It breaks down fat
It helps store fat
It has no role in fat storage
It burns fat
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

