12+ Case Summary Examples to Download
Studying the law can be very confusing and demanding. The law in itself is very complicated and things stated can sometimes mean differently than the literal. However, even if it can get confusing it is important to study the law in order for you to fully understand the how it works and why it is implemented in the first place. You may also see summary writing examples and samples.
What is a Case Summary?
A case summary is a brief document that outlines the key facts, legal issues, and outcomes of a legal case. It simplifies the complex details of the case for easy understanding and reference, highlighting the court’s decision and the rationale behind it. Case summaries are essential tools in legal studies and practice for quick analysis and reference.
Case Summary Format
Title
- Case Name: Include the full name of the case (e.g., Brown v. Board of Education).
- Citation: Provide the legal citation (e.g., 347 U.S. 483 (1954)).
Introduction
- Background: Briefly introduce the context and background of the case.
- Parties Involved: Name the parties involved in the case (plaintiff vs. defendant).
Key Facts
- Situation Overview: Outline the key facts and events leading up to the legal dispute.
- Relevant Details: Highlight any specific details that are crucial to understanding the case’s context.
Legal Issues
Questions at Hand: Identify the main legal questions or issues that the court needed to resolve.
Arguments Presented
- Plaintiff’s Arguments: Summarize the main arguments or claims made by the plaintiff.
- Defendant’s Arguments: Summarize the main arguments or claims made by the defendant.
Decision and Rationale
- Court’s Decision: State the outcome of the case (who won and the verdict).
- Legal Reasoning: Explain the court’s reasoning and the legal principles applied in reaching its decision.
Significance of the Case
- Implications: Discuss the case’s implications for future legal interpretations, law, or society.
- Precedents Set: If applicable, mention any legal precedents the case established.
Conclusion
Summary: Conclude with a brief recap of the case’s importance and its impact on the legal landscape.
References
Sources: List any additional sources or references used in preparing the case summary.
The Purpose of a Case Summary
- Simplifying Complex Information: To distill lengthy and complex legal rulings into concise, understandable formats.
- Quick Reference: To provide a quick and accessible reference to the essential facts, legal issues, and outcomes of a case.
- Educational Tool: To serve as an educational resource for law students and others learning about legal principles and case law.
- Legal Research Aid: To facilitate legal research by offering summaries of key cases, making it easier to identify and understand relevant legal precedents.
- Preparation for Legal Proceedings: To assist lawyers and legal professionals in preparing for court appearances, negotiations, or client advisories by summarizing pertinent cases.
- Highlighting Legal Reasoning: To outline the court’s reasoning and the legal principles applied, aiding in the understanding of how legal decisions are made.
- Time Efficiency: To save time for legal professionals and students by providing quick access to the essence of a case without the need to read through the entire judgment.
- Case Management: To help manage and organize legal cases by summarizing and cataloging important case details and outcomes for future reference.
Types of Case Summary
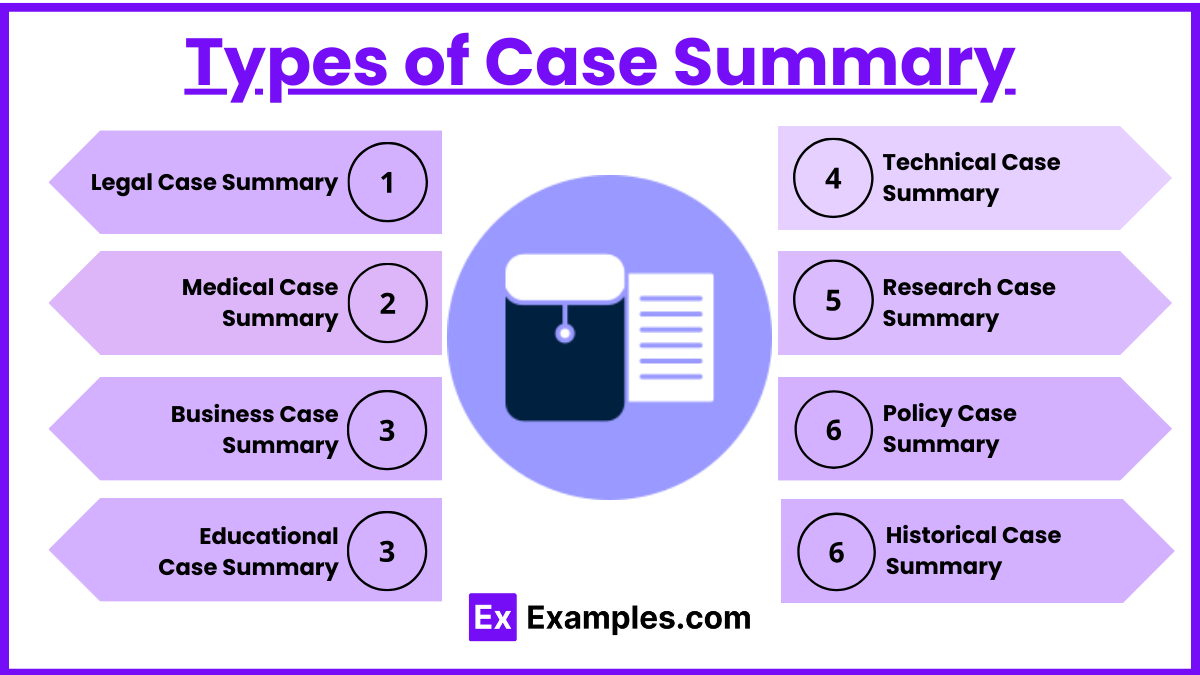
- Legal Case Summary: Focuses on legal cases, outlining the facts, legal issues, arguments, decisions, and reasoning of the court.
- Medical Case Summary: Summarizes patient cases, including medical history, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes, often used in medical education and research.
- Business Case Summary: Provides an overview of business scenarios, including strategic challenges, actions taken, results, and lessons learned, useful for business studies and planning.
- Educational Case Summary: Used in academic research, summarizing educational scenarios, methodologies, findings, and implications for practice or policy.
- Technical Case Summary: Summarizes technical projects or problems, solutions implemented, results, and key takeaways, often used in engineering and IT.
- Research Case Summary: Condenses research studies or experiments, highlighting the purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Policy Case Summary: Outlines policy decisions, the rationale, implementation strategies, outcomes, and impacts, useful in public administration and policy studies.
- Historical Case Summary: Provides concise overviews of historical events, significant figures, and outcomes, aiding in the study of history and social sciences.
Key Components of an Effective Case Summary
- Case Name and Citation: The official name of the case and its citation for easy reference.
- Background Information: A brief overview of the factual background and the events leading up to the legal dispute.
- Parties Involved: Identification of the plaintiff(s) and defendant(s), including their roles and stakes in the case.
- Legal Issues: A clear statement of the legal questions or issues that the court needed to decide.
- Arguments Presented: A summary of the key arguments or positions taken by each party.
- Court’s Decision: The outcome of the case, including which party prevailed and any specific orders or judgments made by the court.
- Reasoning and Legal Principles: An explanation of the court’s reasoning and the legal principles or precedents it applied to reach its decision.
- Significance: An assessment of the case’s significance, including its impact on future legal cases, legislation, or legal principles.
- Concurring or Dissenting Opinions: If applicable, a brief overview of any concurring or dissenting opinions and their rationales.
- Date of Decision: The date when the court delivered its decision, providing context in terms of legal history or development.
How to Write a Case Summary: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Read the Full Case
Begin by thoroughly reading the entire case to understand the factual background, the legal issues involved, the arguments from both sides, and the court’s decision along with its reasoning.
2. Identify the Key Facts
Extract the essential facts of the case. This includes the parties involved, the nature of the dispute, and the specific circumstances that led to the legal confrontation.
3. Outline the Legal Issues
Identify the main legal questions or issues that the court needed to resolve. This could involve interpretations of the law, legal principles, or the application of law to the case’s facts.
4. Summarize the Arguments
Briefly describe the arguments made by each side. Highlight the key points raised in support of their positions, including any legal precedents or statutes they relied on.
5. Detail the Court’s Decision
Summarize the court’s ruling on the case. Include which party won, the reasons for the decision, and any legal principles the court established or applied.
6. Explain the Reasoning
Delve into the rationale behind the court’s decision. This involves explaining how the court interpreted the law, applied it to the facts of the case, and the precedents it considered.
7. Note the Significance
If applicable, mention the broader implications of the case. This could include its impact on future legal cases, changes to the law, or its significance in legal history.
8. Keep It Concise
Ensure your summary is clear and to the point. Use plain language and avoid unnecessary legal jargon. The goal is to make the case understandable to someone not familiar with the case or the law.
9. Review for Accuracy
Double-check your summary to ensure it accurately reflects the case’s facts, legal issues, and the court’s decision. Accuracy is paramount in legal writing.
10. Cite the Case
Finally, provide a proper citation for the case. This allows readers to locate the full text of the decision if they wish to delve deeper into the details.
The Role of Case Summaries
- Efficient Research: Case summaries allow legal professionals and students to quickly identify relevant cases and understand their implications without having to read through entire judgments. This efficiency is crucial in legal research, where time is often of the essence.
- Understanding Legal Precedents: They provide a clear overview of the legal precedents set by previous cases. This understanding is essential for formulating legal arguments and for predicting how current cases may be resolved based on past decisions.
- Educational Purposes: For law students, case summaries are invaluable educational tools that aid in grasping complex legal concepts and learning how to apply them in real-world scenarios.
- Preparation for Legal Practice: They prepare practitioners for court appearances and client consultations by providing quick access to relevant case law, ensuring that legal advice and courtroom arguments are well-informed and up to date.
- Legal Analysis and Writing: Case summaries are often the starting point for deeper legal analysis and academic writing. They provide the foundational knowledge necessary for critiquing legal decisions or exploring their broader implications for the law and society.
- Facilitating Discussion and Debate: By presenting the essential elements of cases succinctly, case summaries facilitate discussion and debate among legal professionals and scholars, helping to foster a deeper understanding of the law.
13+ Case Summary Examples
Case Brief Summary Template
Law Student Case Brief Summary Sheet Template
Case Summary Guide
Case Summary Format Example
Case Summary Template Example
Case Summary Template Example
Case Summary Example
Elements of a Case Summary
Since a case summary or case brief is primarily a tool used for studying, it should be structured to meet your own needs. Here are several basic components of a brief that are present in almost all brief styles:
- Facts
- Simply put, these are all the pertinent information and facts of the case. These are the important facts that heavily influence the case. You may also see examples of writing a narrative summary.
- Issue or issues
- This is the issue or the problem that is addressed in the case. This pertains to the legal questions are posed by the appealing party.
- Holding, including the rule of law
- This is the ruling of the court. This is about the decision of the court and how the court made its decision about the case. You may also like interview summary examples.
- Rationale
- This is your explanation on why the court ruled the way that it did. The rationale is your personal explanation regarding the process of how and why the court decided on its ruling of the case.

Free Case Summary Example
Simple Case Brief Example
Sample Case Brief Summary
People Hall Sample Case Brief
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Case Summary
- Overcomplicating the Summary: Avoid using unnecessary legal jargon or overly complex language. The goal is clarity and accessibility.
- Including Irrelevant Details: Focus on the key facts, legal issues, and outcomes. Extraneous information can detract from the summary’s purpose.
- Omitting Key Information: Make sure to include all crucial aspects of the case, such as the main legal issues, the court’s decision, and the rationale behind it.
- Failing to Clearly Identify Legal Principles: Clearly articulate the legal principles or precedents established by the case, as these are often the most important takeaways.
- Lack of Structure: A well-organized summary with clear headings and a logical flow is much easier to follow. Avoid presenting information in a disorganized manner.
- Misinterpreting the Case: Ensure you have a thorough understanding of the case to avoid inaccuracies in your summary. Misinterpretation can mislead readers.
- Neglecting the Court’s Reasoning: Merely stating the outcome without explaining the court’s reasoning omits a critical component of the case’s significance.
- Forgetting to Cite Properly: Always provide a proper citation for the case at the beginning or end of the summary. This allows readers to find the full text if needed.
- Not Reviewing for Accuracy and Completeness: Double-check your summary to ensure it accurately reflects the case’s facts and legal issues, and that it’s complete.
- Ignoring the Case’s Broader Implications: When relevant, mention the broader legal and societal implications of the case to provide context and enhance understanding.
FAQs
How Do You Read a Case Summary?
To read a case summary, start with the introduction to understand the context, then move through the sections detailing the facts, legal issues, arguments, court’s decision, and reasoning. Focus on understanding the legal principles and outcomes.
How Do You Write a Good Summary for a Case Study?
A good case study summary concisely outlines the situation, the problems or questions posed, the methodology or approach taken, key findings, and the implications or recommendations, maintaining clarity and coherence throughout.
What Does a Case Report Look Like?
A case report typically includes an introduction to the case, a detailed description of the case or patient scenario, the interventions or treatments applied, the outcomes observed, and a discussion on the implications and lessons learned.
How Long Should a Case Summary Be?
A case summary should ideally be brief, often ranging from one to two pages. It needs to succinctly capture the essence of the case, focusing on the most critical elements without extraneous details.
Why Are Case Summaries Important?
Case summaries distill complex legal judgments into accessible overviews, providing essential insights into the case’s facts, legal issues, and outcomes. They are crucial for legal education, research, and practice, facilitating quick and efficient understanding.
How Do You Write a Summary and Conclusion for a Case Study?
Summarize the case study by highlighting the main points, findings, and implications. The conclusion should reflect on the study’s significance, recommend actions based on findings, and suggest areas for future research or consideration.
How to Write a Case Report?
To write a case report, start with an introduction that outlines the reason for the report, describe the case with emphasis on unique aspects, detail the interventions made, present the outcomes, and conclude with the case’s broader implications.
What is an Example of a Case Study?
An example of a case study could be an analysis of a business strategy at a leading tech company, examining how its approach to innovation and market challenges led to its current market position, focusing on specific strategies and outcomes.
How Long Should a Case Report Be?
The length of a case report can vary but is typically concise, often between 500 and 1500 words. It should be long enough to provide a comprehensive overview of the case, yet concise enough to maintain reader interest and focus on key insights
In conclusion, if you a currently studying the law, props to you; it is not an easy feat. In fact even summary a case can be difficult and requires a lot of time and understanding. And perhaps the most important thing to remember before you even start briefing or summarizing a case is that read. If you feel like you know enough about the case read again; thoroughly and carefully so you can objectively comprehend the facts pertaining to the case to make an objective summary.