50+ Nationality Examples
Nationality refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a state, typically defined by birth or naturalization. It determines a person’s legal rights, including the right to vote, work, and reside within a country. Nationality also shapes an individual’s identity, influencing their cultural, social, and political affiliations. Understanding nationality is crucial in global contexts, as it impacts international law, travel, and diplomatic relations.
What is Nationality?
Nationality is a legal relationship between an individual and a state. This relationship grants the individual certain rights and obligations under the state’s laws. Typically, nationality is acquired either by birth within a territory, descent from a national parent, marriage to a national, or naturalization. The concept serves as a means of identifying a person’s legal status within a country, which can include rights to work, vote, and receive protection from the state. Additionally, nationality is a significant aspect of a person’s identity, influencing cultural, social, and political connections and how they are perceived globally. International laws and agreements often take nationality into account to resolve issues related to dual nationality, statelessness, and diplomatic protections.
What is My Nationality?
Nationality is generally defined by the country where you are legally recognized as a citizen, which can be based on where you were born, your parents’ nationality, or through naturalization (a legal process where a non-citizen in a country may acquire citizenship).
For example, if you were born in France to French parents, your nationality would be French. If you were born in India but later moved to Canada and became a Canadian citizen through naturalization, your nationality would be Canadian. Different countries have different laws regarding how nationality is assigned or claimed.
Nationality Examples
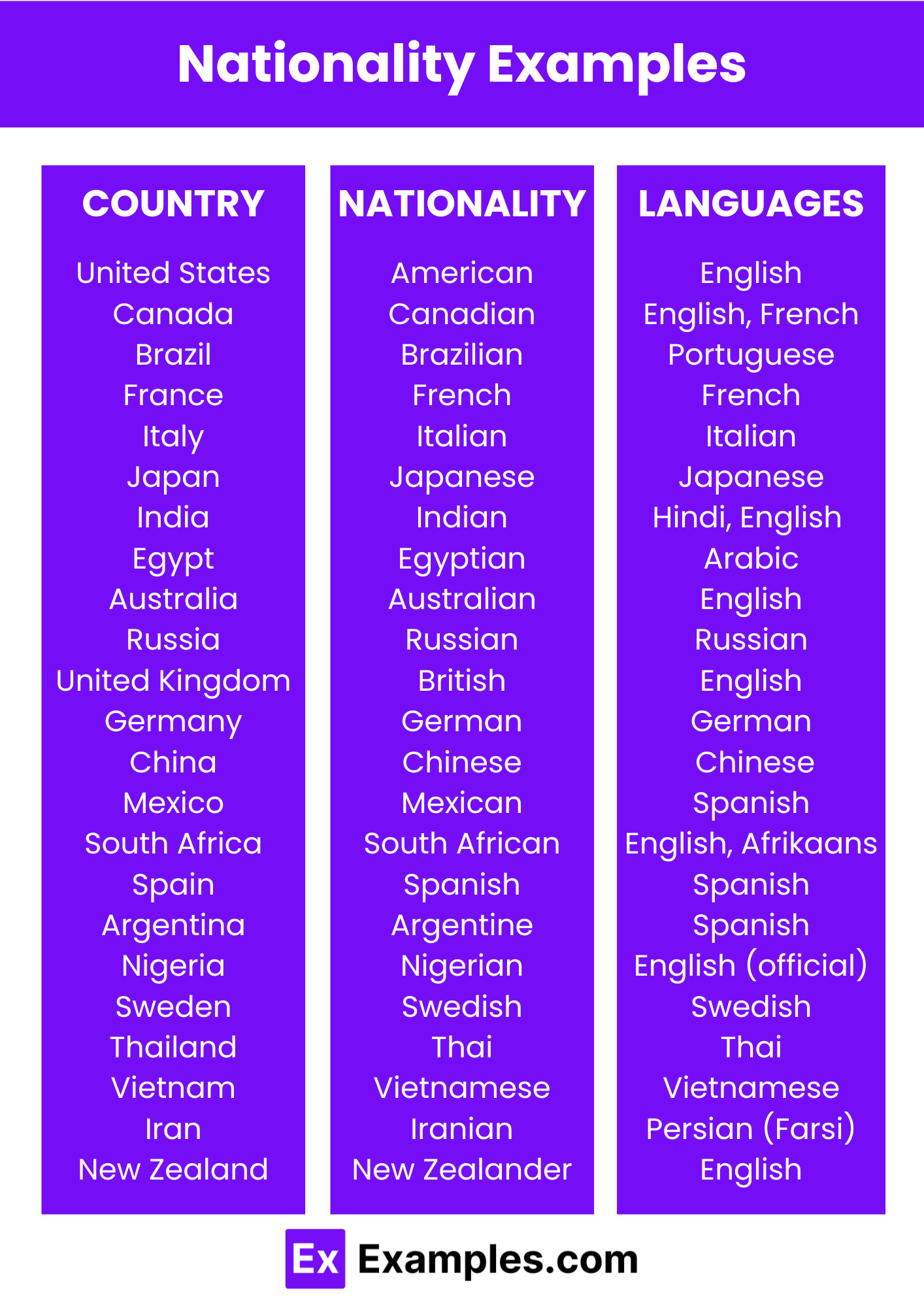
Here are 181 examples of nationalities:
- American (from the United States)
- Canadian (from Canada)
- Brazilian (from Brazil)
- French (from France)
- Italian (from Italy)
- Japanese (from Japan)
- Indian (from India)
- Egyptian (from Egypt)
- Australian (from Australia)
- Russian (from Russia)
- British (from the United Kingdom)
- German (from Germany)
- Chinese (from China)
- Mexican (from Mexico)
- South African (from South Africa)
- Argentine (from Argentina)
- Spanish (from Spain)
- Nigerian (from Nigeria)
- Swedish (from Sweden)
- Polish (from Poland)
- Norwegian (from Norway)
- Turkish (from Turkey)
- Kenyan (from Kenya)
- Vietnamese (from Vietnam)
- Indonesian (from Indonesia)
- Thai (from Thailand)
- Dutch (from the Netherlands)
- Greek (from Greece)
- Colombian (from Colombia)
- Finnish (from Finland)
- New Zealander (from New Zealand)
- Irish (from Ireland)
- Saudi (from Saudi Arabia)
- Pakistani (from Pakistan)
- Ukrainian (from Ukraine)
- Filipino (from the Philippines)
- Iranian (from Iran)
- Belgian (from Belgium)
- Portuguese (from Portugal)
- South Korean (from South Korea)
- Chilean (from Chile)
- Peruvian (from Peru)
- Moroccan (from Morocco)
- Czech (from the Czech Republic)
- Austrian (from Austria)
- Israeli (from Israel)
- Malaysian (from Malaysia)
- Venezuelan (from Venezuela)
- Swiss (from Switzerland)
- Emirati (from the United Arab Emirates)
- Bangladeshi (from Bangladesh)
- Tanzanian (from Tanzania)
- Slovak (from Slovakia)
- Hungarian (from Hungary)
- Danish (from Denmark)
- Jordanian (from Jordan)
- Libyan (from Libya)
- Singaporean (from Singapore)
- Algerian (from Algeria)
- Cuban (from Cuba)
- Bhutanese (from Bhutan)
- Bolivian (from Bolivia)
- Bosnian (from Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Botswanan (from Botswana)
- Bruneian (from Brunei)
- Bulgarian (from Bulgaria)
- Burkinabe (from Burkina Faso)
- Burmese (from Myanmar)
- Burundian (from Burundi)
- Cambodian (from Cambodia)
- Cameroonian (from Cameroon)
- Cape Verdean (from Cape Verde)
- Central African (from Central African Republic)
- Chadian (from Chad)
- Comoran (from Comoros)
- Congolese (from Congo)
- Costa Rican (from Costa Rica)
- Croatian (from Croatia)
- Cypriot (from Cyprus)
- Djiboutian (from Djibouti)
- Dominican (from Dominican Republic)
- East Timorese (from East Timor)
- Ecuadorean (from Ecuador)
- Salvadoran (from El Salvador)
- Equatorial Guinean (from Equatorial Guinea)
- Eritrean (from Eritrea)
- Estonian (from Estonia)
- Eswatini (from Eswatini, formerly Swaziland)
- Ethiopian (from Ethiopia)
- Fijian (from Fiji)
- Gabonese (from Gabon)
- Gambian (from The Gambia)
- Georgian (from Georgia)
- Ghanaian (from Ghana)
- Grenadian (from Grenada)
- Guatemalan (from Guatemala)
- Guinean (from Guinea)
- Guinea-Bissauan (from Guinea-Bissau)
- Guyanese (from Guyana)
- Haitian (from Haiti)
- Honduran (from Honduras)
- Icelander (from Iceland)
- Iraqi (from Iraq)
- Ivorian (from Côte d’Ivoire)
- Jamaican (from Jamaica)
- Kazakhstani (from Kazakhstan)
- Kiribati (from Kiribati)
- Kosovar (from Kosovo)
- Kuwaiti (from Kuwait)
- Kyrgyzstani (from Kyrgyzstan)
- Lao (from Laos)
- Latvian (from Latvia)
- Lebanese (from Lebanon)
- Basotho (from Lesotho)
- Liberian (from Liberia)
- Liechtensteiner (from Liechtenstein)
- Lithuanian (from Lithuania)
- Luxembourger (from Luxembourg)
- Macedonian (from North Macedonia)
- Malagasy (from Madagascar)
- Malawian (from Malawi)
- Malaysian (from Malaysia)
- Maldivian (from Maldives)
- Malian (from Mali)
- Maltese (from Malta)
- Marshallese (from Marshall Islands)
- Mauritanian (from Mauritania)
- Mauritian (from Mauritius)
- Micronesian (from Micronesia)
- Moldovan (from Moldova)
- Monacan (from Monaco)
- Mongolian (from Mongolia)
- Montenegrin (from Montenegro)
- Mozambican (from Mozambique)
- Namibian (from Namibia)
- Nauruan (from Nauru)
- Nepalese (from Nepal)
- Nicaraguan (from Nicaragua)
- Nigerien (from Niger)
- North Korean (from North Korea)
- Omani (from Oman)
- Palauan (from Palau)
- Palestinian (from Palestine)
- Panamanian (from Panama)
- Papua New Guinean (from Papua New Guinea)
- Paraguayan (from Paraguay)
- Qatari (from Qatar)
- Rwandan (from Rwanda)
- Saint Lucian (from Saint Lucia)
- Samoan (from Samoa)
- San Marinese (from San Marino)
- Sao Tomean (from Sao Tome and Principe)
- Senegalese (from Senegal)
- Serbian (from Serbia)
- Seychellois (from Seychelles)
- Sierra Leonean (from Sierra Leone)
- Solomon Islander (from Solomon Islands)
- Somali (from Somalia)
- South Sudanese (from South Sudan)
- Sri Lankan (from Sri Lanka)
- Sudanese (from Sudan)
- Surinamese (from Suriname)
- Syrian (from Syria)
- Tajikistani (from Tajikistan)
- Tanzanian (from Tanzania)
- Togolese (from Togo)
- Tongan (from Tonga)
- Trinidadian or Tobagonian (from Trinidad and Tobago)
- Tunisian (from Tunisia)
- Turkmen (from Turkmenistan)
- Tuvaluan (from Tuvalu)
- Ugandan (from Uganda)
- Uruguayan (from Uruguay)
- Uzbekistani (from Uzbekistan)
- Vanuatuan (from Vanuatu)
- Vatican (from Vatican City)
- Venezuelan (from Venezuela)
- Vietnamese (from Vietnam)
- Yemeni (from Yemen)
- Zambian (from Zambia)
- Zimbabwean (from Zimbabwe)
Nationality Examples for Students
When discussing examples of nationality in a classroom or educational setting, you might consider using various approaches to help students understand the concept more clearly. Here are some practical examples:
- Case Studies: Choose individuals from various countries and discuss their nationality, the rights it grants them, and the obligations it entails. For example, a person born in Japan has Japanese nationality, which allows them to vote in Japanese elections and receive consular protection abroad.
- Comparison of Laws: Compare how different countries handle nationality. For instance, the U.S. generally grants nationality to anyone born on its soil (jus soli), whereas Germany primarily uses jus sanguinis, basing nationality on the nationality of one’s parents.
- Interactive Map: Use an interactive world map in the classroom to allow students to click on a country and learn about its nationality laws and the rights and duties of its nationals.
- Role-Playing: Organize a role-playing session where each student acts as a citizen of a different country. They can discuss what they can do with their nationality, like travel without a visa to certain countries, or their right to work and live in their country.
- Real-Life Scenarios: Discuss scenarios involving people with dual nationality or statelessness to explore complex issues related to nationality. For example, a child born in the UK to French parents might have both British and French nationality.
- Debates: Organize debates on topics like whether nationality should grant automatic rights to work and live in other countries, such as within the EU, where nationals of member states can live and work in other EU countries.
American Nationality Examples
Here are some examples that fall under the category of American nationality, emphasizing the diversity within the United States:
- African American – Individuals in the United States with African ancestry.
- Caucasian American – People in the U.S. of European descent.
- Hispanic American – Americans with origins from Spanish-speaking countries, predominantly from Latin America or Spain.
- Asian American – Americans of Asian descent, including countries like China, Japan, Korea, the Philippines, and India.
- Native American – The indigenous peoples of the United States, including numerous tribes and nations such as the Navajo, Cherokee, Sioux, and many others.
- Pacific Islander American – Americans originating from the Pacific Islands, including Hawaii, Guam, Samoa, and other islands.
- Middle Eastern American – Americans who originate from Middle Eastern countries such as Syria, Iran, Iraq, and Lebanon.
- Mixed Race American – Americans who identify with two or more racial or ethnic backgrounds.
- European American – Americans with ancestry from any of the countries of Europe, not limited to the British Isles.
Indian Nationality Examples
Here are some examples that reflect the diversity within the Indian nationality, emphasizing different ethnic and cultural groups within India:
- Bengali – People from the eastern region of India, particularly West Bengal and the neighboring country of Bangladesh.
- Punjabi – Individuals from the northern state of Punjab, known for their distinct language, culture, and festivals.
- Gujarati – People from the western state of Gujarat, noted for their business acumen and vibrant cultural traditions.
- Tamil – People from the southern state of Tamil Nadu, with a rich history and a language that is one of the world’s oldest living languages.
- Marathi – Individuals from the state of Maharashtra, including its capital city Mumbai, with their own distinct culture and language.
- Kannadiga – People from Karnataka in the south of India, speaking the Kannada language.
- Malayali – Individuals from Kerala in the southwest of India, known for their backwaters and unique traditions in dance and music.
- Telugu – People from the Telugu-speaking states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Rajasthani – People from Rajasthan, known for their colorful attire and historical forts.
- Assamese – People from the northeastern state of Assam, with a distinct cultural heritage influenced by their geography.
These examples represent just a small sampling of the diverse ethnic groups within India, each with its own unique language, customs, and historical background.
United Kingdom Nationality Examples
In the United Kingdom, the concept of nationality is often intertwined with distinct national identities based on the country’s constituent countries. Here are examples of the main groups:
- English – People from England, the largest and most populous part of the UK.
- Scottish – Individuals from Scotland, known for its distinct culture, language (Scottish Gaelic), and legal system.
- Welsh – People from Wales, who often speak both English and Welsh, a language that has seen a revival in recent years.
- Northern Irish – Individuals from Northern Ireland, which has a unique history and cultural identity within the UK.
- Cornish – People from Cornwall, recognized as a distinct ethnic group within England, with their own language and cultural practices.
- Manx – People from the Isle of Man, though not part of the UK itself, share British citizenship and have their own unique cultural identity and language (Manx Gaelic).
Australia Nationality Examples
These identities reflect the diverse cultural landscapes and histories within the UK, each contributing to the broader British identity.
In Australia, the concept of nationality typically encompasses various ethnic and cultural groups, including indigenous communities and those descended from immigrants. Here are some examples that reflect this diversity:
- Anglo-Australian – Australians with ancestral ties to the British Isles, who form the majority of the population due to historical British colonization.
- Indigenous Australians – This includes both Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders, each with distinct cultures, languages, and histories.
- Italian Australian – Australians of Italian descent, one of the larger and more influential immigrant communities in Australia.
- Greek Australian – Another significant community, particularly in cities like Melbourne, which is known to have one of the largest Greek populations outside of Greece.
- Chinese Australian – Australians with Chinese heritage, representing one of the fastest-growing and largest ethnic groups in Australia.
- Vietnamese Australian – Australians of Vietnamese descent, many of whom arrived as refugees during and after the Vietnam War.
- Lebanese Australian – A prominent community within Australia, especially in Sydney.
- Indian Australian – A rapidly growing community with a significant presence in major urban areas.
- Irish Australian – Australians whose ancestors came from Ireland, especially during the potato famine of the 19th century.
- German Australian – Australians of German descent, who have been settling in Australia since the early days of European colonization.
These groups represent a broad spectrum of Australia’s multicultural landscape, highlighting the country’s diverse heritage and the influence of both indigenous cultures and immigrant communities.
Types of Nationality
Nationality generally refers to the legal relationship between an individual and a state, and it can manifest in various forms depending on legal principles and historical contexts. Here are some common types of nationality:
- Jus soli (Right of the Soil): Nationality is granted to anyone born on the territory of the state, regardless of the parents’ nationality. This principle is prevalent in the Americas, including the United States and Canada.
- Jus sanguinis (Right of Blood): Nationality is determined by having one or both parents who are nationals of the state. This principle is common in European countries, such as Germany and Italy.
- Dual or Multiple Nationality: This occurs when a person is legally recognized as a national by more than one state. Dual nationality can arise from a combination of jus soli and jus sanguinis policies, or because of changes in national borders.
- Naturalized Nationality: Nationality acquired through legal processes after birth. This process typically requires the individual to meet certain conditions, such as residency duration, language proficiency, and knowledge of the country’s culture and laws.
- Economic Nationality: Some countries offer citizenship through significant financial investment in the country, often referred to as “economic citizenship” or “citizenship by investment.” Countries like Malta, St. Kitts and Nevis, and others offer such programs.
- Stateless: A person who does not hold nationality in any state. Stateless people may be born into statelessness or become stateless due to laws that limit nationality transmission or due to the dissolution of countries.
Each type of nationality has specific legal implications and can affect an individual’s rights, responsibilities, and identity.
Nationality vs Citizenship
The terms “nationality” and “citizenship” are often used interchangeably, but they can have distinct meanings depending on the context, especially in legal and international discussions. Here’s how they generally differ:
- Nationality: This primarily refers to a person’s legal relationship with a state, and it usually denotes the state in which the person has been born or has significant ties. Nationality is a broader term that is often used in international law to determine which country has the right to represent and protect the person, particularly in diplomatic matters. It includes the right to consular protection abroad and to return to the country of nationality. Nationality can sometimes include multiple countries if a person is a dual national.
- Citizenship: Citizenship is a more specific term and typically refers to the status of being a citizen within a nation, with specific rights, duties, and benefits that come with it. This includes political, economic, and social rights such as voting, healthcare, and welfare benefits, which may not always be available to non-citizens. Citizenship can be more exclusive, as not all nationals (especially in cases involving territories or special administrative regions) may have full citizenship rights.
Examples to Illustrate the Difference:
- In the context of the United Kingdom, a person might be a British national but not a British citizen. For instance, British Overseas Nationals (BON) do not have the same rights to live and work in the UK as British citizens.
- In the U.S., all citizens are nationals, but not all nationals are citizens. For example, people born in American Samoa are U.S. nationals but not citizens; they cannot vote in federal elections but can travel to and reside anywhere in the U.S.
Determining factors of Nationality
Nationality, or citizenship, is determined based on a variety of legal principles and factors. These are governed by each country’s laws and international agreements. Here are some of the primary determining factors for nationality:
- Place of Birth (Jus Soli): In countries that follow the jus soli principle, nationality is granted to individuals based on their place of birth. For example, anyone born in the United States is automatically a U.S. citizen, regardless of their parents’ citizenship.
- Parentage (Jus Sanguinis): Many countries, particularly in Europe, grant nationality based on parentage. If one or both parents are citizens of a country, their children usually inherit their nationality, no matter where they are born.
- Marriage: Some countries allow a foreign national to acquire nationality through marriage to a citizen. This process typically involves residency requirements and, sometimes, renunciation of the previous nationality.
- Naturalization: This is a process for a non-citizen to become a citizen, often requiring the applicant to live in the country for a certain period, demonstrate language proficiency, pass a citizenship test, and show good moral character.
- Adoption: Children adopted by citizens of a country can usually acquire the nationality of their adoptive parents.
- Investment: Economic citizenship or citizenship by investment is offered by some countries, allowing individuals to acquire nationality through substantial financial investments in the country’s economy.
- Legislation or Administrative Decisions: Changes in laws or political circumstances can affect nationality. For example, when a new country is formed or when territorial changes occur, affected individuals might automatically receive new nationalities or have choices to make.
- Renunciation and Loss: Individuals can lose their nationality through renunciation (voluntarily giving up nationality), or it can be revoked by the state under certain conditions, such as fraud in the naturalization process.
Each country has its own specific laws and regulations regarding these factors, which can lead to a complex interplay of conditions determining nationality.
Dual nationality
Dual nationality, also known as dual citizenship, occurs when a person is legally recognized as a national of two different countries at the same time. This status can arise through various means:
- Birth: A person might be born in a country that grants nationality based on birthplace (jus soli) while having a parent from another country that grants nationality based on descent (jus sanguinis).
- Marriage: Some countries offer the option to apply for nationality through marriage to a citizen.
- Naturalization: A person may become naturalized in a second country while retaining their original nationality, if both countries permit dual nationality.
What is an Example of Nationality?
American, British, or Japanese—all refer to a person’s legal alignment with a country.
Is Nationality Where You Were Born?
Not always. Nationality can be based on parentage or naturalization, not just birthplace.
Is Your Citizenship Your Nationality?
Yes, citizenship and nationality are generally used interchangeably, denoting legal membership in a country.
What Does Nationality Mean on a Passport?
It indicates the country that issued the passport and the holder’s legal national status.
What is My Nationality if I am a US Citizen?
If you are a US citizen, your nationality is American.
Are Ethnicity and Nationality the Same Thing?
No, ethnicity refers to cultural identity and heritage, while nationality is legal citizenship.
What is My Nationality?
Your nationality is determined by the country where you hold citizenship.
Does Nationality Mean Ethnicity?
No, nationality is a legal status, whereas ethnicity relates to cultural or racial identity.
Can You Have Two Nationalities?
Yes, you can have dual nationality through birth, parents, or naturalization in multiple countries.
What is the Most Powerful Passport?
The Japanese passport is often ranked as the most powerful, allowing visa-free access to most countries.