Which of the following is not considered a simple machine?
Lever
Pulley
Gear
Inclined plane
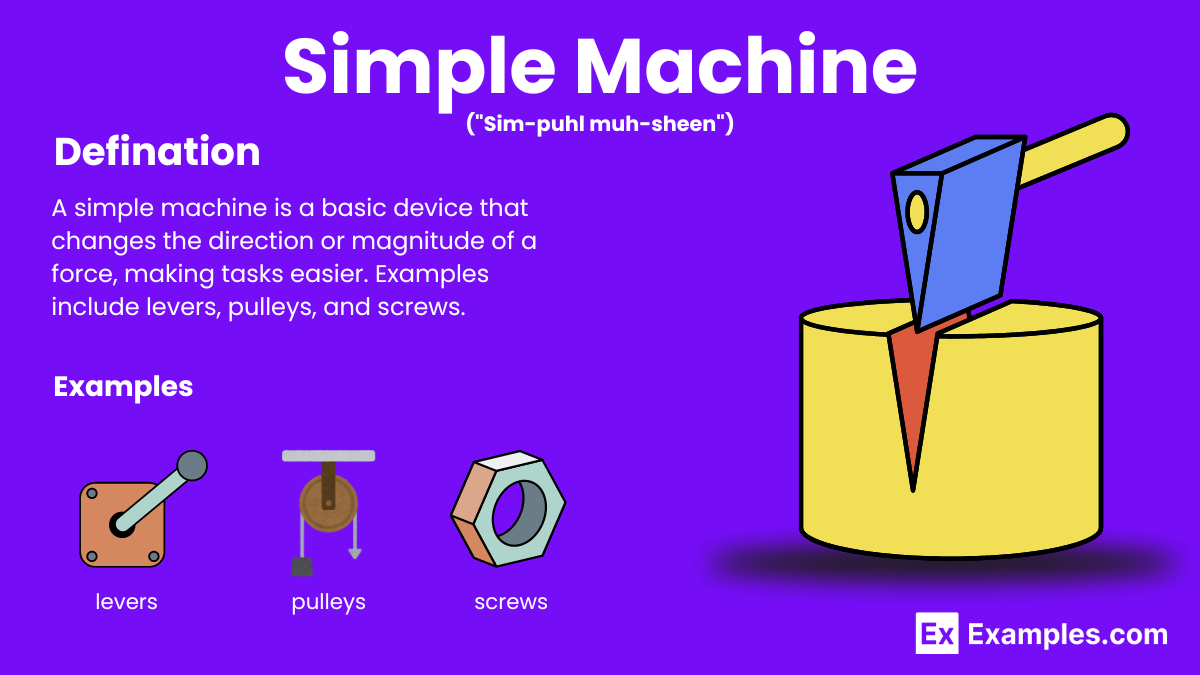
Simple machines are basic mechanical devices that alter the direction or magnitude of a force, making work easier. They include the lever, wheel and axle, pulley, inclined plane, wedge, and screw. These tools have been used since ancient times to lift heavy loads, split objects, and perform tasks with minimal effort. Understanding simple machines is fundamental in physics and engineering, as they form the basis for more complex machinery.
A simple machine is a basic mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force, making tasks easier. Examples include levers, pulleys, wheels and axles, inclined planes, wedges, and screws.
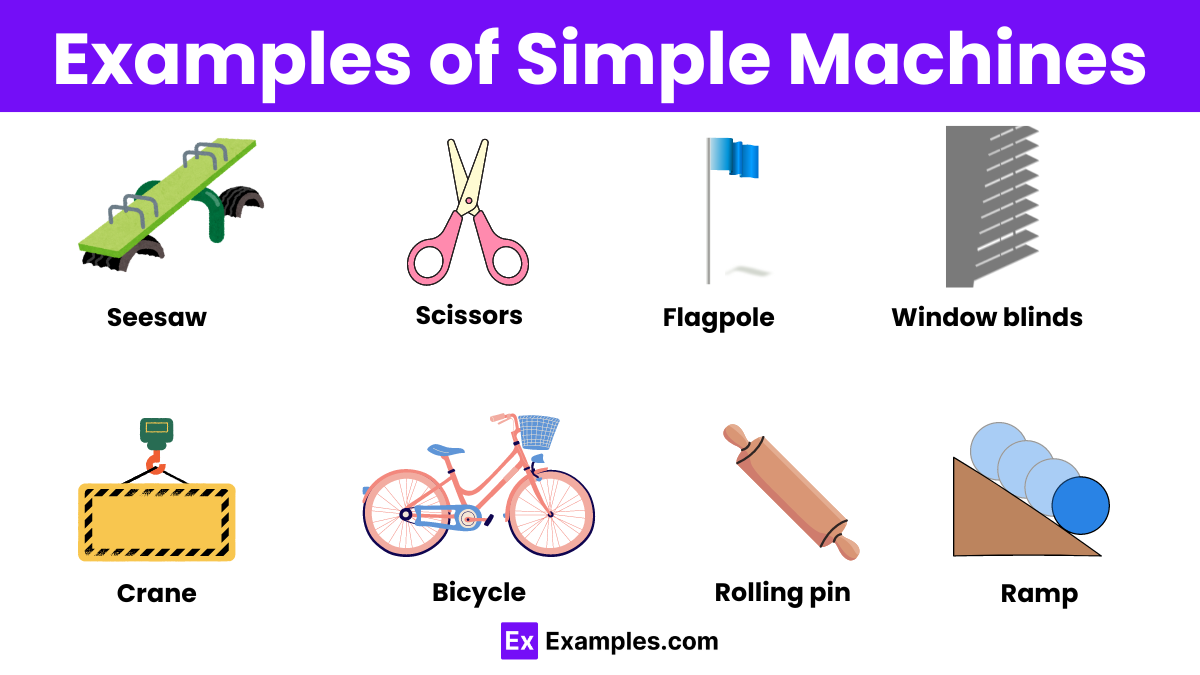
Simple machines are basic mechanical devices that help us perform tasks with less effort. Here are the six main types of simple machines:
1. Lever: Seesaw
2. Lever: Crowbar
3. Pulley: Flagpole
4. Pulley: Crane
5. Wheel and Axle: Bicycle
6. Wheel and Axle: Door Knob
7. Inclined Plane: Ramp
8. Inclined Plane: Slide
9. Wedge: Knife
10. Screw: Jar Lid
| Aspect | Simple Machines | Complex Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Basic mechanical devices that change the direction or magnitude of a force. | Combinations of two or more simple machines working together. |
| Examples | Lever, pulley, wheel and axle, inclined plane, wedge, screw | Bicycle, car engine, washing machine, clock, crane |
| Components | Consist of one or two parts | Consist of multiple parts and mechanisms |
| Operation | Operate on a single principle of physics | Operate on multiple principles and involve more complex physics |
| Energy Source | Typically manual or simple mechanical energy | Often require external power sources like electricity or fuel |
| Maintenance | Generally easy to maintain | More complex maintenance due to multiple interconnected parts |
| Usage | Used for basic tasks such as lifting, cutting, and moving objects | Used for more complex tasks involving multiple steps and functions |
| Efficiency | Generally less efficient due to manual operation | More efficient as they can perform complex tasks faster and with less effort |
| Examples in Daily Life | Scissors, bottle opener, ramp, knife | Cars, computers, refrigerators, elevators |
| Cost | Typically inexpensive and simple to manufacture | More expensive due to complexity and need for multiple materials |
1. Lever : Levers amplify force to lift heavy objects or pry things apart. They are used in tools like crowbars, scissors, and bottle openers.
2. Pulley : Pulleys change the direction of force, making it easier to lift objects. They are used in flagpoles, cranes, and window blinds.
3. Wheel and Axle : Wheels and axles reduce friction, facilitating smooth movement. They are found in bicycles, rolling pins, and door knobs.
4. Inclined Plane : Inclined planes reduce the effort needed to lift objects by spreading the work over a longer distance. Examples include ramps and slides.
5. Wedge : Wedges concentrate force on a small area to split, cut, or lift objects. Common examples are knives, axes, and chisels.
6. Screw : Screws convert rotational force to linear motion, holding objects together or lifting them. They are used in jar lids, light bulbs, and clamps.
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Effort Reduction | Reduce the amount of force needed to perform tasks, making work easier and more efficient. | Can be less effective for extremely heavy or resistant tasks. |
| Versatility | Used in a variety of applications, from lifting to cutting. | Limited to basic tasks, not suitable for complex applications. |
| Ease of Use | Straightforward to operate, requiring minimal training or expertise. | Often rely on human effort, which can be tiring and less efficient. |
| Low Maintenance | Fewer moving parts, requiring less maintenance and more durability. | Tasks can be slower compared to automated or motorized systems. |
| Cost-Effective | Inexpensive to produce and purchase, offering economical solutions. | Some require significant physical space to function effectively. |
Examples include seesaws, crowbars, scissors, and hammers.
Pulleys are used in flagpoles, cranes, window blinds, and clothesline systems.
By allowing the wheel to roll over a surface rather than sliding, which reduces the friction between surfaces.
Inclined planes are used in ramps, slides, and stairs to make it easier to move objects to different heights.
Wedges concentrate force on a small edge to split or cut objects efficiently, as seen in knives and axes.
The inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder allows screws to grip tightly, providing strong holding power.
Yes, simple machines can be combined to form complex machines, which perform more intricate tasks.
Mechanical advantage is the ratio of output force to input force provided by a simple machine, making work easier.
By positioning the fulcrum, a lever can increase output force, making it easier to lift or move loads.
Simple machines have few parts and perform basic tasks, while complex machines combine multiple simple machines for more advanced functions.
They make tasks easier, more efficient, and less labor-intensive, improving productivity in various applications.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which of the following is not considered a simple machine?
Lever
Pulley
Gear
Inclined plane
What type of simple machine is a seesaw?
Pulley
Wheel and axle
Lever
Inclined plane
Which simple machine changes the direction of force applied?
Screw
Wedge
Pulley
Lever
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is determined by:
Its length
Its width
Its height
The friction it produces
Which of the following is an example of a compound machine?
Screwdriver
Lever
Pulley
Inclined plane
What is the primary function of a wedge?
To multiply force
To change the direction of force
To split objects
To reduce friction
Which simple machine is essentially a wrapped inclined plane?
Pulley
Screw
Lever
Wheel and axle
The mechanical advantage of a wheel and axle system is given by:
The radius of the wheel divided by the radius of the axle
The radius of the axle divided by the radius of the wheel
The length of the wheel divided by the length of the axle
The height of the axle divided by the height of the wheel
Which simple machine would you use to lift a heavy object with less effort?
Lever
Wedge
Pulley
Screw
Which simple machine is most effective in changing the direction of force but not necessarily multiplying force?
Lever
Inclined plane
Pulley
Wedge
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

