What is the square of 12?
144
136
128
78
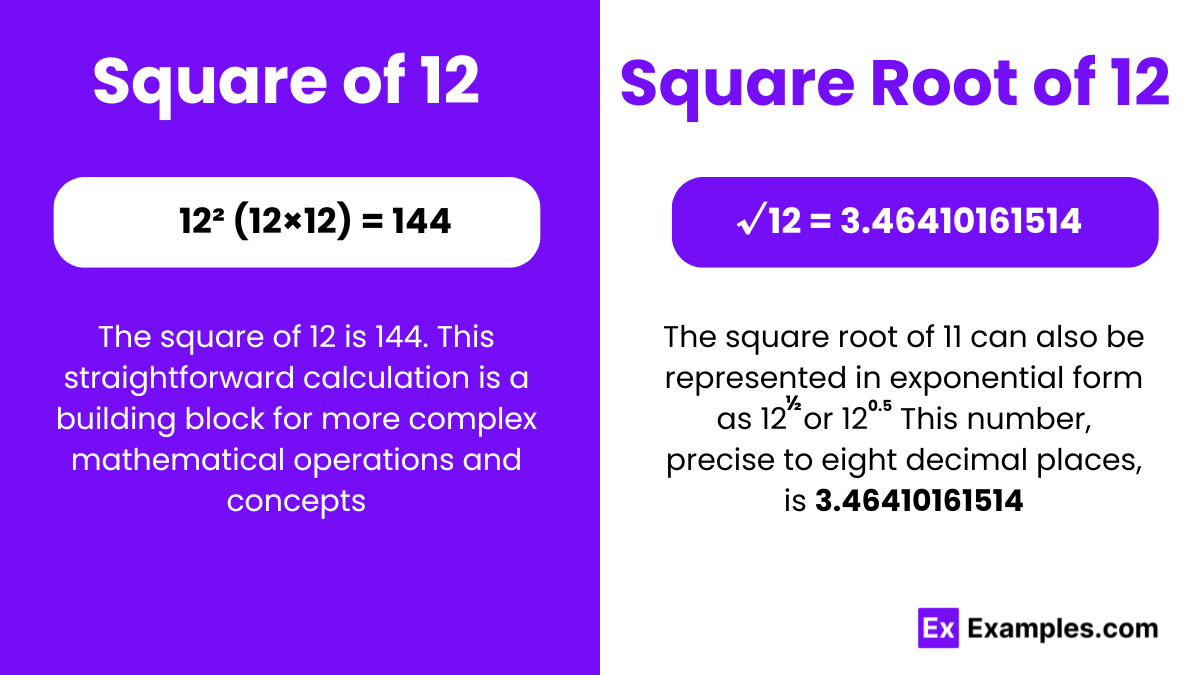
The square of 12, represented as 12, is calculated by multiplying 12 by itself, resulting in 144. This is a fundamental arithmetic operation where 12 is both the multiplicand and multiplier, leading to its squared value, 144.
Or
√12 = 3.464 up to three places of decimal.
The square root of 12, represented as √12, falls into the category of irrational numbers, meaning it cannot be precisely expressed as a fraction. The approximate numerical value of √12 is 3.4641, situating it between the whole numbers 3 and 4. The fact that 12 is not a perfect square (a number that is an integer’s square) underlines why its square root, √12 does not simplify to an exact whole number.
Exponential Form of 12: = (12)½ or (12)0.5
Radical Form of 12: √12 or 2√3
The square root of 12 irrational number
The square root of 12 is a mathematical concept that prompts an exploration into its rationality or irrationality. To determine whether the square root of 12 is rational or irrational, we must first understand these terms.
Rational numbers are those that can be expressed as a quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. In other words, they can be written in the form a/b, where a and b are integers and b≠0. Rational numbers include integers, fractions, terminating decimals, and repeating decimals.
Conversely, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. They are non-repeating and non-terminating decimals. Examples of irrational numbers include the square root of non-perfect squares, such as 22, 33, and π.
Now, let’s apply this understanding to the square root of 12.
To find the square root of 12, we need to determine a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 12. We can approximate the square root of 12 to be approximately 3.464. However, this is just an approximation.
To delve deeper into whether the square root of 12 is rational or irrational, let’s consider its exact value.
To find the value of √12 without directly calculating square roots, consider these alternative approaches:
Estimate the value by recognizing it lies between two known values. Since 12 is between the squares of 3 and 4 (9 and 16, respectively), its square root must be between 3 and 4. Observing that 12 is closer to 9 suggests the square root is just above 3.
This method, akin to traditional long division, allows you to approximate the value digit by digit. It involves a systematic process of guessing, subtracting, and bringing down digits, akin to standard division but tailored for finding square roots.
This iterative numerical technique refines an initial guess to find better approximations. Starting with a guess near the expected value, apply the iterative formula to converge on a more accurate approximation.
For a straightforward approach, use a calculator’s square root function. Inputting “12” and pressing the square root button will give you a precise approximation instantly.
Some advanced mathematical series or sequences converge to square roots based on their properties. By calculating the terms of such a series, you can approximate the square root value.
Each method offers a different pathway to approximation, from quick and practical to more detailed and insightful, catering to various needs and contexts.
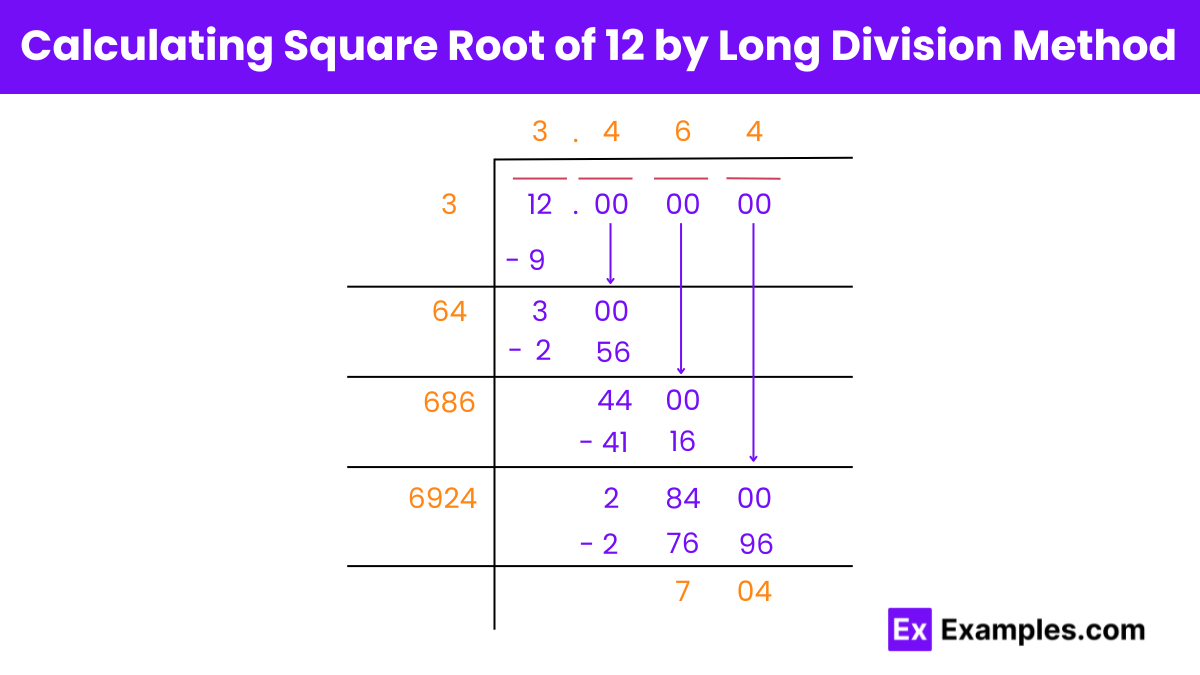
To find the square root of 12 using the long division method, we follow these steps:
So, the square root of 12 by the long division method is approximately 3.4641016151377544.
The simplified form of √12 involves factoring out the largest perfect square from 12, which is 4. This leaves you with 2√3, where 2 is the square root of 4, and √3 remains under the radical because 3 is a prime number.
Equivalent to the square root of 12 is the expression 2√3. This is derived by factoring out the square root of the largest perfect square factor of 12, which is 4, leaving the square root of 3 as the remaining factor
No perfect cube root equals 12. Cube roots are typically associated with numbers that are the product of a number multiplied by itself three times. For 12, there’s no whole number that, when cubed, equals 12.
Yes, you can take the square root of 12. It results in an irrational number, which cannot be precisely expressed as a fraction. The process involves either estimation, numerical methods, or factoring out the square root of a perfect square factor.
Yes, 12 is a natural number. Natural numbers are the set of positive integers beginning from 1 and extending indefinitely. The number 12 falls into this category, being a whole, positive number.
In conclusion, the square of 12 is 144, and its square root is approximately 3.464. These mathematical values are fundamental in various disciplines, aiding in calculations and problem-solving. Understanding the relationship between squares and square roots enhances mathematical proficiency and facilitates applications in fields such as science, engineering, and finance.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the square of 12?
144
136
128
78
What is the square root of 144?
10
11
12
13
If you square 12, what is the result?
144
121
169
132
What is the result of squaring the square root of 12?
12
24
26
28
If x² = 12, what is the approximate value of x?
3.46
1
2
4
What is the square of 3.5?
10.25
12.25
13.25
14.25
What is the result of 12 divided by its square root?
3.3
3.5
3.46
2.5
What is the approximate square root of 144?
9
10
11
12
Find the number whose square root is 3.46.
12
11.5
10
14
Calculate the square of the result obtained by adding the square root of 12 to 2.
36
38
40
42
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

