Which type of electromagnetic radiation is commonly used in remote controls?
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
X-rays

Electromagnetic waves are oscillating electric and magnetic fields that travel through space at the speed of light, carrying energy. These waves are generated by the movement of charged particles and are governed by the principles of Electromagnetism. They can propagate through a vacuum as well as through various media. Electromagnetic waves cover a broad spectrum, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays, each differing in units of wavelength and frequency. The behavior of these waves is described by the laws of electrodynamics. They are fundamental to numerous technologies and natural processes, including heat transfer, playing a critical role in communication, medical imaging, and even the behavior of the universe.
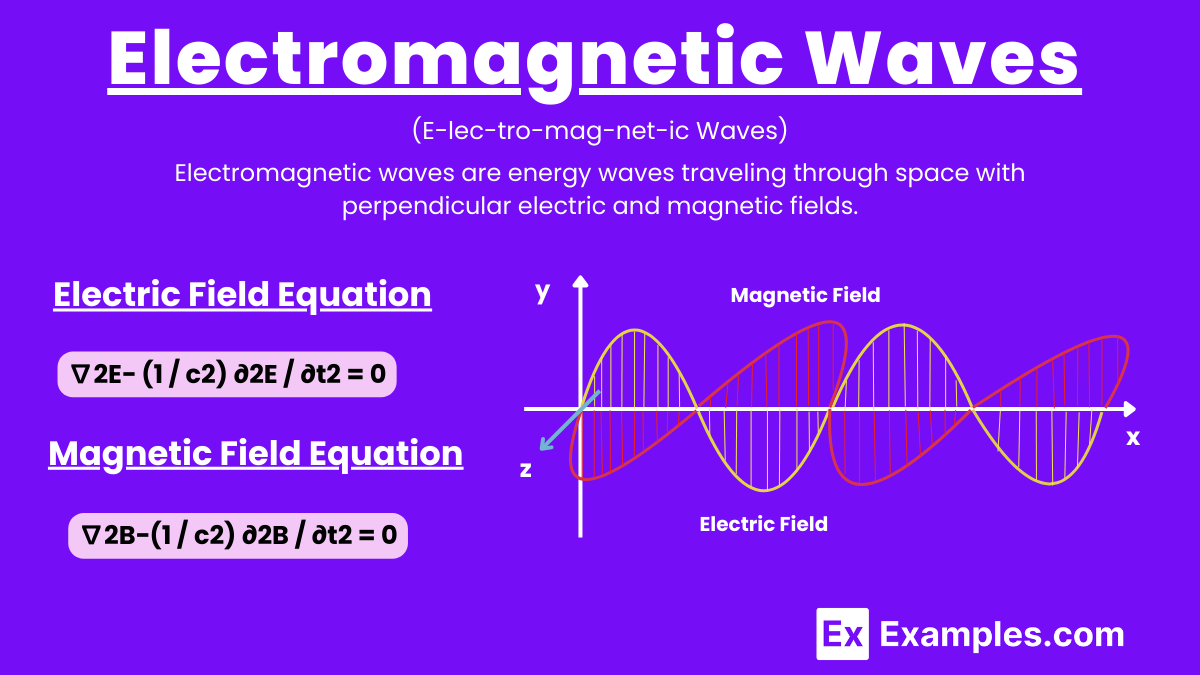
Electromagnetic waves are energy waves that travel through space, consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other. They include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves can travel through a vacuum at the speed of light and are essential in technologies like communication and medical imaging.
The electromagnetic wave equation describes how electromagnetic waves propagate through space and time. It is derived from Maxwell’s equations, which govern the behavior of electric and magnetic fields.
This equation shows how the electric field E changes in space and time. It indicates that changes in the electric field propagate as waves at the speed of light.
Similarly, this equation describes the propagation of the magnetic field B\mathbf{B}B. The magnetic field also travels as waves at the speed of light.
where:

Electromagnetic waves span a wide range of frequencies and wavelengths, forming the electromagnetic spectrum. Here are some key examples:
Radio waves have the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Uses: They are used in communication systems, such as AM/FM radio, television broadcasts, and cell phones. Radio waves are also used in radar and navigation systems.
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths than radio waves but longer than infrared waves.
Uses: Common uses include cooking food in microwave ovens, satellite communications, and radar systems.
Infrared waves have wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves.
Uses: Infrared waves are used in remote controls, thermal imaging cameras, and night-vision equipment.
Visible light is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen by the human eye.
Uses: Visible light is essential for vision, photography, illumination, and various optical instruments.
Ultraviolet light has a shorter wavelength than visible light and higher energy.
Uses: UV light is used in sterilization processes, fluorescent lights, and tanning beds.
X-rays have shorter wavelengths and higher energy than UV rays.
Uses: X-rays are widely used in medical imaging (X-ray radiography), security scanning at airports, and material analysis.
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and the highest energy in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Uses: Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment (radiotherapy), sterilizing medical equipment, and studying nuclear reactions.
Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are the main types of electromagnetic waves along with their key applications:
Electromagnetic waves are generated by accelerating charges, such as electrons, which create changing electric and magnetic fields.
The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (about 300,000 kilometers per second).
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays.
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies, used for communication and broadcasting.
The Hartree energy (Eh) is 4.359×10-18 joules, a unit of energy used in atomic physics and quantum chemistry.
The Compton wavelength (𝜆𝐶) is2.426×10−12 meters, representing the wavelength increase of a photon when scattered by a particle.
The Faraday constant (𝐹) is 96485.33212 C/mol, the total electric charge carried by one mole of electrons.
The Wien displacement constant (b) is 2.897771955×10−3 m·K, describing the relationship between the temperature of a blackbody and the wavelength at which it emits most strongly.
The universal gas constant (𝑅) is 8.3144621 J/mol·K, the constant in the equation of state of an ideal gas, relating energy scale to temperature scale.
The Rydberg constant (𝑅∞) is1.097373×107m−1, used in atomic physics to describe the wavelengths of spectral lines.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Which type of electromagnetic radiation is commonly used in remote controls?
Radio waves
Microwaves
Infrared
X-rays
What is the primary source of ultraviolet radiation on Earth?
The Moon
The Sun
Artificial lights
Radio waves
What is the main difference between ultraviolet and infrared radiation?
Wavelength
Speed
Medium of travel
Amplitude
Which electromagnetic wave has the highest frequency?
Radio waves
Microwaves
X-rays
Gamma rays
What property of electromagnetic waves allows them to travel through a vacuum?
They have mass
They have charge
They are transverse waves
They require a medium
What is the primary use of infrared waves in technology?
Communication
Heating
Medical imaging
Sterilization
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is visible to the human eye?
Ultraviolet
Infrared
Visible light
Radio waves
Which electromagnetic wave is most commonly used in medical imaging to view bones?
X-rays
Infrared
Microwaves
Radio waves
What type of electromagnetic wave is used in microwave ovens?
Infrared
Ultraviolet
Microwaves
Gamma rays
Which of the following electromagnetic waves has the longest wavelength?
Gamma rays
X-rays
Visible light
Radio waves
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

