5+ Financial Portfolio Optimisation Examples to Download
Due to the globalised market and unpredictable market situation, where at anytime any shares may fall against the other. In such a situation the need for a mechanism that can reduce the financial risks, utilise the funds and capital and gives high returns is utterly required. Financial portfolio optimisation does that buy collecting the best asset distributed based on the decided objectives
What is the Financial portfolio?
A financial portfolio is a collection of financial assets, stocks, capital, bonds, closed and open funds, mutual funds, commodities, etc. Financial portfolios can also comprise properties and securities like private investments, real estate, etc. Investors hold Financial portfolios designed by financial managers. Such portfolios are designed according to the objectives of different business ventures and can be designed variously for various purposes.
The financial or investment portfolio is a huge amount that is divided and invested in many trade-related works either in a small or big budget. This is done to ensure an appropriate return with all the risk tolerance. Such portfolios solely include and are composed of stocks, cash, bonds, and other assets.
5+ Financial Portfolio Optimisation Examples
1. Financial Portfolio Management Optimisation Example
2. Sample Financial portfolio optimisation Example
3. Standard Financial Portfolio Optimisation Example
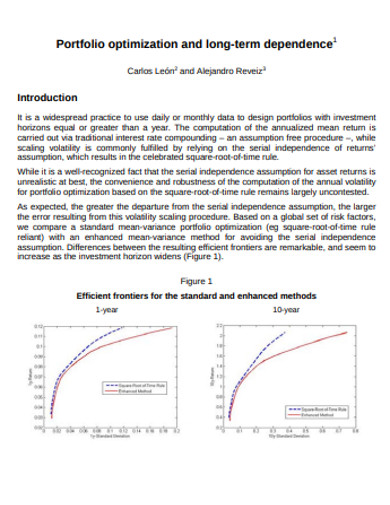
4. Financial Portfolio Optimisation Tong-Term Dependence
5. Portfolio Optimisation Portfolio Optimisation Example
6. Financial Portfolio Optimisation in DOC
How Risk Tolerance Impact Financial Portfolio Allocation?
An investor can reshape the financial portfolio given to them by the mangers and advisers with risk tolerance. Businesses are challenged by the market competition to stay among the top or ahead of trade objectives, several plans, and liquidity. The traders are often pressurised to with several guidelines. Investors should have patience and support stress testing programs. A bottom-up approach for measuring this impact with significant exposure to credits can be done in the portfolio.
The portfolio structure can be improved for revenue generation by emphasising the generation process again and again and focusing on business objectives. This can increase the level of pressure to do better and specifically to make higher returns. Such revenue growth can be improved by limiting aspects that address concentrated correlations in the portfolio itself while strategizing and planning the business credits and level of portfolio diversification. Defining the credit risk strategies with portfolio profitability along with pricing objectives to ease the work.
What are the Models of Optimisation?
Model 1: Background research
Proper background research and good base design can help to get high returns and good performance apart from the presence of the greatest risks. There are two options that the investor may choose while selecting the portfolios. One is the maximum expected returns for different risks or the other one with the lowest risk but different levels of returns.
Model 2: Assumptions
Assumptions can be made on the market and investors to assess the risk that may include several things.
- Investors might expect more returns in a particular situation of risk.
- Investors are only worried about the maximised profits with the available capital.
- Investors can freely access accurate information on the risk and the expected returns.
- Investor tries to avoid risk to secure their investment and get profit.
- Investors base their decisions on investment seeing the expected performance and risk measurement.
Model 3: Mean-Variance
The oldest model in practice since risk and investment in securities began. The simplified process of this model is the reason that it is still in practice. It helps to understand the mathematical aspects but raises complexity in the solution to get the best portfolio.
Model 4: Mean Semi-Variance
If you are more concerned about increasing the performance level, this model is best and more appropriate for your use. This model considers the expected outcomes of the securities and their semi-variance and thus seeks to identify the optimal portfolio.
Model 5: Conditional Value at Risk
The Conditional Value at Risk or CVaR is designed as an extended form of value at risk. It estimates the losses of adverse conditions minutely of the investments and addresses theoretical problems. CVaR has more attractive properties and aspects than VaR for general distributions.
Model 6: Mean Absolute Deviation
This model is said to be the average of the absolute deviation of the mean. This helps to measure exclusively linear constraints.
Never Forget the Key points
- A portfolio is a collection and exhibition of your different institutional or trade’s irremovable parts and counterparts.
- Portfolio also includes the property securities if you want to add them like you can add the real estate, private investment, and other securities in it if you want.
- While you are designing the financial portfolio never forget to add and adjust all the crucial aspects and factors of it like, risk tolerance, asset allocation, time frame, equity capital, etc.
Tips for Framing Financial Portfolio Optimisation
- Make a list of all that belongs to you and all you owe.
- Stay honest with your partners and shareholders.
- Maintain a finely crafted financial statement to maintain transparency with your stakeholders and shareholders.
- When time requires to accept changes welcome it wholeheartedly.
- Pay off the debts and interests to the loaners and the lenders.