What is the formula for calculating heat gain (Q) in terms of mass (m), specific heat capacity (c), and temperature change (ΔT)?
Q = mcΔT
Q = m/cΔT
Q = mc/ΔT
Q = mΔTc

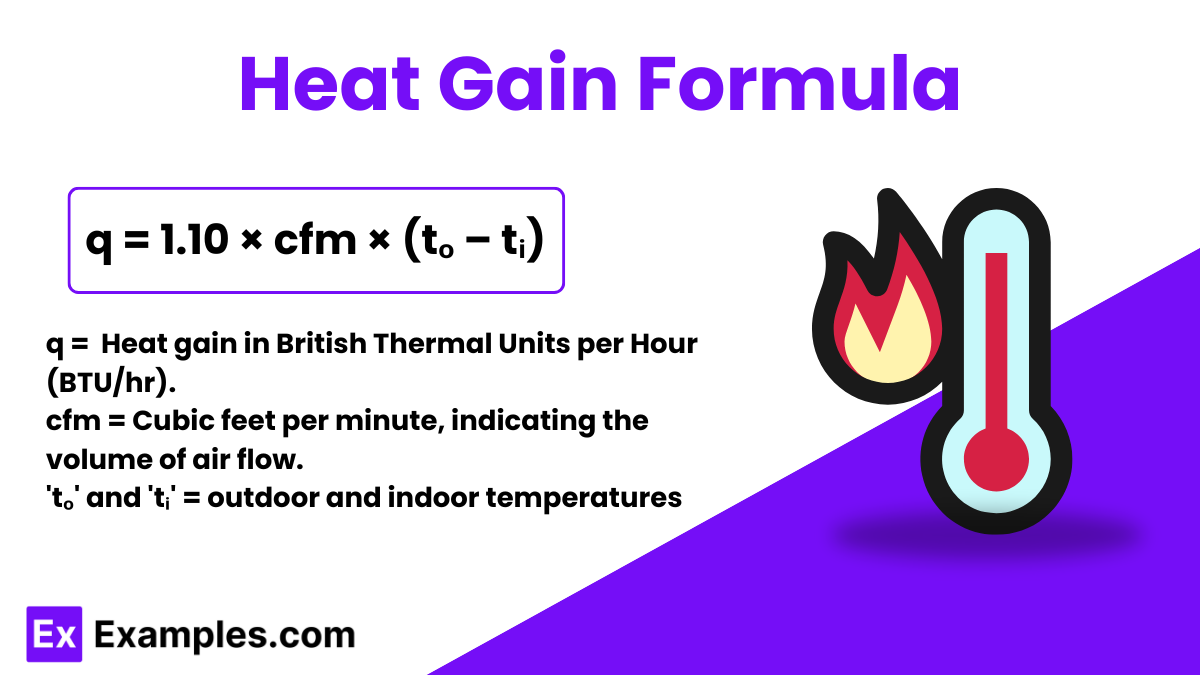
Heat gain refers to the increase in thermal energy of a space due to various external factors like sunlight, electrical appliances, and even the number of people in the room. In simpler terms, it measures how much warmer a room becomes over a period of time due to these influences.
The formula to calculate heat gain is expressed as:
This formula derives from the principle that the energy change in a system (in this case, a room or building) relates directly to the air flow rate and the temperature difference between the indoor and outdoor environments. The constant 1.10 includes the specific heat of air and its density under standard conditions, facilitating the conversion to BTU/hr, which is a unit of power indicating the energy transfer rate.
The concept of measuring and calculating heat gain became prominent with the development of modern heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, although it wasn’t the work of a single discoverer. Instead, it evolved from the basic principles of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics established by pioneers like Lord Kelvin and other scientists in the field of thermodynamics. This formula is particularly useful for engineers and technicians designing and optimizing HVAC systems to ensure comfort and efficiency in buildings.
Problem: Suppose an HVAC system moves air at a rate of 500 cubic feet per minute (cfm). If the outdoor temperature is 95°F and the indoor temperature is 75°F, calculate the heat gain.
Solution: Using the formula: q = 1.10 × cfm × (tₒ – tᵢ)
𝑞=1.10×500×(95−75)
𝑞=1.10×500×20
𝑞=11000 BTU/hrq
Result: The heat gain is 11,000 BTU per hour.
Problem: How does the heat gain change if the airflow increases to 800 cfm under the same temperature conditions as in Example 1?
Solution: Using the formula: q = 1.10 × cfm × (tₒ – tᵢ)
𝑞=1.10×800×(95−75)
𝑞=1.10×800×20
𝑞=17600 BTU/hr
Result: The heat gain increases to 17,600 BTU per hour.
Problem: With the airflow rate at 500 cfm, if the indoor temperature is adjusted to 70°F while the outdoor temperature remains 95°F, calculate the new heat gain.
Solution: Using the formula: q = 1.10 × cfm × (tₒ – tᵢ)
𝑞=1.10×500×(95−70)
𝑞=1.10×500×25
𝑞=13750 BTU/hr
Result: The heat gain is 13,750 BTU per hour.
Calculate total heat gain using the formula: 𝑞=1.10×cfm×(𝑡ₒ−𝑡ᵢ), where 𝑞 is in BTU/hr.
The heat gain loss formula adjusts for thermal transfers: 𝑞=U-factor×Area×(𝑡ₒ−𝑡ᵢ).
To calculate heat gain through walls, use: 𝑞=U-value×Area×(𝑡ₒ−𝑡ᵢ), where q measures in BTU/hr.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating heat gain (Q) in terms of mass (m), specific heat capacity (c), and temperature change (ΔT)?
Q = mcΔT
Q = m/cΔT
Q = mc/ΔT
Q = mΔTc
If a substance has a mass of 10 kg, a specific heat capacity of 2 J/kg°C, and a temperature change of 5°C, what is the heat gain?
50 J
100 J
10 J
200 J
What does the term "specific heat capacity" refer to in the context of heat gain?
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius
The amount of heat lost by a substance
The total heat capacity of a substance
The change in temperature of a substance
Which unit is used to measure heat gain in the International System of Units (SI)?
Calorie
Joule
Watt
Kelvin
If 500 J of heat is added to a 2 kg substance and its temperature rises by 5°C, what is its specific heat capacity?
25 J/kg°C
50 J/kg°C
10 J/kg°C
100 J/kg°C
What is the significance of the heat gain formula Q = mcΔT in thermal physics?
It describes the energy required to change the state of a substance
It calculates the total energy content of a substance
It quantifies the heat energy absorbed or released by a substance as it undergoes a temperature change
It measures the electrical energy used by a substance
What is the heat gain if 1 kg of water (specific heat capacity = 4.18 J/g°C) is heated from 25°C to 75°C?
2090 J
4180 J
20900 J
41800 J
In the context of heat gain, what does the symbol ΔT represent?
Specific heat capacity
Mass of the substance
Temperature change
Total heat energy
How does the heat gain of a substance change if its mass is halved while keeping the specific heat capacity and temperature change constant?
It remains the same
It doubles
It is halved
It becomes zero
In what unit is specific heat capacity commonly measured?
J/kg
J/g°C
W/m²
Cal/g
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

