31+ Schema Examples to Download
In the vast landscape of information and data, creating a structured framework to organize and understand various elements is crucial. This is where schema examples come into play. A schema serves as a blueprint for structuring data, providing a common language that enables effective communication and comprehension. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of schema examples, from understanding what schema is to crafting your own, step by step. Whether you’re new to the concept or seeking to refine your knowledge, this guide will illuminate the process and importance of schemas in various contexts.
1. Schema Theory and Concept Formation

web.mit.edu
2. Oracle Database Sample Schemas

docs.oracle.com
3. Schema Theory in Reading

academypublication.com
4. Schema Languages Example

brics.dk
5. RDF and RDF Schema Example

sti-innsbruck.at
6. Schema Mappings and Data Examples

drops.dagstuhl.de
7. Designing a Database Schema Example
cs.toronto.edu
8. MySQL Sample Database Schema
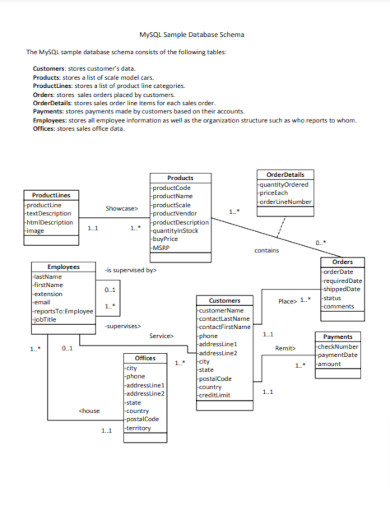
home.csulb.edu
9. Meta-Mappings for Schema Mapping Reuse
vldb.org
10. Schema Registry Overview Example

docs.cloudera.com
11. Creative Schema Theory Example

engineering.purdue.edu
12. Logic and Specification and Z Schema

cs.ecu.edu
13. Database Schema
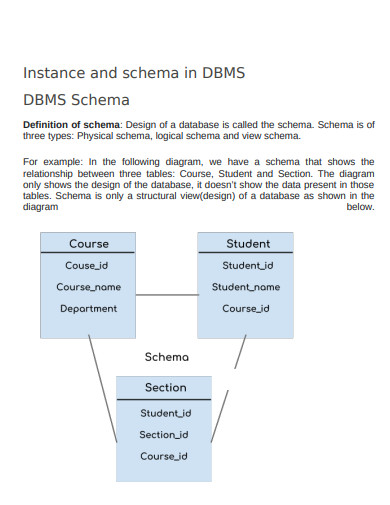
14. Instance and schema in DBMS
15. Relational Schema
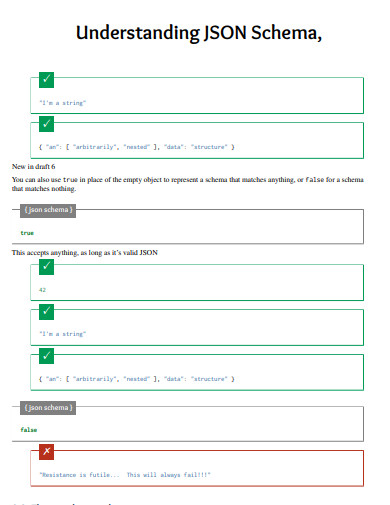
16. JSON Schema
17. Schema Modeling
18. Schema Therapy
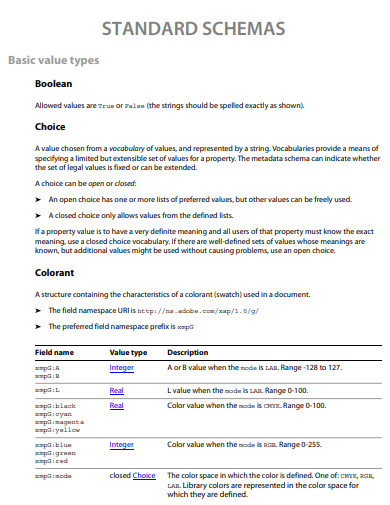
19. Standard Schema
20. XML Schema
21. MySQL Information Schema
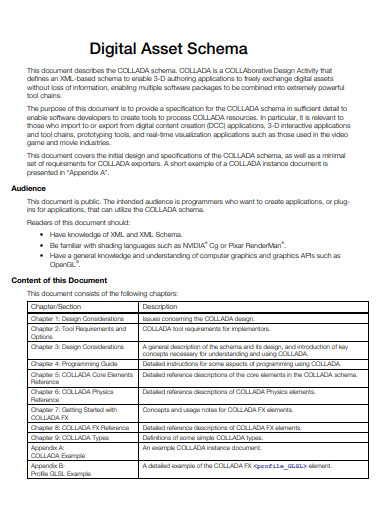
22. Digital Asset Schema
23. Schema Flexibility
24. SchemaOnRead
25. Naming Schema
26. File Schema
27. Sample Schemas
28. Schema Design
29. Schema User Guide
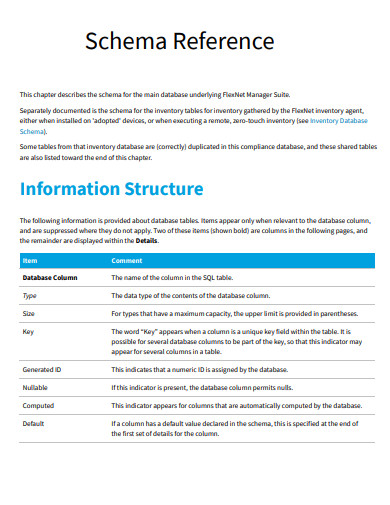
30. Schema Reference
31. Schema and Interface
32. Schema for Survey Questions
What is a Schema?
At its core, a schema is a structured representation of concepts or ideas that facilitates understanding, communication, and organization. Think of it as a framework that outlines the relationships between different elements within a given context. Schemas serve as cognitive shortcuts, allowing individuals to process information efficiently by relying on prior knowledge and experiences. They can be found in various domains, from scientific methods to interpreting human behavior and even comprehending the tone of a book.
How to Create a Schema
Creating a schema might seem daunting, but with a systematic approach, you can effectively organize complex information and gain deeper insights. Let’s explore a step-by-step guide to creating a schema.
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Context
Begin by clearly defining the purpose of your schema and the context in which it will be applied. Identify the specific elements you want to categorize and understand how they relate to one another. For example, if you’re creating a schema for a research project, determine the key variables you’ll be working with.
Step 2: Identify Relationships and Dependencies
Examine the cause-and-effect relationships, correlations, and dependencies among the elements. This step involves careful observation and analysis to identify how different elements influence one another. Analogies can also be helpful in establishing connections. For instance, if you’re creating a schema for a literature review, consider how different books relate to each other thematically or historically.
Step 3: Organize and Structure
With a clear understanding of relationships, begin organizing the elements into categories or groups. This step involves creating a hierarchy that reflects the importance and relevance of each element. Determine whether subcategories are necessary and ensure that the schema’s structure aligns with the context you’ve defined.
Step 4: Validate and Refine
Once the initial schema is created, it’s crucial to validate its accuracy and effectiveness. Seek feedback from peers or experts in the relevant field. Their insights can help identify any potential gaps or inaccuracies in your schema. Refine the schema based on the feedback received, ensuring that it accurately represents the relationships and concepts you intend to convey.
FAQs
Can a schema change over time?
Absolutely. Schemas are not static entities. They evolve as new information is acquired and our understanding deepens. As context changes, so might the relationships and categories within a schema.
How does a schema aid in understanding behavior?
Schemas provide a framework for interpreting behavior by helping us recognize patterns and potential causes. For instance, in psychology, schemas can help explain how past experiences influence an individual’s actions.
Are observations and correlations the same within a schema?
No, they’re distinct concepts. Observations involve gathering data and information, while correlations indicate a statistical relationship between variables. A schema can help you understand how these concepts interrelate.
Schemas are the hidden architects of our understanding, shaping the way we process and interact with the world around us. By creating and utilizing schemas, we harness the power of organization and categorization to make sense of complex information. Whether you’re exploring the nuances of scientific methods, deciphering the tone of a book, or unraveling the intricacies of human behavior, schemas are the guiding light that illuminates the path to comprehension.