What does Huygens' Principle state about every point on a wavefront?
It is a source of secondary waves
It reflects waves
It absorbs waves
It refracts waves


Huygens’ Principle is a fundamental concept in the field of wave theory in physics. Proposed by the Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens in 1678, this principle provides a method to understand the propagation of wavefronts.
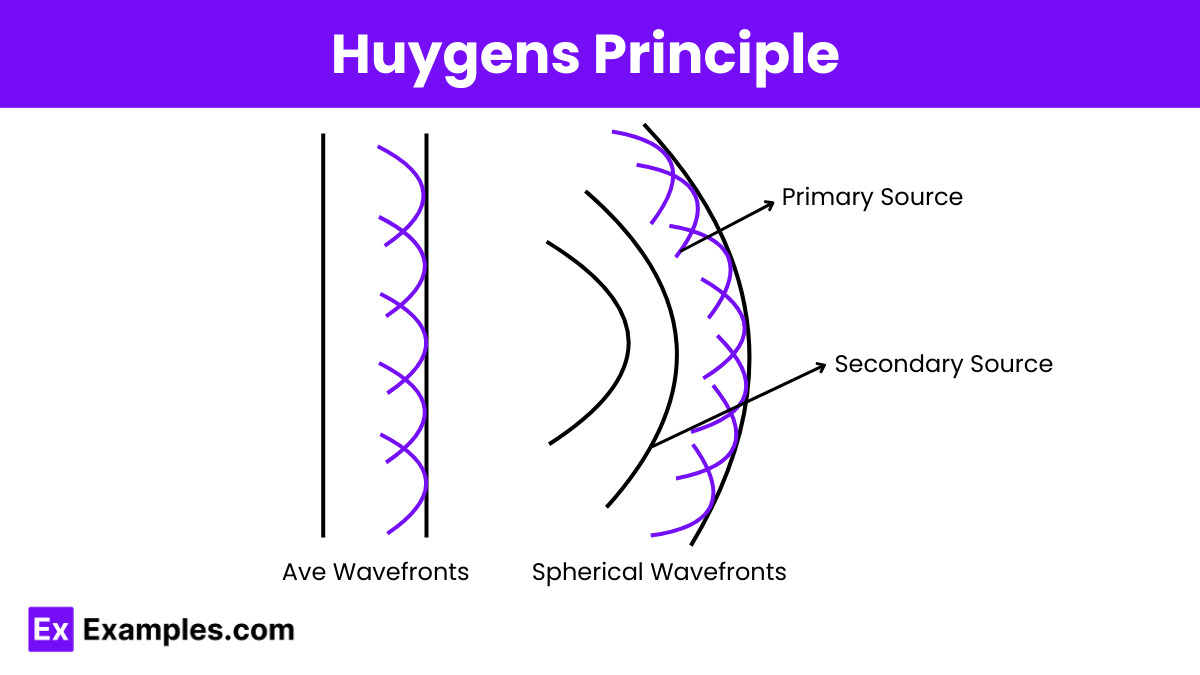
Huygens’ Principle states that “Every point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary spherical wavelets, and the wavefront at any subsequent time is the envelope of these secondary wavelets.“
Huygens proposed that light behaves as a wave propagating through space, much like ripples in water or sound waves in air. Therefore, light spreads out from a source in all directions. The path traced by points that have moved a certain distance in a given time interval is known as a wavefront. Thus, from a point light source, the path traced by light over a fixed time period forms a sphere (or a circle if considered in 2D).
After the initial wavefront is formed, secondary wavefronts arise from each point on the primary wavefront. Additionally, every point on the primary wavefront serves as a secondary source of light, emitting further wavefronts. Consequently, a light wave propagates by generating secondary sources and wavefronts. The overall wavefront is formed tangentially to all the secondary wavefronts created by these secondary sources, as illustrated in the figure. The direction of wave propagation is always perpendicular to the wavefronts.
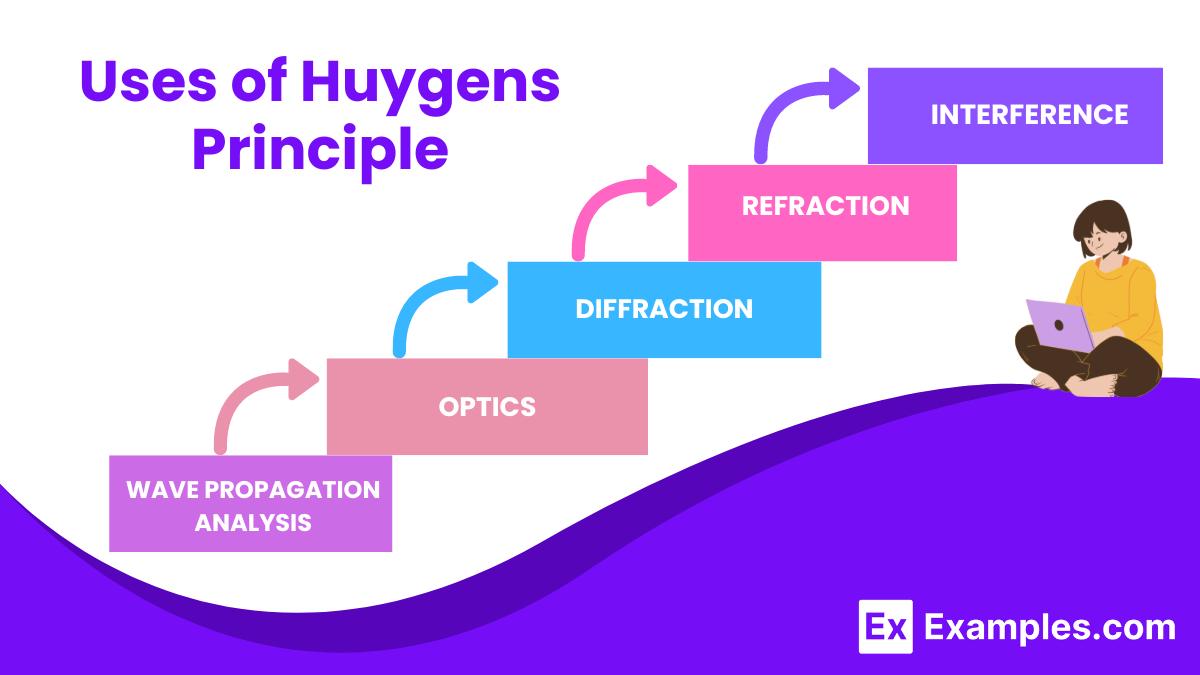
Huygens’ principle effectively explains various wave phenomena, such as diffraction, interference, reflection, and refraction. Despite being proposed centuries ago, it remains relevant to modern wave theory, explaining how light waves interact with different mediums and obstacles.
Huygens’ Principle is a key concept in wave theory that provides a comprehensive understanding of wave propagation and phenomena such as diffraction. Proposed by the Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens in 1678, this principle is fundamental in explaining how waves travel and interact with obstacles.
Huygens’ Principle states that every point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary spherical wavelets, and the new wavefront at any subsequent time is the envelope of these secondary wavelets.
Huygens’ Principle is instrumental in understanding diffraction. It explains how waves bend around obstacles and through slits by considering each point on a wavefront as a source of secondary wavelets. The constructive and destructive interference of these wavelets results in the characteristic diffraction patterns observed in experiments.

Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens proposed Huygens’ Principle in 1678.
The principle explains wave propagation by treating each point on a wavefront as a source of secondary wavelets that combine to form the new wavefront.
A wavefront is a surface over which an oscillation or wave has a constant phase.
Huygens’ Principle applies to light waves by describing how light spreads and bends around obstacles and through apertures.
Yes, Huygens’ Principle explains reflection by showing how secondary wavelets from a wavefront reflect off a surface to form a new wavefront.
Huygens’ Principle is crucial in understanding wave phenomena like interference, diffraction, and the behavior of light.
Huygens’ Principle explains diffraction by showing how secondary wavelets bend around edges and openings, forming new wavefronts.
Secondary wavelets are spherical waves that originate from points on a wavefront, spreading out in all directions.
The principle helps understand interference by showing how secondary wavelets from different wavefronts can constructively or destructively combine.
Huygens’ Principle focuses on wavefronts and secondary wavelets, while Fermat’s Principle states that light takes the path of least time.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does Huygens' Principle state about every point on a wavefront?
It is a source of secondary waves
It reflects waves
It absorbs waves
It refracts waves
Which phenomenon can be explained using Huygens\' Principle?
Reflection
Refraction
Diffraction
All of the above
How does Huygens' Principle explain the bending of waves around obstacles?
By reflection of waves
By the creation of new wavelets at the obstacle edge
By increasing wave speed
By absorption of waves
What is the shape of the wavelets produced according to Huygens' Principle?
Linear
Spherical
Elliptical
Cylindrical
How does Huygens' Principle help in understanding the law of reflection?
By considering the wavelets reflected at different angles
By considering the wavelets refracted at different angles
By considering the wavelets absorbed by the surface
By considering the wavelets scattered randomly
Which scientist is credited with formulating Huygens' Principle?
Isaac Newton
Albert Einstein
Christiaan Huygens
James Clerk Maxwell
How does Huygens' Principle explain refraction at the boundary between two media?
By bending the wavelets towards the normal
By bending the wavelets away from the normal
By changing the speed of the wavelets in the second medium
By stopping the wavelets at the boundary
According to Huygens' Principle, what happens to the wavelets when a wave passes through a narrow slit?
They stop
They spread out
They get absorbed
They speed up
What role do secondary wavelets play in the propagation of waves according to Huygens' Principle?
They slow down the wave
They maintain the wavefront's shape
They stop the wave
They increase the wave's amplitude
Which wave property is directly explained by Huygens' Principle?
Amplitude
Wavelength
Wavefront
Frequency
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

