19+ MLA Citation Examples
Writing a research report, you may have encountered works cited that may vary with regards to the kind of research paper you are writing about. When you cite your sources, always remember that there are two kinds of citations, the MLA format and the APA format. Each of these citations has different formatting, so be careful when preparing your MLA citations to ensure accuracy and consistency.
1. MLA Citation Format
2. MLA Citation Example
3. MLA Citation Sample
4. MLA Citation PDF
5. Bibliography MLA In-Text Citation
6. MLA Citation Purdue Owl
7. MLA Citation Article on a Website
9. MLA Citation Book Example
10. MLA Citation with Heading
11. MLA Citation with Journal Newspaper
12. MLA Citation 8Th Edition
13. MLA Parenthetical Citation
14. MLA Citation with Author
15. Sample MLA Works Cited Page
16. MLA Citation with Title Page
17. MLA Automatic Citation Sample
18. MLA Citation Style for Academic Work
19. MLA Speech Citation
20. MLA Cover Page Citation
What Is an MLA Citation?
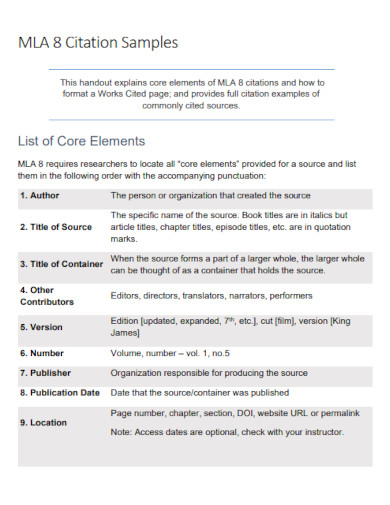
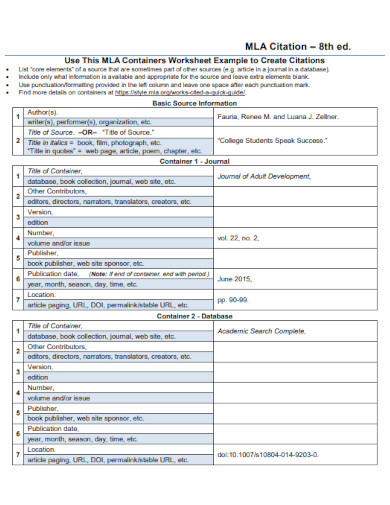
To start, MLA stands for Modern Language Association. When you are making your academic research paper outline, you are often told to do the MLA citations. An MLA citation format is a kind of citation outline format that academic researchers, teachers and students who are told to write research papers use a reference list for their research paper.
How to Make an MLA Citation?
Making an MLA citation is easy enough if you have all the correct information in order. As well as if you have all the elements of what makes an MLA citation. It is important that you will know what begins and what ends, how you make it and what should be avoided when using this kind of citation format.
Step 1. Everything Must Be Written in Chronological Order
Citing out your sources, you must write them the same way a bibliography is written. In chronological order. This will mean that regardless of their first names beginning with what part of the alphabet, what matters most is the author’s last name and first name next.
Step 2. The Author’s Last Name Is Written First
Another thing you can take notice of when using the MLA citation style is that, The author’s last name is written first and followed by the first name. As well as the fact that the title of the research paper or article they have written follows after their names. It is different from the APA format, which follows a different citing style. For the APA it is the author’s name followed by the date.
Step 3. Use Quotations for the Title
MLA citations when adding the title after the author’s name, you must add the open and close quotations. This is to specify that the word next to the author’s name is their works. The title of their works that you have used in your research paper or your thesis paper. Not quoting the title may make your citations not be an MLA format but something different.
Step 4. Add the Date of Publishing
After the title of the works, books or articles, the last thing you can add is the date of publishing and the place it was published. The date of publishing is important as you must arrange the entire citation in chronological order, this will mean the latest one is on top while the oldest will be at the bottom.
FAQs
What does the acronym MLA stand for?
The acronym MLA stands for Modern Language Association. This is just one of the many kinds of formats that are used in research papers, thesis, and academic papers.
Why is it important to cite your sources?
When you are writing your research paper or your thesis, in order to avoid any copyright or plagiarism, it is always best to cite the sources you took to support your idea. You use the MLA citation when your research paper follows the MLA format, and the purpose of an MLA citation is to make sure that as you write your research paper you are acknowledging the sources used to make your research paper even more authentic. Lastly, the format for an MLA citation is chronological order. The author, the title of your sources, the version, numbers and of course the date of publication and it was published.
What is the difference between MLA citing and APA citing?
When you are citing your sources, the difference between MLA and APA is in MLA the author’s name comes first followed by the title of the source, the version of the source, the date and the location of publishing. As for the APA, the author’s name is followed by the date, and then the title of the book or the resources.
It goes without saying, when you are using citations for your research paper or for your thesis paper, there are a lot of kinds of citing formats and each with its own purpose. Being careful is not enough, you must also understand the differences and see to it what kind of format your paper would fall under. For MLA citations and APA citations have different outline formats that may look almost the same and can be confusing at times, but the difference is for MLA the author and title of sources goes first. For APA it is the author and the year of publication.