What does Ohm’s Law state in the context of solid state physics?
Voltage is inversely proportional to current
Current is directly proportional to voltage
Resistance is directly proportional to voltage
Power is inversely proportional to resistance
Solid State Physics, a crucial branch of physics, explores how matter behaves when atoms are arranged in solids. At its core, this field is governed by the laws of physics, which help us understand and predict the properties of materials like metals, semiconductors, and insulators. These laws delve into the arrangement of atoms, the forces between them, and the resulting properties of the material. By knowing these fundamental principles, we gain insights into the behavior of materials and how they can be manipulated for various technological applications. This makes Solid State Physics essential for innovations in electronics, computing, and many other fields.
The journey of solid state physics began in the early 20th century when scientists first started to understand the atomic structure of materials. In 1900, Paul Drude applied classical physics to explain the electrical properties of solids, which marked the inception of theoretical solid state physics. Then, in 1912, Max von Laue discovered the diffraction of X-rays by crystals, proving that crystals are periodic lattices of atoms. This discovery further cemented the atomic theory of matter.
The development of quantum mechanics in the 1920s revolutionized this field. Felix Bloch Formulated the theory of quantum mechanics for electrons in crystals in 1928, introducing the concept of electron bands. This was a critical advancement in understanding the electrical, thermal, and optical properties of materials.
Through the 20th century, the integration of quantum mechanics with solid state physics led to the invention of semiconductors and transistors, sparking the digital revolution. These discoveries and theories collectively shaped modern technology and continue to drive innovations in materials science and engineering.
Thermal Properties: The crystal structure also dictates how a material conducts heat. Metals generally have high thermal conductivity due to the mobility of free electrons in their crystal lattice.
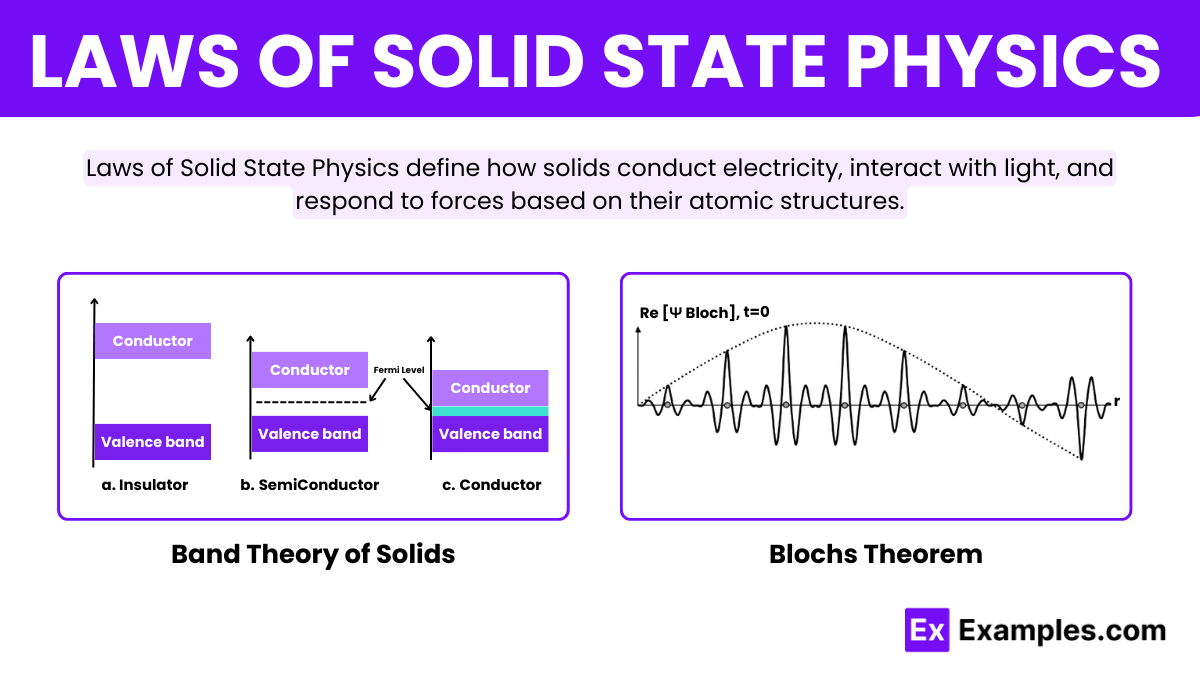
Bloch’s Theorem revolutionizes our understanding of electron behavior in crystalline solids. It states that electrons in a periodic lattice, like that of a crystal, can be described by wave functions called Bloch functions. These wave functions, characterized by their wave-like nature, allow electrons to move through the lattice as if they are waves spreading across the crystal. The theorem simplifies the complex interactions within crystals and is fundamental in explaining the quantum behavior of electrons in solids.
Band Theory of Solids provides a framework for understanding the electronic structure of materials. According to this theory, the close proximity of atoms in a solid causes the atomic orbitals to overlap, forming bands of energy levels. Electrons occupy these bands, and the distribution of electrons across these bands determines the material’s electrical properties. Specifically, the presence or absence of a band gap between the occupied valence band and the unoccupied conduction band dictates whether a material behaves as a Conductor, Semiconductor, or Insulator. This theory is crucial for designing and understanding electronic devices.
Felix Bloch earned the title “Father of Solid State Physics” for pioneering electron behavior in crystals with his work, known as Bloch’s Theorem.
The Fermi level indicates the highest occupied electron energy state at absolute zero, crucial for determining electrical properties.
In crystals, Electron waves spread uniformly across the lattice, facilitated by the periodic structure that shapes their wave functions.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does Ohm’s Law state in the context of solid state physics?
Voltage is inversely proportional to current
Current is directly proportional to voltage
Resistance is directly proportional to voltage
Power is inversely proportional to resistance
According to Hooke’s Law, what is the relationship between stress and strain in an elastic material?
Stress is inversely proportional to strain
Stress is directly proportional to strain
Stress is directly proportional to the square of strain
Stress is independent of strain
What principle does the Pauli Exclusion Principle describe?
Electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins
Electrons in different orbitals must have the same spin
Electrons can occupy the same quantum state
Protons can occupy the same energy level
What does the Debye Model explain in solid state physics?
Conductivity of metals
Magnetic properties of materials
Heat capacity of solids
Elastic properties of materials
According to Bragg’s Law, what condition must be met for constructive interference of X-rays scattered by a crystal?
nλ = 2d sinθ
nλ = d sinθ
λ = 2d sinθ
λ = d sinθ
What does Bloch’s Theorem describe?
Behavior of free electrons in a vacuum
Magnetic properties of solids
Motion of electrons in a periodic potential
Elastic deformation of materials
What is the main concept behind Fermi-Dirac statistics?
Distribution of bosons at thermal equilibrium
Distribution of fermions at thermal equilibrium
Distribution of protons in a nucleus
Distribution of photons in a cavity
What does the Hall Effect demonstrate in a solid material?
Generation of an electric field by a magnetic field
Polarization of light by a magnetic field
Absorption of heat by a magnetic field
Deflection of electrons by a magnetic fiel
What does the Wiedemann-Franz Law relate in a metallic conductor?
Electrical resistance and heat capacity
Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity
Magnetic susceptibility and thermal expansion
Specific heat and magnetic permeability
According to the Kronig-Penney model, what is the nature of electronic band structure in a crystal?
Continuous energy levels
Random energy levels
Discrete energy levels with band gaps
Uniform energy levels
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

