What is the square of 104?
10,816
11,232
10,400
11,000

In algebra, squares and square roots are indispensable, serving as keystones in myriad calculations and analyses. They unlock deeper insights into numerical systems, bridging the realms of rationality and irrationality. Mastery of these fundamentals empowers mathematicians to navigate complexities, from basic arithmetic to advanced equations, fostering a holistic understanding of mathematical principles. Thus, the study of squares and square roots transcends mere computation, evolving into a profound exploration of mathematical structure and logic.
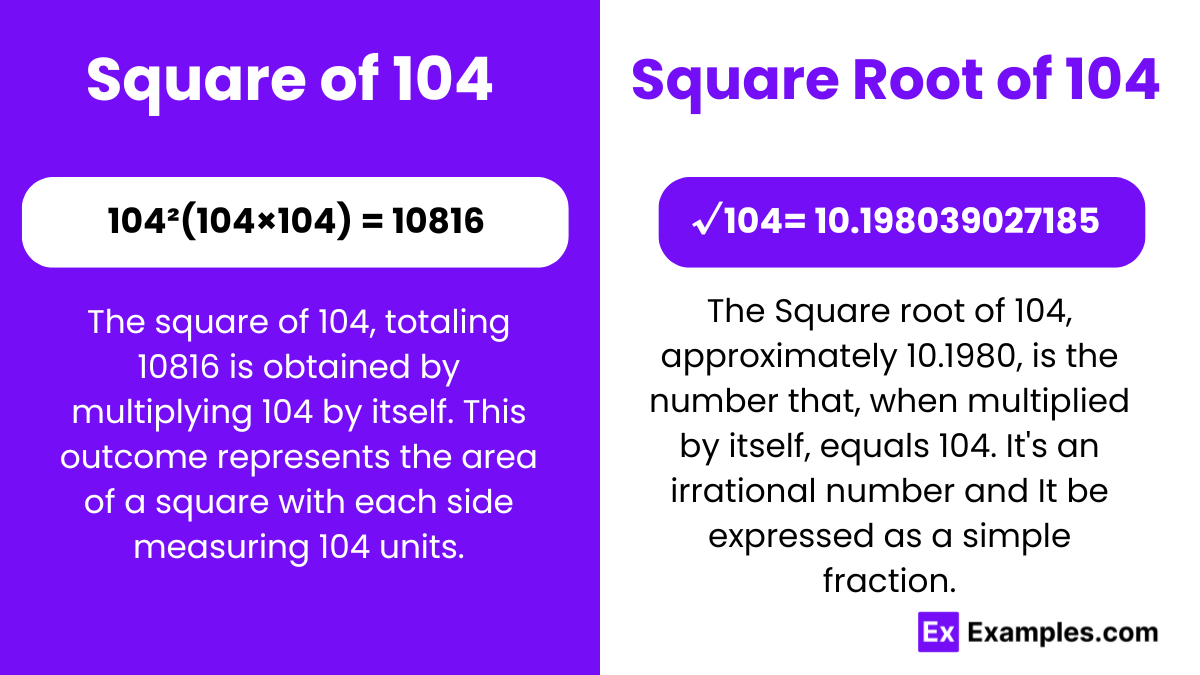
A square number results from multiplying an integer by itself. The square of 104 is 10816. In mathematics, square numbers exhibit distinct properties, crucial for understanding algebraic relationships and patterns. Exploring the square of 104 unveils fundamental principles, enriching comprehension of mathematical structures and operations.
or
√104=10.198 upto 3 Decimals
The square root, a fundamental concept in mathematics, reveals the number that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. The square root of 104 is approximately 10.198039027185. Understanding square roots elucidates the properties and relationships underlying numbers, offering insights into the square of 104 and its mathematical significance.
Exponential Form: (104^1/2) or (104^0.5)
Radical Form: √104
This is because 104 is not a perfect square, and its square root cannot be expressed as the quotient of two integers. Therefore, the square root of 104 cannot be represented as a rational number.
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. They include both terminating and repeating decimals.
Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be expressed as the quotient of two integers. Their decimal expansions are non-terminating and non-repeating.
1. Prime Factorization Method:
Factorize 104 into its prime factors:
104 = 2³ × 13
Take the square root of each factor:
√104 = √2³ × 13
Simplify by taking the square root of each component:
√2³ = 2 √2
√13
Combine the results:
√104 = 2 √2 ×√13
2. Using a Calculator:
Simply input 104 and press the square root (√) button.
The display will show the approximate value of the square root of 104.
3. Decimal Approximation:
Start with an initial guess, such as 10.
Test your guess by squaring it: (10² = 100) (too low).
Increase your guess and repeat until you find a number close to 104:
(11² = 121) (too high)
(10.5² = 110.25) (still too high)
(10.3² = 106.09) (getting closer)
(10.2² = 104.04) (even closer)
Refine your guess until you reach the desired level of accuracy.
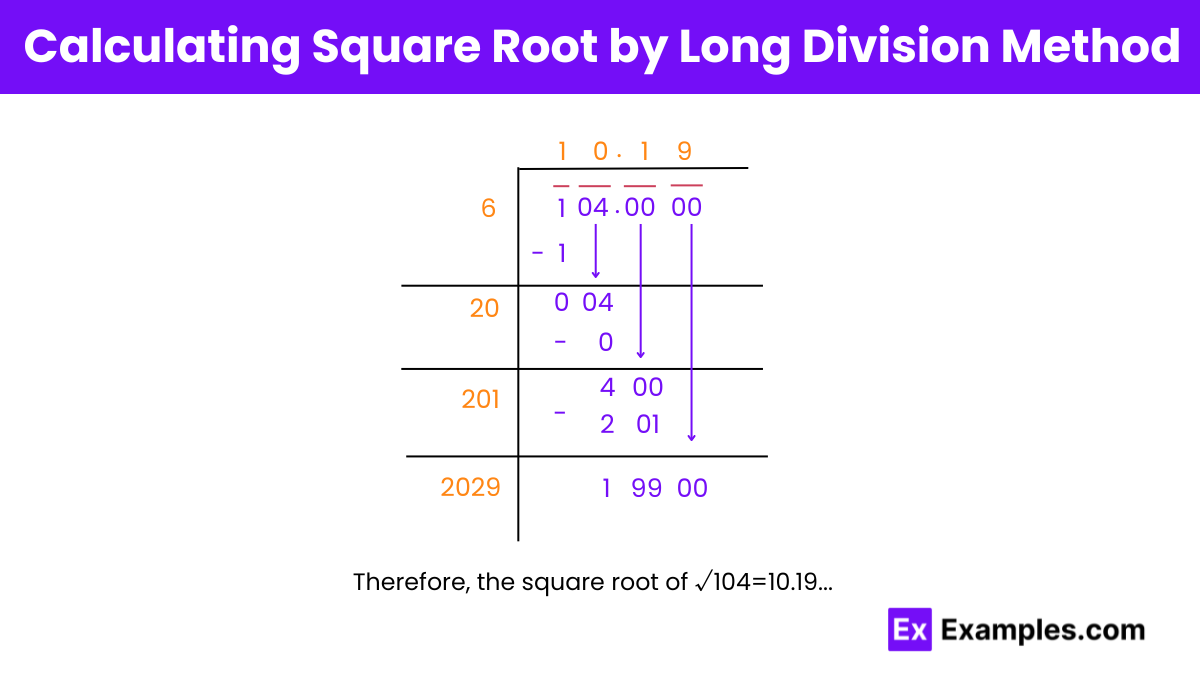
Step 1: Starting from the right, pair up the digits by placing a bar above 04 and 1 separately. Also, pair the 0s in decimals in pairs of 2 from left to right.
Step 2: Find a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives a product less than or equal to 1. This will be 1 here, so place 1 in the quotient and the divisor’s place, resulting in a remainder of 0.
Step 3: Drag down 04 beside the remainder 0. Also, add the divisor to itself and write it below. (1+1=2)
Step 4: Find a number X such that (2X × X) results in a number less than or equal to 04. The number 0 fits here, so fill it next to 2 in the divisor as well as next to 1 in the quotient.
Step 5: Find the remainder and now drag down the pair of 0s from the decimal part of the number. Adding X to the divisor, the new divisor remains 20.
Step 6: Repeat this process to get the desired decimal places.
In other words, there is no integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals 104. Therefore, the square root of 104 is an irrational number.
A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the square of another integer, resulting in a whole number when squared.
The cube root of 104 is approximately 4.682, rounded to three decimal places.
The approximate value of the square root of 104 is approximately 10.198.
The square of 104 is 10816, an even number. It is also a composite number, having factors other than 1 and itself.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 104?
10,816
11,232
10,400
11,000
What is the square root of 104?
10.2
10.5
11
12
Find the square of 104.
10,800
10,816
10,900
11,200
What is the approximate square root of 104?
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.4
What is 104²?
10,304
11,024
10,816
11,040
Calculate the square root of 104 to the nearest tenth.
10.0
10.1
10.2
10.4
What is the value of 104 × 104?
10,900
11,016
10,816
11,100
Determine the square root of 104 rounded to the nearest whole number.
10
11
12
13
What is 104² in numerical terms?
10,800
11,024
10,816
11,200
Find the square root of 104.
10.3
10.4
10.5
10.6
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

