24+ Risk Management Examples to Download
Risk management aims to identify, assess, and prioritize risks for the purpose of minimizing, monitoring, and control of the probability and impact of such risks. There are different areas where the application of risk management is important and created as a base in creating the next strategic and work plans.
Risk management examples shown on the page vary from the risk of project management, event risk management, financial risk management, and disaster risk management among others. All of the risk management samples are available for download to aid you in your specific task of identifying potential risks in your work, event, or location.
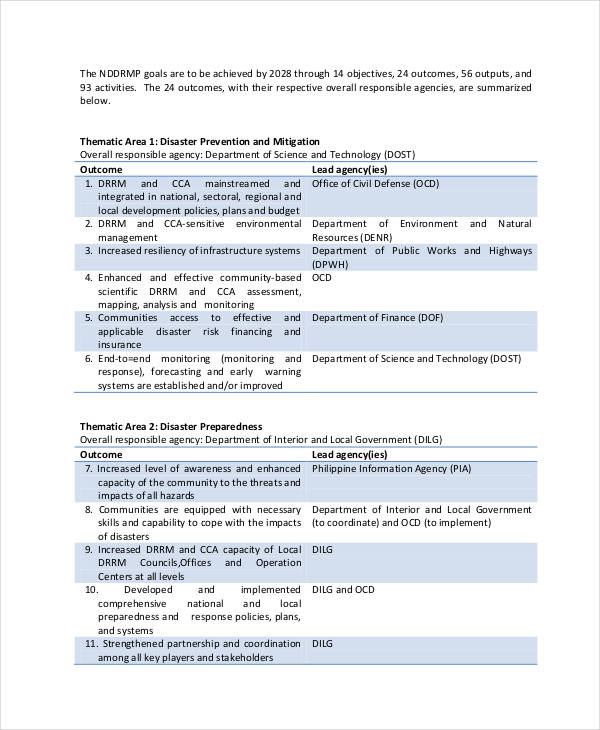
Disaster Risk Management
Disaster Risk Reduction Management Plan
Enterprise Risk Management Example
Enterprise Risk Management For Banks
Enterprise Risk Management For Financial Institutions
Security Risk Management
Information Security Risk Management
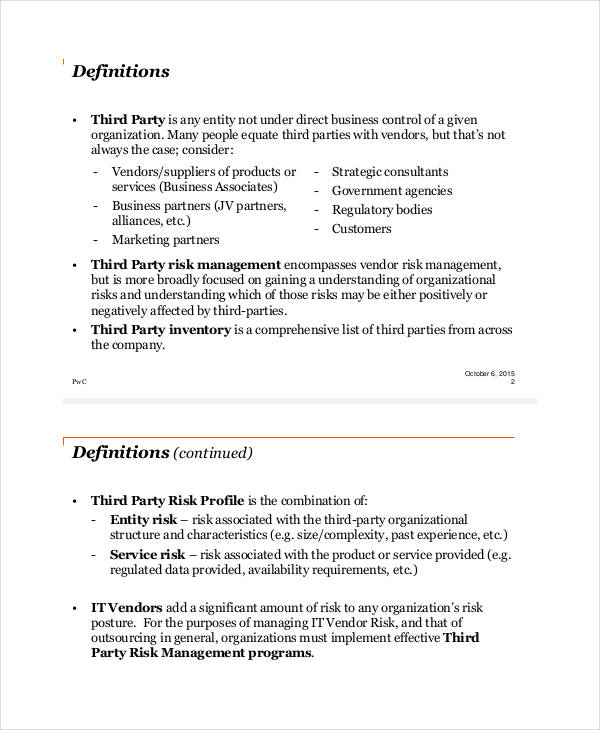
Vendor Risk Management
IT Vendor Risk Management
Event Risk Management
Event Safety Risk Management
Student Event Risk Management
Project Risk Management Sample
Quality Risk Management
Basic Risks in Risk Management
The first and foremost smart goal for risk management is to identify the risks. Early identification gives ample time for correction or reducing the possibility of the risk to occur.
This risk may have a big impact on an individual or company in the implementation plan of any task or operation. Risks potentially come from either internal or external sources.
Physical Risks
These are present in most working environments and thus need to be identified right away before any problem statement arises from them. This would include but not be limited to the following:
- Forceful Exertions – This would entail work that requires a lot of physical effort or considerable contraction force by an individual’s muscles that may result to muscle strain, soreness, or even damage. Lifting and carrying of heavy objects is a basic example.
- Insufficient Recovery Time – Often occurs in jobs that involve repetitive tasks. Examples abound in areas of construction work, as can be seen from the Construction Risk Management example.
- Repetitive Motions – closely associated with the aforementioned risk, repetitive motions involve using the same set of muscles in the entirety of their work day including awkward postures. Health risks associated with joints are identified to prevent injury to an individual or employee.
- Work Surfaces – Working with surfaces that are either too high or too low and vibrating stations.
- Reach – This risk occurs when objects involved with work are too far or too low to reach.
- Floor Surfaces – Health hazards exist when the working floor is slippery, in an uneven terrain, or sloped area.
- Movement – Risks involved are due to work involving bending and twisting of the body.
Operational Risk Management
Example Risk Management in Healthcare
Pre-Trade Risk Management Example
Construction Risk Management
Financial Risk Management
Credit Risk Management Example
Supplier Risk Management
Business Risk Management
Basic Risk Identification Continued
Mental Risks – Are vital sources of risk that should be considered in every company or organization. Ensuring the mental health of employees should take priority in every company plans. Sources for mental risk vary from stress and fatigue from the actual work to any depression or psychological disorder that an employee may be facing or would face.
Chemical and Biological Risks – Are risks involving the usage of hazardous chemicals at work like asbestos, aerosols, and cleaning fluids. Infectious diseases cause biological risks at the work place.
Market or Business Risks – Involve factors affecting overall performance management of financial markets, as can be seen on the Enterprise Risk Management for Financial Institutions example in the page. Another example which discusses the different factors involving business risks is seen in the Business Risk Management example and Corporate Risk Management example.
Environmental Risks – Closely related with chemical and biological risks, these are risks whether physical, chemical, or biological that induce a harmful response and effect land, air, water and natural resources as a result of an individual or organization’s activities. In effect, damages reflected back to the organization can be that of company image, penalties for violations, property and material liabilities, cleanup expenses, interruption of business, among others.
Inflation and Interest Rate Risks – Happens when prices of an investment change in relation to inflation. Any investor losing purchasing power is at risk especially during an inflation. The Market Risk Management example on this page discusses more pertaining risks that happen in any business market of choice.
Assess and Analyze Risks – Upon identification of risks, the severity of the impact it poses to your organization and the probability of occurrence is then determined. Having information on the probability of the extent of damage a risk has helps organizations in addressing the risk and in taking counter measures against it.
Evaluate and Rank the Risks – It is important to rank the risks according to their impact and the frequency that they occur in order for management to formulate strategic plans in parallel with the risks. Knowing which risk to prioritize in preventing from happening smooths out tasks that have to be carried out.
Corporate Risk Management
Environmental Risk Management
Legal Risk Management Example
Market Risk Management
Model Risk Management Example
Professional Risk Management
Quantitative Risk Management
Strategic Risk Management Sample
Basic Risks Further Discussed
- Treat Risks (Risk Response Plan) – Different potential ways in reducing or treating the risks are discussed in the Risk Response Plan. This step in risk management allocates the needed resources to respond to the risk and minimize the probability of any negative risk. This is incorporated into the company or organization’s preventive and contingency plans. A great example can be found in the Strategic Risk Management example found in this page.
- Review and Monitor Risks – After preventive measures have been put in place and treatments done, this part of risk management assesses and monitors the results of the action or contingency plans made and either changes or updates the quality plan as required based on the results.
Potential Risk Treatment
Treatments are made after the identification of such risks. They can be classified thus:
- Avoidance – This treatment eliminates any risk by withdrawing from doing actions that lead to the risk.
- Reduction – As the name indicates, this involves reducing the number of times an action or operation is done thereby minimizing the potential risk from happening.
- Sharing – This treatment involves distributing any action plan to a number of people to reduce any potential risk of occurring.
- Retention – Happens after acceptance of a treatment and the allocation of funds for the immediate treatment to continuous treatment. Continuous risk treatments often occur or are applied to Corporate, Supplier, and Professional Risk Management plans as shown in the page.
Project Risk Register
As with all daily plans for risk management, a project risk register exists to record details of all risks involved at the beginning and during the entirety of the project. This would be a basis in the future in identifying potential risks and the impact that risk would present to the organization or individual. The register would aid in the consistency of rating risks and in treating these risks. See Project Risk Management example for your reference.