140+ Interjection Examples
Interjections can make your sentences more engaging and expressive. These short exclamations can add a dash of emotion, tone, or sentiment, making your writing more dynamic. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what interjections are, provide you with the best sentence examples, and offer professional tips on how to use them effectively. Read on to become an expert in incorporating interjections in your sentences.
What is the Interjectio? – Definition
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a spontaneous emotion or reaction and is typically set apart from a sentence by an exclamation point, or by commas if it’s not as forceful. Interjections are often used to convey strong emotions such as surprise, disgust, joy, or excitement, and they can stand alone or be incorporated into sentences.
Types of Interjections
1. Emotive Interjections
These interjections express personal feelings or emotional reactions and are often used in exclamatory sentences, typically followed by an exclamation point.
- Examples:
- Joy: Yay, Hooray, Woohoo
- Surprise: Wow, Oh my, Whoa
- Pain: Ouch, Ow
- Sadness: Alas, Sigh
2. Cognitive Interjections
Cognitive interjections express cognitive processes such as realizations or decisions.
- Examples:
- Realization: Ah, Oh
- Decision: Okay, Alright
3. Volitive Interjections
These are used to express a wish or a command, often indicating the speaker’s intent towards the listener.
- Examples:
- Commands: Shh, Hush
- Wishes: Cheers, Bless you
4. Filler Interjections
Filler interjections are used in speech to allow the speaker time to think and are not necessarily related to emotions.
- Examples:
- Hesitation: Um, Uh, Er
- Pausing: Well, So
5. Greeting Interjections
These are used to greet someone or respond to a greeting.
- Examples:
- Greetings: Hello, Hi, Hey
- Responses: Hey, Hi there, What’s up?
6. Farewell Interjections
Used when parting ways or ending a conversation.
- Examples:
- Farewell: Goodbye, Bye, See you
7. Exclamatory Interjections
These interjections strongly emphasize statements and are often used to support an expressed opinion or reaction.
- Examples:
- Agreement: Yes, Exactly, Right
- Disagreement: No, Nope
8. Laughter and Humor Interjections
Interjections that mimic laughter or are used in humorous contexts to indicate amusement.
- Examples:
- Laughter: Ha, Haha, LOL
- Humor: Heh, Teehee
9. Attention Interjections
These are used to grab the listener’s attention or to make an interruption.
- Examples:
- Calling Attention: Hey, Yo, Listen
- Interruption: Oops, Hey
10. Sound Imitation Interjections
Interjections that mimic sounds or environmental noises.
- Examples:
- Animal Sounds: Meow, Woof, Quack
- Environmental Sounds: Bang, Splash, Clap
How are interjections used in sentences?
Standalone Interjections
Interjections can function as standalone sentences, especially when expressing sudden emotions or reactions. In these cases, they are often followed by an exclamation mark to emphasize the emotion.
- Example: “Wow! That was an incredible performance.”
- Example: “Ouch! That really hurts.”
Interjections Within Sentences
Interjections can also be woven into the fabric of longer sentences. Depending on their placement and function, they may be set off by commas, dashes, or exclamation points.
1. Beginning of a Sentence
When placed at the beginning, interjections can set the tone for the sentence that follows. They are typically followed by a comma if the emotion is mild, or an exclamation mark for stronger reactions.
- Example: “Well, I suppose we could try that approach.”
- Example: “Oh! I didn’t see you there.”
2. Middle of a Sentence
Interjections inserted into the middle of a sentence add emotional nuance and are often surrounded by commas or dashes, especially if they serve as parenthetical elements that provide a pause or emotional break.
- Example: “I believe, oh, it was around two years ago.”
- Example: “That is, well, quite a problem you’ve got there.”
3. End of a Sentence
At the end of a sentence, interjections can underscore or amplify the sentiment expressed. They may be preceded by a comma or not, depending on how closely they are tied to the rest of the sentence.
- Example: “I can’t believe we won, yes!”
- Example: “You’re moving to Spain, huh?”
Special Uses of Interjections
1. Dialogue
In dialogue, interjections can reflect natural speech patterns, helping to convey the speaker’s emotional state quickly and effectively. They enhance the realism of conversations.
- Example: “‘Hey!’ she called out. ‘Wait for me!'”
2. Narrative
In narrative writing, interjections can provide insight into a character’s immediate reactions or feelings, often punctuating dramatic moments.
- Example: “Alas, he knew it was too late to save the day.”
3. Informal Writing
In informal texts, such as personal letters, blogs, or social media posts, interjections can make the writing feel conversational and lively.
- Example: “LOL, that’s the funniest thing I’ve seen all day!”
Punctuation with Interjections
Punctuation plays a crucial role in how interjections are perceived:
- Exclamation Points: Used for strong, sudden outbursts of emotion.
- Commas: Soften the interjection, making it seem more like a part of the surrounding sentence.
- Dashes: Emphasize a pause or break in thought, often enhancing the dramatic effect.
Interjections for Everyday Communication
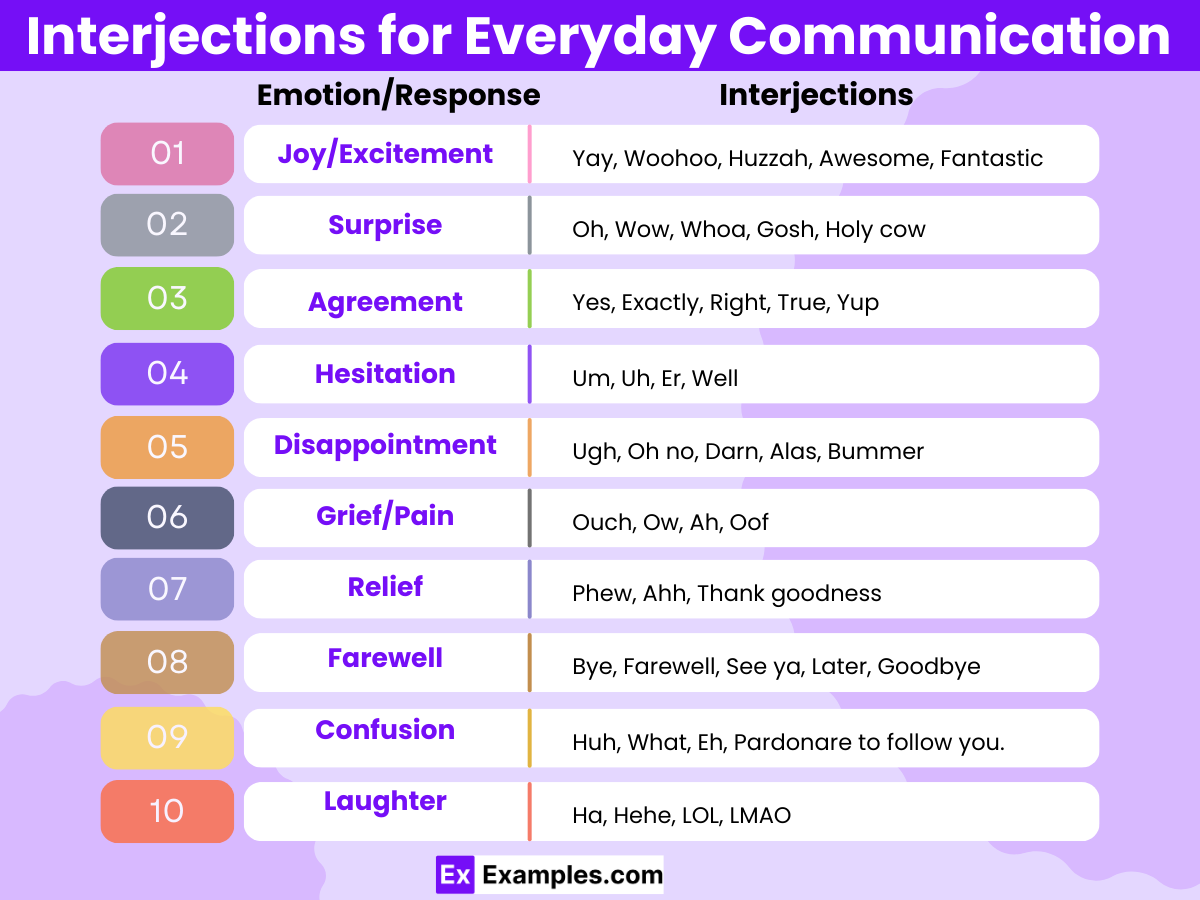
| Emotion/Response | Interjections |
|---|---|
| Joy/Excitement | Yay, Woohoo, Huzzah, Awesome, Fantastic |
| Surprise | Oh, Wow, Whoa, Gosh, Holy cow |
| Agreement | Yes, Exactly, Right, True, Yup |
| Hesitation | Um, Uh, Er, Well |
| Disappointment | Ugh, Oh no, Darn, Alas, Bummer |
| Grief/Pain | Ouch, Ow, Ah, Oof |
| Greetings | Hey, Hi, Hello, Yo |
| Farewell | Bye, Farewell, See ya, Later, Goodbye |
| Attention | Hey, Listen, Look, Shh |
| Confusion | Huh, What, Eh, Pardon |
| Laughter | Ha, Hehe, LOL, LMAO |
| Relief | Phew, Ahh, Thank goodness |
| Filler | Like, You know, So, Anyway, Basically |
| Amazement/Wonder | Wow, Amazing, Incredible, Unbelievable |
| Reluctance | Hmm, Nah, Meh, Nope |
How and When to Use Interjections?
How to Use Interjections
- Express Emotion: Use interjections to express surprise, happiness, disappointment, or other emotions vividly and spontaneously.
- Create Impact: To draw attention to a particular point or to emphasize a reaction, interjections can be strategically placed.
- Enhance Dialogue: Make written or spoken conversations more realistic and engaging by including interjections that reflect how people actually talk.
- Indicate Pauses: Employ interjections like “um”, “er”, and “uh” to indicate hesitations or pauses in speech, which can make dialogue seem more natural.
- Inject Humor: Use humorous interjections to add a light-hearted tone to communication, often making interactions more enjoyable.
- Convey Sounds: Mimic real-world sounds through onomatopoeic interjections (e.g., “bang”, “splash”) to enhance the sensory experience of a narrative.
When to Use Interjections
- During Emotional Reactions: When characters or speakers undergo strong emotions, interjections can succinctly and effectively express these feelings.
- In Casual or Informal Texts: Interjections are perfect for informal settings such as personal letters, dialogues in fiction, or casual conversations.
- While Writing Dialogue: To reflect natural speech patterns in scripts or fiction, interjections help break up the monotony and add authenticity.
- When Imitating Sounds: In storytelling, especially in genres like children’s books or comic strips, sound imitating interjections add a fun, engaging element.
- To Grab Attention: At the beginning of announcements or important statements to ensure the listener is engaged right from the start.
- For Rhetorical Flair: In speeches or persuasive texts, interjections can make the delivery more powerful and emotionally charged.
10+ Sentences using Interjection

- Woof! That was a rough workout.
- Zing! You got me good with that comeback.
- Crikey! That’s a huge spider.
- Blurt! I didn’t mean to say that aloud.
- Huzzah! The project was a complete success.
- Harrumph! I expected better from you.
- Booyah! We aced the test!
- Click! The door locked behind us.
- Swish! Nothing but net!
- Whoop! There it is!
100 Interjection in a Sentence Usage Examples
Mastering the use of interjections in sentences can bring life and vibrancy to your writing or speech. These standalone words or short phrases capture a wide range of emotions, attitudes, or reactions, often punctuated for effect. Whether you’re aiming for dramatic flair or everyday expressiveness, the strategic use of interjections can make all the difference. Below are 100 distinct and unique examples showcasing interjections in a sentence:
- Wow! That cake looks delicious.
- Oops! I forgot to bring the keys.
- Yikes! That was a close call.
- Hey! Can you pass me the salt?
- Oh! I didn’t know you were here.
- Hooray! We won the match.
- Alas! The hero was defeated.
- Ouch! That really hurt.
- Gee! I wonder what this button does.
- Ahem! May I have your attention?
- Well! That’s an interesting choice.
- Darn! I missed the train.
- Whoa! Slow down there.
- Whew! That was tough.
- Uh-oh! Something went wrong.
- Brrr! It’s cold in here.
- Eek! A mouse!
- Phew! We made it in time.
- Aha! I finally understand.
- Hmm! Let me think about it.
- Shh! Be quiet.
- Bravo! Excellent performance.
- Boo! That was a terrible call.
- Oh no! I left the stove on.
- Ha! I told you so.
- Grr! I can’t believe he did that.
- Hmmph! I disagree with you.
- Aww! Look at that cute puppy.
- Psst! Over here.
- Meh! It was okay, I guess.
- Blah! I’m so bored.
- Yum! This ice cream is tasty.
- Zap! And it was gone.
- Heavens! What a beautiful sunset.
- Jeez! Could you be any louder?
- Yeah! Let’s do it.
- Nah! I’d rather not.
- Tsk! You should know better.
- Duh! Of course, it’s obvious.
- Nuh-uh! I don’t agree.
- Eh! It could be worse.
- Yahoo! No more exams.
- Ick! That looks nasty.
- Sigh! I’m tired.
- Ding! Time’s up.
- Snap! That was a smart comment.
- Yawn! This is boring.
- Yeesh! That’s a lot of work.
- Hi! Nice to meet you.
- Pshaw! I don’t believe you.
- Eureka! I’ve found the solution.
- Lo! Look at that!
- Zip! That was quick.
- Mmm! Smells good.
- Oopsie! A minor mistake.
- Aargh! I can’t figure this out.
- Uh! I can’t believe this.
- Kaboom! And the fireworks started.
- Yay! The weekend is here.
- Woo! That’s exciting.
- Bingo! That’s the right answer.
- Pfft! That was useless.
- Heya! What’s new?
- Huh! Are you serious?
- Nope! That’s not correct.
- Ooh! That’s interesting.
- Bye! See you later.
- Ack! This is frustrating.
- Cheers! To the new year.
- Wham! The door slammed shut.
- Crash! The dishes fell.
- Haha! That’s funny.
- Fiddlesticks! That’s unfortunate.
- Wah! I want it.
- Ding-dong! The doorbell rang.
- Poof! Like magic, he disappeared.
- Hush! Don’t tell anyone.
- Okey-dokey! I understand.
- Thud! The book fell.
- Yippee! School’s out.
- Voila! There you have it.
- Plop! It landed in the water.
- Clang! The bell rang.
- Argh! This is annoying.
- Rats! Missed it by a second.
- Cripes! That was unexpected.
- Zoinks! That scared me.
- Oof! That was a heavy box.
- Tada! And it’s done.
- Whoopee! It’s a party.
- Grunt! That’s a lot of weight.
- Splat! It hit the ground.
- Rip! The paper tore.
- Yowza! That’s impressive.
- Blimey! What a surprise.
- Ho-ho! Merry Christmas.
- Chirp! The bird sang.
- Achoo! I sneezed.
- Clap! Well done.
- Smack! The pie hit his face.
Feel free to incorporate these examples into your writing to add emotion, nuance, and emphasis.
Is an Interjection a Full Sentence?
Technically, an interjection is not a complete sentence as it usually doesn’t have a subject and a verb forming an independent clause. However, interjections are often used in colloquial language as stand-alone sentences, especially in dialogue. For example, “Wow!” or “Ouch!” might appear as individual sentences in casual conversation or in written dialogue, but they aren’t complete sentences by the standard grammatical definition.
Importance of Interjection in a Sentences
- Expresses Emotions Clearly: Interjections convey emotions vividly and immediately, helping to communicate feelings such as surprise, joy, anger, or pain efficiently.
- Enhances Verbal and Written Communication: In both spoken and written forms, interjections add dynamism and tone, making messages more engaging and impactful.
- Adds Realism to Dialogues: By using interjections, dialogue in stories and plays becomes more realistic and relatable, as they mimic the natural ways people express emotions spontaneously.
- Provides Rhythmic Breaks: Interjections can break up monotonous sentence structures, providing pauses that enhance the rhythmic quality of prose.
- Emphasizes Statements: They can be used to emphasize a point or reaction within a conversation, drawing the listener’s or reader’s attention to specific details.
- Facilitates Quick Communication: Quick exclamations or responses can speed up interactions in fast-paced conversations or urgent communications.
- Introduces Informality: Interjections help to create a casual or informal tone, which can make texts more personable and approachable.
- Reflects Cultural Speech Patterns: They often reflect idiomatic expressions particular to a culture, thereby enriching the language with local color and flavor.
Tips for Using Interjection in a Sentences
- Be Context-Aware: Choose interjections that fit the mood and setting. A formal document may not be the best place for casual or slang interjections.
- Use Sparingly: Overuse of interjections can make the content seem unprofessional or too emotional.
- Match Tone: The interjection should align with the overall tone of the content. A serious article about a tragic event, for example, should not have jubilant or frivolous interjections.
- Consider the Audience: Different cultures or age groups may interpret interjections differently, so choose words that are universally understood or explain their meaning.
- Revise and Edit: After using an interjection, go back and read the sentence to ensure it still flows well and makes sense within the context.
Test Your Understanding of Interjections
Question 1: Which of the following is an interjection commonly used to express surprise?
A) Because
B) Although
C) Wow
D) Since
Question 2: What punctuation is most commonly associated with interjections expressing strong emotion?
A) Period (.)
B) Exclamation mark (!)
C) Comma (,)
D) Question mark (?)
Question 3: Which interjection would you use to express pain?
A) Oh
B) Alas
C) Ouch
D) Well
Question 4: In which situation might you use the interjection “Yay”?
A) When someone is hesitating to answer a question.
B) When you are upset about something.
C) When you are expressing happiness about an achievement.
D) When you are trying to be formal.
Question 5: Choose the correct interjection to fill in the blank: “____! I didn’t expect to see you here.”
A) Um
B) Wow
C) Er
D) Right
Question 6: Which type of interjection is “hmm”?
A) Emotion
B) Cognitive
C) Volitive
D) Filler
Question 7: What is the function of the interjection “shh”?
A) To express sorrow
B) To express surprise
C) To command silence
D) To indicate agreement
Question 8: Identify the interjection in this sentence: “Oh, I didn’t realize you were in a meeting.”
A) I
B) Oh
C) you
D) meeting
Question 9: Which interjection could be used to mimic the sound of a dog barking?
A) Meow
B) Bang
C) Woof
D) Splash
Question 10: How would you appropriately use the interjection “alas” in a sentence?
A) “Alas, we finally found the lost keys!”
B) “Alas, he missed the bus again.”
C) “Come here, alas, quickly!”
D) “I won the game, alas!”
Answers:
- C) Wow
- B) Exclamation mark (!)
- C) Ouch
- C) When you are expressing happiness about an achievement.
- B) Wow
- D) Filler
- C) To command silence
- B) Oh
- C) Woof
- B) “Alas, he missed the bus again.”
FAQ’s
What is Interjection for Kids?
An interjection is a word that expresses strong feelings or emotions. It’s like a quick way to show excitement, surprise, happiness, or other emotions, and is often followed by an exclamation point. Examples include “Wow!”, “Ouch!”, and “Yay!”.
What is Interjection Examples for Students?
Interjections are words used to express emotions quickly and are often found in both spoken and written English. Examples include “Ah” for realization, “Eek” for surprise, “Yikes” for fear, and “Oops” for a minor error.
What are the Three Rules for Interjection?
- Punctuation: Use an exclamation point for strong emotions, and a comma for milder expressions.
- Independence: Interjections can stand alone or be incorporated into sentences but don’t grammatically link to other words.
- Frequency: Use interjections sparingly in formal writing as they can make text seem informal.