What is the formula for calculating speed?
Speed = Distance × Time
Speed = Distance/Time
Speed = Time × Acceleration
Speed = Time/Distance

Measurement is a key concept in science. We measure various quantities using base or fundamental physical units. Speed is one of these quantities. It calculates how far an object travels over a certain period. This session will focus on understanding speed in more detail, including its physics and units.
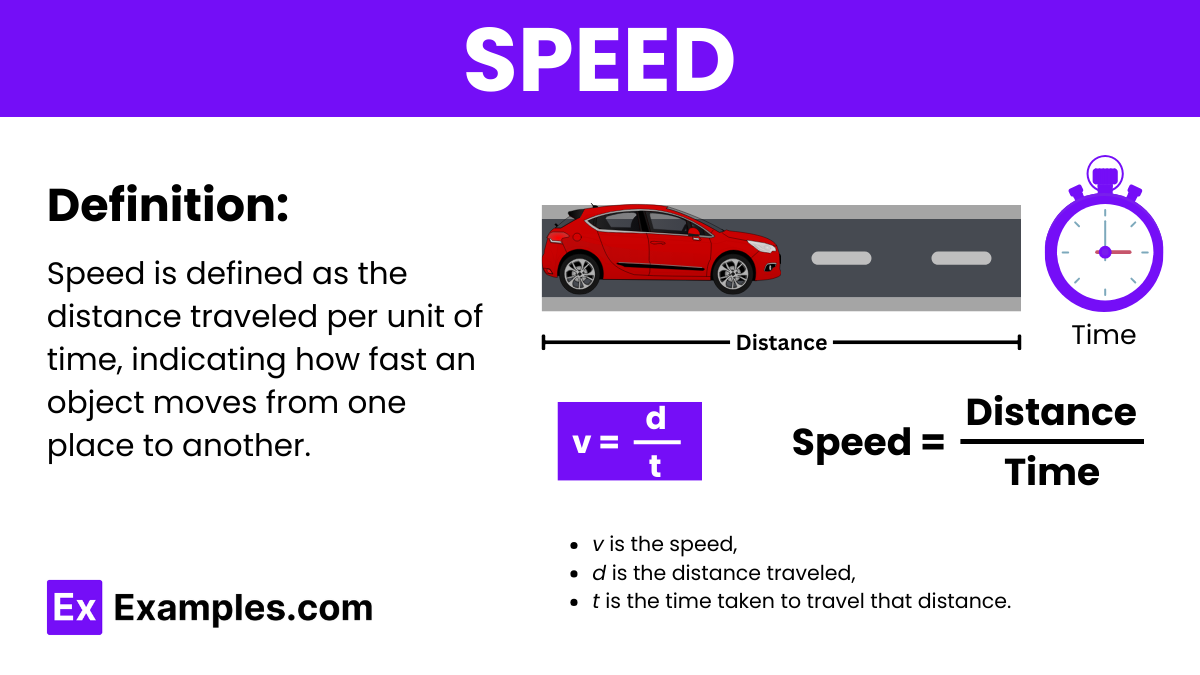
Speed is defined as the rate at which an object covers distance. It measures how quickly something is moving from one place to another, typically expressed in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
Speed is a fundamental concept in physics, represented by the symbol v. The formula to calculate speed is:
Where:
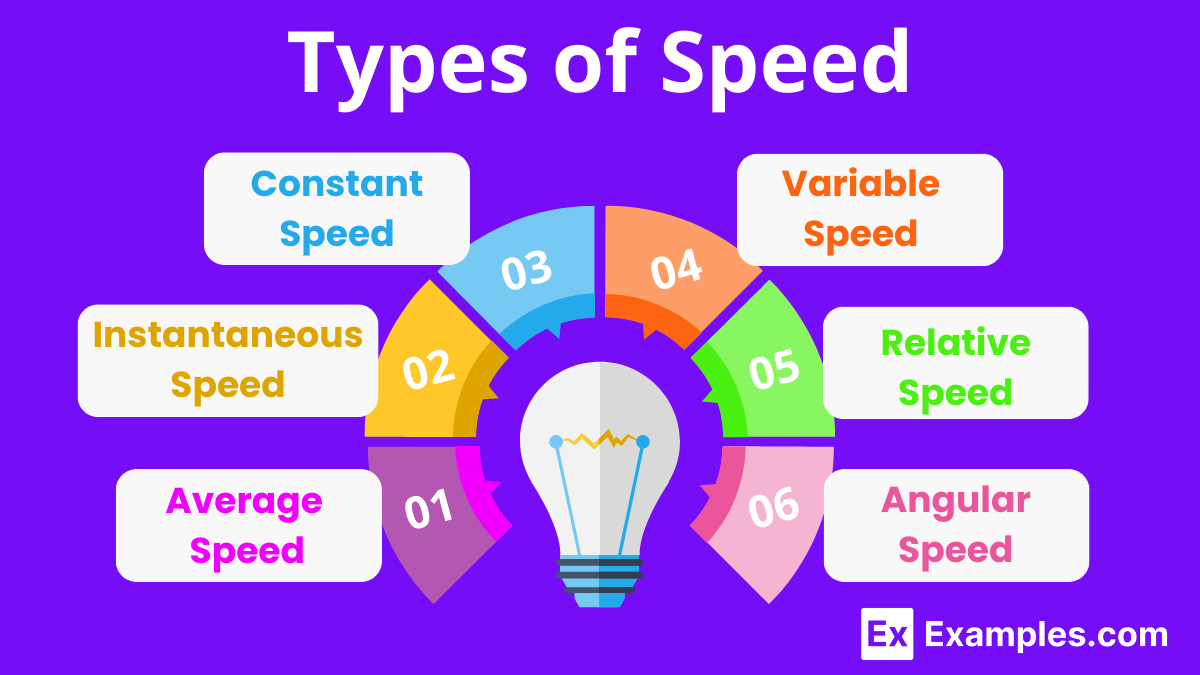
Average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken to travel that distance. It is a useful measurement when assessing the overall rate of travel over a journey that may include varying speeds. For example, if you drive 100 kilometers in 2 hours, including stops and starts, your average speed is 50 kilometers per hour.
Instantaneous speed measures the speed of an object at a specific instant. It is often recorded using speedometers in vehicles, which show the speed at any given moment. This type of speed is crucial for understanding dynamic conditions, such as a car’s speed as it maneuvers around a curve or when adjusting for road conditions.
Constant speed occurs when an object moves at a steady rate with no changes in velocity — no acceleration or deceleration. An example of constant speed is a clock’s second hand which moves at a consistent pace around the clock face. Constant speed is rare in everyday situations because external factors often cause speed to vary.
Variable speed describes an object whose speed changes over time. This can involve acceleration (speeding up) or deceleration (slowing down). Variable speed is commonly seen in vehicles navigating through traffic or during athletic activities, like running a race where speed may vary dramatically based on the racer’s strategy and endurance.
Relative speed considers the speed of one object in relation to another. It is particularly relevant when objects are moving in different directions or at different speeds. For example, if two trains move towards each other, each at a speed of 60 km/h, their relative speed is the sum of their speeds, which is 120 km/h. This concept is critical in scenarios like avoiding collisions or in sports where players move towards or away from each other.
Angular speed is used in scenarios involving rotational motion and describes how quickly an object spins around an axis. It’s typically expressed in radians per second or revolutions per minute. Angular speed is crucial in engineering applications involving gears, turbines, and engines, as well as in observing celestial objects in astronomy. For example, the angular speed of Earth’s rotation can be described as about 0.0000727 radians per second, equating to approximately 360 degrees per 24 hours (a full rotation each day).
Speed measures how fast an object moves. The SI unit of speed is meters per second (m/s).
Speed is a scalar quantity indicating how fast an object moves, while velocity is a vector, including direction and magnitude.
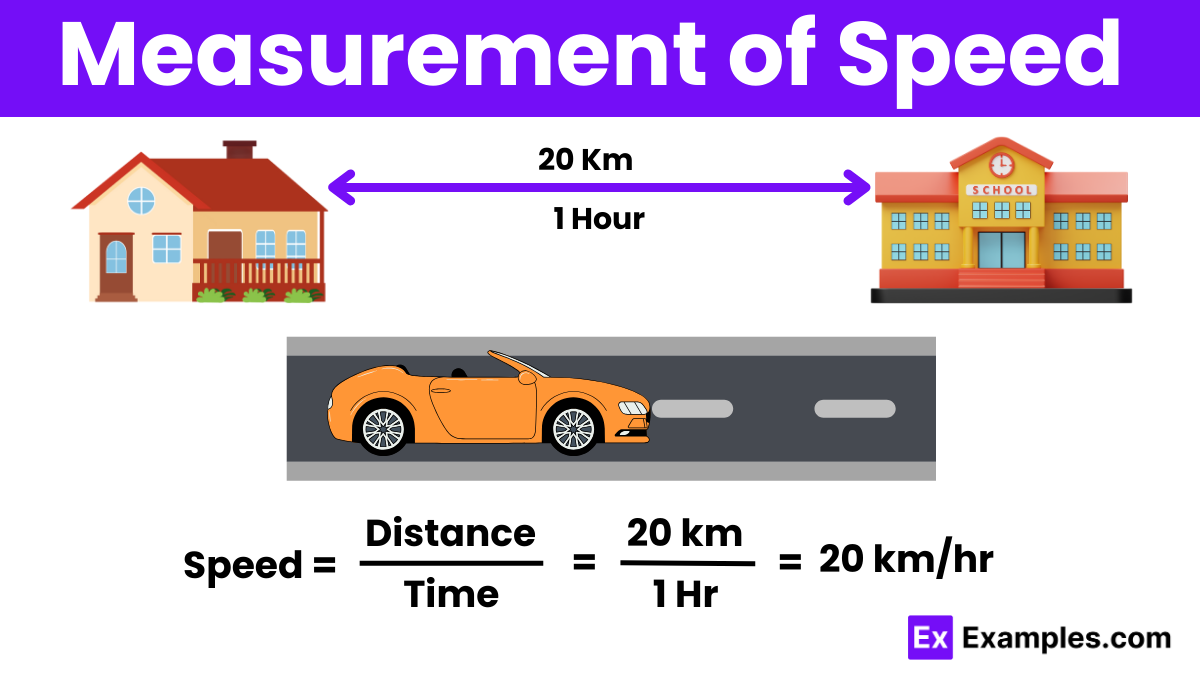
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance.
Speed equals the distance traveled divided by the time it takes (speed = distance/time).
In physics, velocity refers to speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity, whereas speed is scalar.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating speed?
Speed = Distance × Time
Speed = Distance/Time
Speed = Time × Acceleration
Speed = Time/Distance
If a car travels 150 kilometers in 3 hours, what is its average speed?
25 km/h
50 km/h
75 km/h
100 km/h
Which unit is commonly used to measure speed in the metric system?
Miles per hour
Feet per second
Meters per second
Kilometers
A runner completes a 400-meter race in 50 seconds. What is their average speed?
6 m/s
7 m/s
8 m/s
9 m/s
If an object moves at a constant speed, what can be said about the distance it travels over equal time intervals?
It travels different distances
It travels the same distance
It travels less distance
It travels more distance
A cyclist covers a distance of 30 kilometers in 2 hours. What is their speed in meters per second?
4.17 m/s
5.83 m/s
6.25 m/s
7.50 m/s
Which of the following statements is true about speed and velocity?
Speed has direction, velocity does not
Velocity has direction, speed does not
Both speed and velocity have direction
Neither speed nor velocity have direction
What is the average speed of an object that travels 100 meters in 20 seconds?
2 m/s
4 m/s
5 m/s
10 m/s
If a boat travels at 8 m/s and covers a distance of 400 meters, how long did the journey take?
40 seconds
50 seconds
60 seconds
80 seconds
A person walks at a speed of 5 km/h. How far can they walk in 3 hours?
10 km
15 km
20 km
25 km
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

