What is the primary characteristic that differentiates semiconductors from conductors and insulators?
Variable conductivity
Fixed electrical resistance
High thermal conductivity
Magnetic properties

Semiconductors are materials that have electrical conductivity between conductors (like metals) and insulators (like ceramics). They are essential in modern electronics, enabling the function of devices such as diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Made from elements like silicon, germanium, gallium, and hafnium, semiconductors can be modified through doping, where impurities are added to change their electrical properties. This ability to control conductivity makes semiconductors fundamental to the operation of computers, smartphones, and solar cells. Their unique properties facilitate the development of miniature, high-performance electronic components, driving advancements in technology and industry.
Semiconductors are materials with electrical conductivity between that of conductors and insulators, essential for modern electronics like computers and smartphones. Primarily made from silicon, their properties can be modified through doping to control electrical behavior. This enables their use in components such as diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits, crucial for switching and amplifying electrical signals.
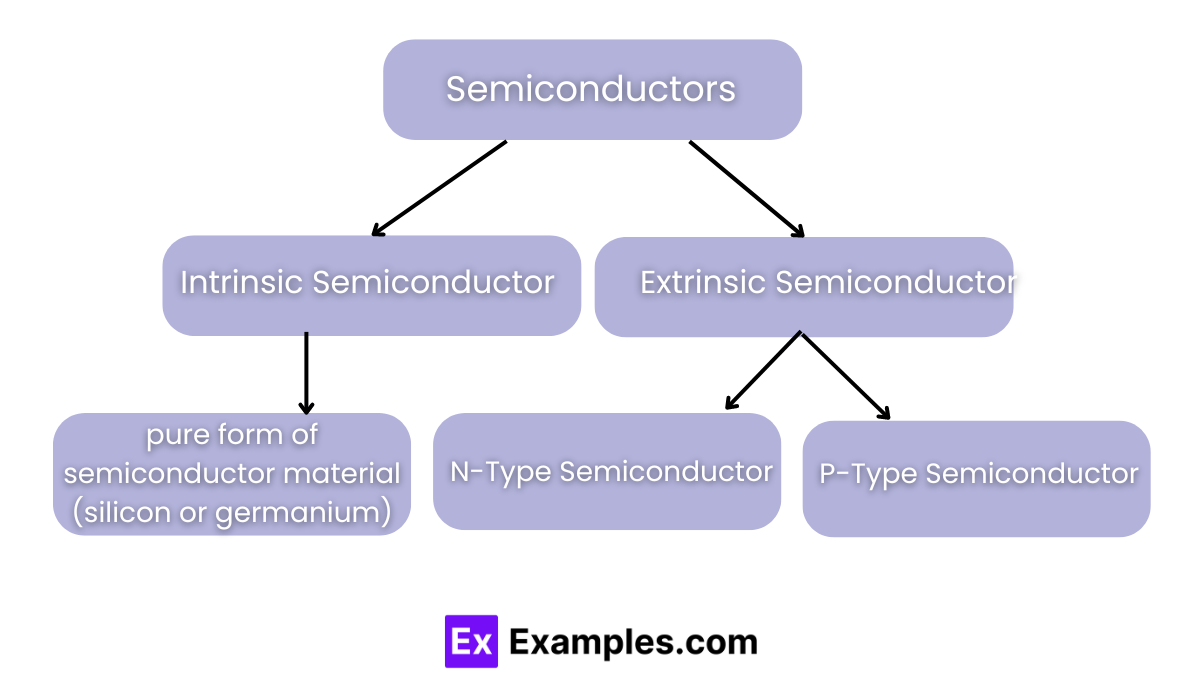
An intrinsic semiconductor is a pure form of semiconductor material, such as silicon or germanium, without any significant impurities added. The electrical conductivity of intrinsic semiconductors is solely dependent on the properties of the material itself and temperature. At absolute zero temperature, an intrinsic semiconductor behaves like an insulator. As the temperature increases, thermal energy excites electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, creating electron-hole pairs that contribute to electrical conduction. Intrinsic semiconductors are foundational in understanding the behavior of more complex, doped semiconductors used in various electronic devices.
An extrinsic semiconductor is a type of semiconductor that has been intentionally doped with impurities to modify its electrical properties. There are two main types of extrinsic semiconductors:
Extrinsic semiconductors are crucial in the fabrication of electronic components such as diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits, as the doping process allows precise control over their electrical characteristics.
| Feature | Intrinsic Semiconductors | Extrinsic Semiconductors |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pure semiconductor materials with no intentional impurities added. | Semiconductor materials doped with impurities to modify electrical properties. |
| Conductivity | Relatively low, dependent on temperature and material properties. | Significantly higher, dependent on type and concentration of dopant impurities. |
| Charge Carriers | Equal numbers of electrons and holes created by thermal excitation. | Majority carriers determined by doping: n-type has more electrons, p-type has more holes. |
| Doping | No doping; pure elements like silicon or germanium. | Doped with donor (n-type) or acceptor (p-type) atoms to increase free charge carriers. |
| Examples | Pure silicon (Si), pure germanium (Ge). | Silicon doped with phosphorus (n-type), silicon doped with boron (p-type). |
| Applications | Used in research and study of semiconductor properties. | Used in diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits for enhanced electrical properties. |
| Temperature Dependence | Conductivity increases significantly with temperature. | Less dependent on temperature changes, stable number of charge carriers due to doping. |
Transistors, made from semiconductor materials like silicon, act as switches and amplifiers in electronic circuits. They are essential in:
Computers
Mobile phones
Televisions
Integrated circuits consist of multiple semiconductor devices on a single chip, used in:
Microprocessors
Memory devices
Digital signal processors
Solar cells convert sunlight into electrical energy using semiconductor materials, found in:
Solar panels
Solar chargers
Photovoltaic power plants
LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them, used in:
Display screens
Indicator lights
General lighting
Semiconductors are crucial in controlling and converting electric power, used in:
Power inverters
Motor drives
Power supplies
Doping involves adding impurities to a semiconductor to change its electrical properties, creating either n-type (electron-rich) or p-type (hole-rich) materials.
Electrons are negatively charged particles, while holes are positively charged vacancies. Their movement under an electric field enables current flow in semiconductors.
An intrinsic semiconductor is a pure semiconductor without any significant impurities. Its electrical properties are determined by the material itself.
An extrinsic semiconductor is a doped semiconductor, where impurities are added to modify its electrical properties, making it either n-type or p-type.
A p-n junction is the boundary between p-type and n-type semiconductors, crucial for the operation of diodes, transistors, and other electronic devices.
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only, typically made from a p-n junction.
Transistors control the flow of current between two terminals using a third terminal (gate), acting as a switch or amplifier in circuits.
The band gap is the energy difference between the valence band and conduction band in a semiconductor, determining its conductivity.
Silicon and germanium have suitable band gaps and can be easily doped, making them ideal for a wide range of electronic applications.
Moore’s Law predicts the doubling of transistors on a semiconductor chip approximately every two years, driving advancements in technology.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary characteristic that differentiates semiconductors from conductors and insulators?
Variable conductivity
Fixed electrical resistance
High thermal conductivity
Magnetic properties
Which type of semiconductor has an excess of electrons?
P-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductor
Intrinsic semiconductor
Dielectric material
What is the function of a PN junction in semiconductor devices?
To increase the resistance
To rectify current
To conduct magnetic fields
To insulate electrical signals
Which semiconductor material is commonly used in the production of photovoltaic cells?
Silicon
Germanium
Gallium Arsenide
Indium Phosphide
What is the purpose of doping in semiconductors?
To change the physical shape
To alter the electronic properties
To increase thermal resistance
To reduce electrical insulation
In a P-N junction diode, what happens when it is forward-biased?
The junction is non-conductive
The current flows through the junction
The diode blocks all current
The diode acts as a capacitor
Which property of semiconductors is utilized in a transistor?
Magnetism
Variable resistance
Variable conductivity
Thermal expansion
What type of semiconductor is formed when an element from Group 3 of the periodic table is doped with an element from Group 5?
P-type
N-type
Intrinsic
Insulating
Which semiconductor material is known for its high-speed applications, such as in microwave and RF circuits?
Silicon
Gallium Arsenide
Germanium
Silicon Carbide
Which characteristic is crucial for a material to be used as a semiconductor in electronic devices?
High electrical conductivity
High thermal conductivity
Band gap energy
Magnetic permeability
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

