What is heat in terms of physics?
A type of temperature
A form of energy
A state of matter
A type of force

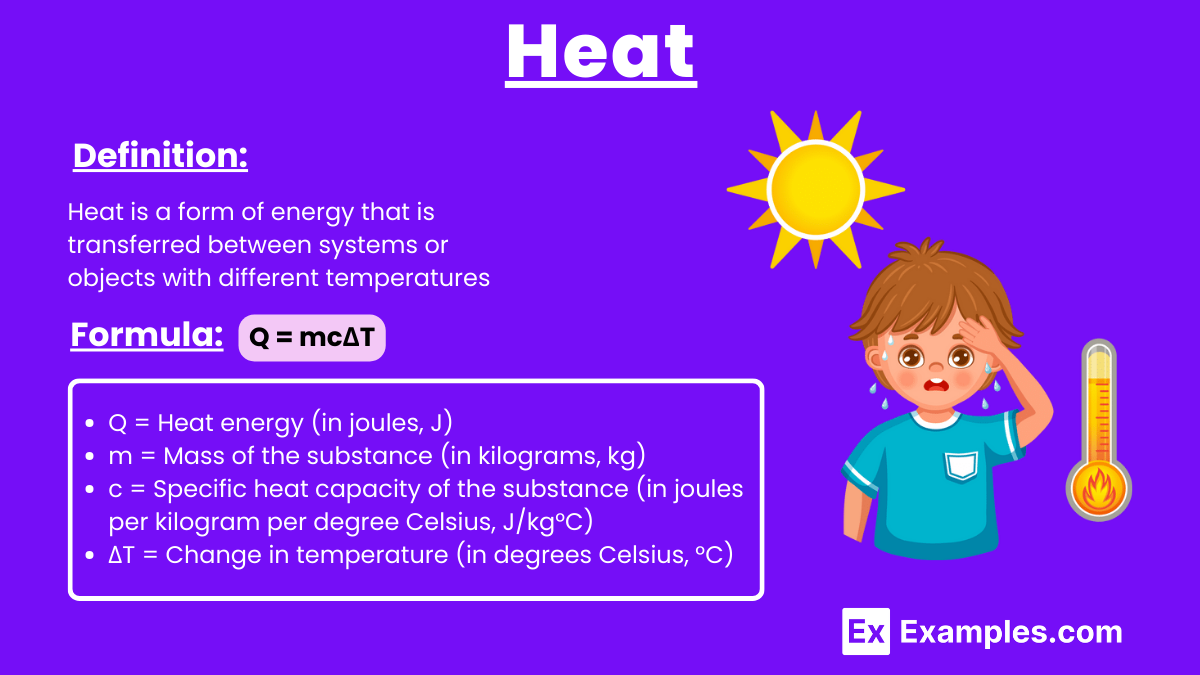
Heat is a form of energy transfer between systems or objects with different temperatures, flowing from the hotter system to the cooler one. Heat Transfer occurs through conduction (direct contact), convection (fluid movement), and radiation (electromagnetic waves). The Heat Formula is Q=mcΔT, In the International System of Units of Heat (SI), heat is measured in joules (J).
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between systems or objects with different temperatures, flowing from the hotter system to the cooler one until thermal equilibrium is reached. This transfer occurs through conduction, convection, or radiation and is measured in units of joules or calories.
The formula for calculating heat is
where:
Heat can be classified into three main types based on its method of transfer:
Heat energy can be categorized based on its transfer methods and sources. Here are the main types:
Sure, here is the comparison between heat and temperature presented in a table format:
| Aspect | Heat | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Form of energy transfer between systems due to a temperature difference. | Measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance. |
| Nature | Energy transfer process; depends on mass, specific heat capacity, and temperature change. | Scalar quantity; does not depend on the amount or type of substance. |
| Measurement Instruments | Calorimeters | Thermometers, thermocouples, infrared sensors |
| Conceptual Understanding | Total energy of molecular motion in a substance (potential and kinetic energy). | Intensity of heat, reflecting average particle motion. |
| Effects | Can change the temperature and phase of a substance. | Indicates the degree of hotness or coldness. |
| Examples | Energy added to a pot of water to increase its temperature. | The temperature reading of the water in the pot. |
| Mathematical Relation | Q=mcΔT | No direct formula; measures thermal energy intensity. |
| Units of Measurement | Joules (J), Calories (cal), British thermal units (BTU) | Degrees Celsius (°C), Kelvin (K), Degrees Fahrenheit (°F) |
Heat plays a crucial role in a wide array of applications across various fields. Here are some of the key applications:
Heat, a form of energy, plays a crucial role in various aspects of daily life and industrial processes. Below are some of the most common uses of heat:
Heat is essential in cooking food. It transforms raw ingredients into edible and often more nutritious meals. The process involves:
Boiling: Cooking food by immersing it in boiling water.
Baking: Using dry heat in an oven to cook food.
Frying: Cooking food in hot oil.
Heat provides warmth and comfort in homes and buildings through various heating systems:
Central Heating: Distributes heat from a central source (like a furnace) throughout a building.
Space Heaters: Portable devices that heat small areas.
Underfloor Heating: Radiant heating installed under floors to warm a space evenly.
Heat is crucial in numerous industrial processes, including:
Smelting: Extracting metals from ores by heating and melting.
Welding: Joining materials by melting them together with heat.
Chemical Manufacturing: Reactions often require heat to produce desired compounds.
Heat is a primary component in electricity generation:
Thermal Power Plants: Convert heat from burning fossil fuels into electricity.
Nuclear Power Plants: Use heat from nuclear reactions to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity.
Geothermal Energy: Utilizes heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity.
Heat is vital for various transportation systems:
Internal Combustion Engines: Use heat from burning fuel to power vehicles.
Steam Engines: Operate by using heat to convert water into steam, driving pistons or turbines.
Aerospace: Heat shields protect spacecraft from intense heat during re-entry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
Heat is measured in joules (J) or calories (cal).
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one kilogram of a substance by one degree Celsius.
Thermal equilibrium occurs when two objects in contact reach the same temperature and heat transfer stops.
A calorimeter is a device used to measure the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical or physical process.
Latent heat is the heat absorbed or released during a phase change without changing the temperature.
Thermal conductivity is a material’s ability to conduct heat.
Insulation reduces heat transfer by trapping air or other gases, which are poor conductors of heat.
Metal conducts heat away from your hand faster than wood, making it feel colder.
The greenhouse effect is the warming of Earth’s surface due to the trapping of heat by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Conduction, convection, and radiation are the three modes of heat transfer.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is heat in terms of physics?
A type of temperature
A form of energy
A state of matter
A type of force
Which unit is commonly used to measure heat energy in the International System of Units (SI)?
Watt
Newton
Joule
Calorie
What is the primary mode of heat transfer in solids?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Evaporation
Which law states that heat energy cannot be created or destroyed?
Law of Conservation of Mass
First Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Newton's Law of Cooling
What does the specific heat capacity of a substance represent?
The total amount of heat in the substance
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of the substance by 1 degree Celsius
The speed at which the substance absorbs heat
The temperature at which the substance melts
What is the primary mode of heat transfer in fluids like liquids and gases?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Sublimation
Which of the following is an example of heat transfer by radiation?
A spoon getting hot from a cup of tea
The sun warming the Earth
Boiling water
Melting ice
What happens to the molecules of a substance when it is heated?
They stop moving
They move more slowly
They move faster
They get smaller
Which of the following materials is a good conductor of heat?
Wood
Plastic
Copper
Rubber
What is latent heat?
Heat required to raise the temperature of a substance
Heat required to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature
Heat lost during cooling
Heat that can be sensed with a thermometer
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

