What is the primary function of a diode in an electronic circuit?
To amplify signals
To convert AC to DC
To store electrical energy
To control the current flow


A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only, acting as a one-way valve for electric current. It has two terminals: the anode (positive side) and the cathode (negative side). When the anode is more positive than the cathode, the diode is forward-biased and permits current flow; when the anode is less positive than the cathode, the diode is reverse-biased and blocks current flow. Diodes are essential components in electronic circuits, used for rectification, voltage regulation, signal modulation, and various other applications.
A diode is a semiconductor device that permits current to flow in only one direction, acting as a one-way valve. It has two terminals, an anode and a cathode, and is commonly used for rectification, signal modulation, and voltage protection in electronic circuits.
A diode is constructed using semiconductor materials, primarily silicon or germanium. The basic structure consists of a p-n junction, which is formed by joining a p-type semiconductor (with an abundance of holes or positive charge carriers) and an n-type semiconductor (with an abundance of electrons or negative charge carriers). The p-type region is doped with acceptor impurities, while the n-type region is doped with donor impurities.
The interface where the p-type and n-type regions meet creates a depletion region, devoid of free charge carriers, which acts as a barrier to current flow. The anode of the diode is connected to the p-type material, and the cathode is connected to the n-type material. In a typical diode, these regions are encapsulated in a protective casing, with external leads or terminals extending from the anode and cathode to allow connection to an external circuit.
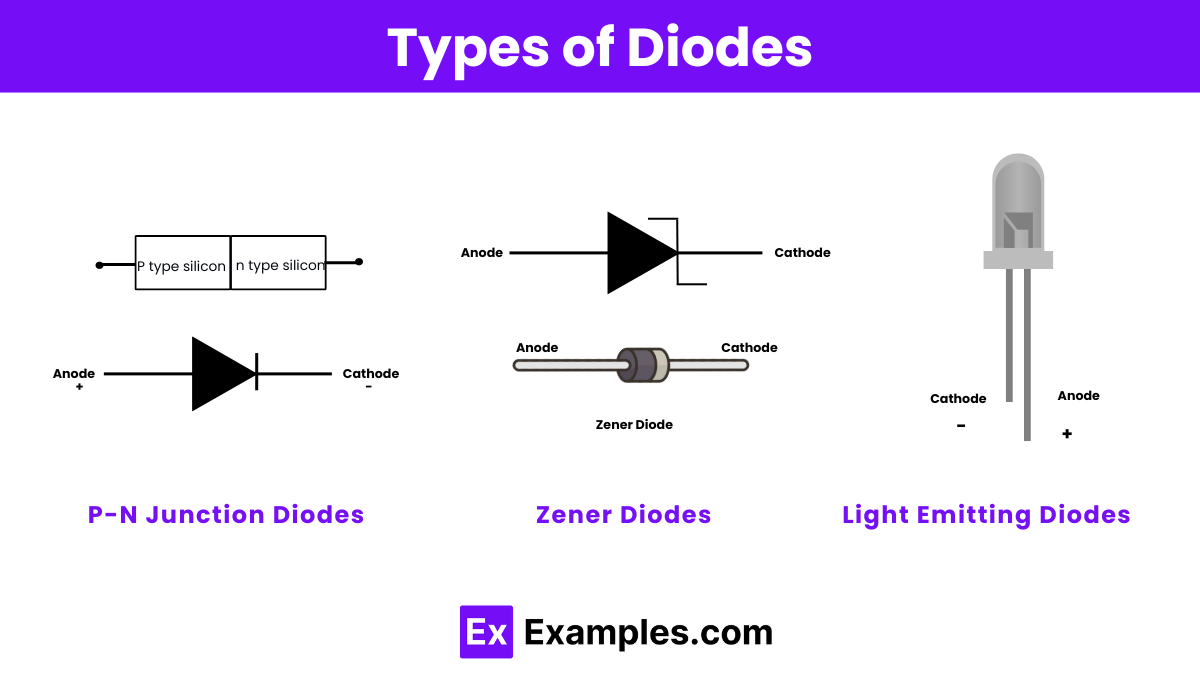
Diodes come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Here are some of the most common types of diodes:
P-N junction diodes are the most basic type of diodes, consisting of a p-type and an n-type semiconductor joined together. When forward-biased, current flows easily; when reverse-biased, current flow is blocked. They are used in rectification, signal demodulation, and voltage regulation. An example is the 1N4148, widely used in signal processing.
Standard diodes are used for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). They are commonly found in power supplies, battery chargers, and rectification circuits. An example of a standard diode is the 1N4007, which is widely used for general-purpose rectification.
Zener diodes allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached. These diodes are used for voltage regulation, overvoltage protection, and voltage reference circuits. A typical Zener diode is the 1N4733A, often used for its stable voltage characteristics.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) emit light when current flows through them. They are used in display screens, indicators, and lighting applications. LEDs come in various colors and sizes, such as the popular 5mm red LED used in many electronics projects.
Schottky diodes have a lower forward voltage drop and faster switching speed compared to standard diodes. They are used in high-speed and high-frequency applications, including power rectification and RF systems. The 1N5819 is a common Schottky diode used for its efficiency and speed.
Photodiodes generate current when exposed to light, making them ideal for light detection and photovoltaic systems. They are used in solar cells, light meters, and optical communication devices. The BPW34 is a commonly used photodiode known for its sensitivity and response time.
Tunnel diodes exhibit negative resistance due to quantum tunneling, allowing them to function in high-frequency oscillators and amplifiers. These diodes are used in microwave and radio frequency applications. An example is the 1N3716, used for its high-speed performance.
Varactor diodes act as variable capacitors when reverse biased. They are used in voltage-controlled oscillators and RF design, such as tuning circuits in TV and radio receivers. The MV2109 is a widely used varactor diode known for its capacitance range and stability.
Diodes exhibit several key characteristics that determine their functionality and suitability for various applications. Understanding these characteristics is essential for selecting the appropriate diode for a specific purpose.
Diodes are versatile components used in a wide range of electronic applications. Here are some of the most common uses of diodes :
Diodes are used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This process, known as rectification, is essential in power supplies for converting the AC mains voltage to a stable DC output. Full-wave and half-wave rectifiers are common circuits utilizing diodes for this purpose.
Zener diodes are specifically designed to maintain a constant voltage level. They are used in voltage regulation circuits to provide a stable reference voltage, protecting sensitive electronic components from voltage fluctuations.
Diodes are used to demodulate amplitude-modulated (AM) signals in radio receivers. By allowing current to pass only during the positive half-cycles of the signal, the diode extracts the a information from the carrier wave.
Diodes protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes and surges. Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes and Zener diodes clamp excess voltage to prevent damage to sensitive components, ensuring circuit reliability.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) emit light when a current flows through them. LEDs are widely used in display screens, indicator lights, and general illumination due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
Schottky diodes are used in power conversion applications due to their low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. They improve the efficiency of power supply circuits, especially in switch-mode power supplies (SMPS).
PIN diodes are used in radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications for switching, attenuation, and modulation. Their ability to handle high frequencies makes them suitable for use in communication systems and radar.
A diode works by allowing current to pass when the anode is positive relative to the cathode, and blocking it when reversed.
The forward voltage is the minimum voltage required to make the diode conduct electricity, typically 0.7V for silicon diodes.
Reverse bias occurs when the diode’s anode is connected to a lower voltage than the cathode, preventing current flow.
An LED emits light when current flows through it, whereas a regular diode does not emit light.
Rectifier diodes convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) in power supply circuits.
Schottky diodes are used in high-speed switching applications due to their low forward voltage drop and fast recovery time.
Diodes are used to direct current flow, protect circuits from reverse polarity, and convert AC to DC.
When forward biased, the diode conducts current with minimal resistance, allowing current to pass through.
Reverse leakage current is the small current that flows through the diode when it is reverse biased.
The maximum current rating is the highest current a diode can safely conduct without damage, varying by diode type.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary function of a diode in an electronic circuit?
To amplify signals
To convert AC to DC
To store electrical energy
To control the current flow
In which direction does current flow through a diode when it is forward-biased?
From cathode to anode
From anode to cathode
From negative to positive
From positive to negative
What happens to the resistance of a diode when it is reverse-biased?
It becomes zero
It becomes very high
It remains constant
It fluctuates
What is the typical forward voltage drop across a silicon diode?
0.1 V
0.3 V
0.7 V
1.2 V
What material is most commonly used to make diodes?
Silver
Copper
Silicon
Gold
What is a Zener diode primarily used for?
Rectification
Amplification
Voltage regulation
Signal modulation
What is the main difference between an LED and a regular diode?
LED emits light
LED has a higher forward voltage
LED operates at lower frequencies
LED is less efficient
Which type of diode is used to protect circuits from high voltage spikes?
Light-emitting diode
Schottky diode
Zener diode
Rectifier diode
In a diode, what is the region where current does not flow called when the diode is reverse-biased?
Forward region
Breakdown region
Reverse blocking region
Conduction region
What is the purpose of a diode bridge rectifier?
To convert DC to AC
To amplify AC signals
To rectify AC signals to DC
To regulate voltage
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

