What is the formula for linear speed in terms of distance and time?
v = d/t
v = t/d
v = d*t
v = 2d/t
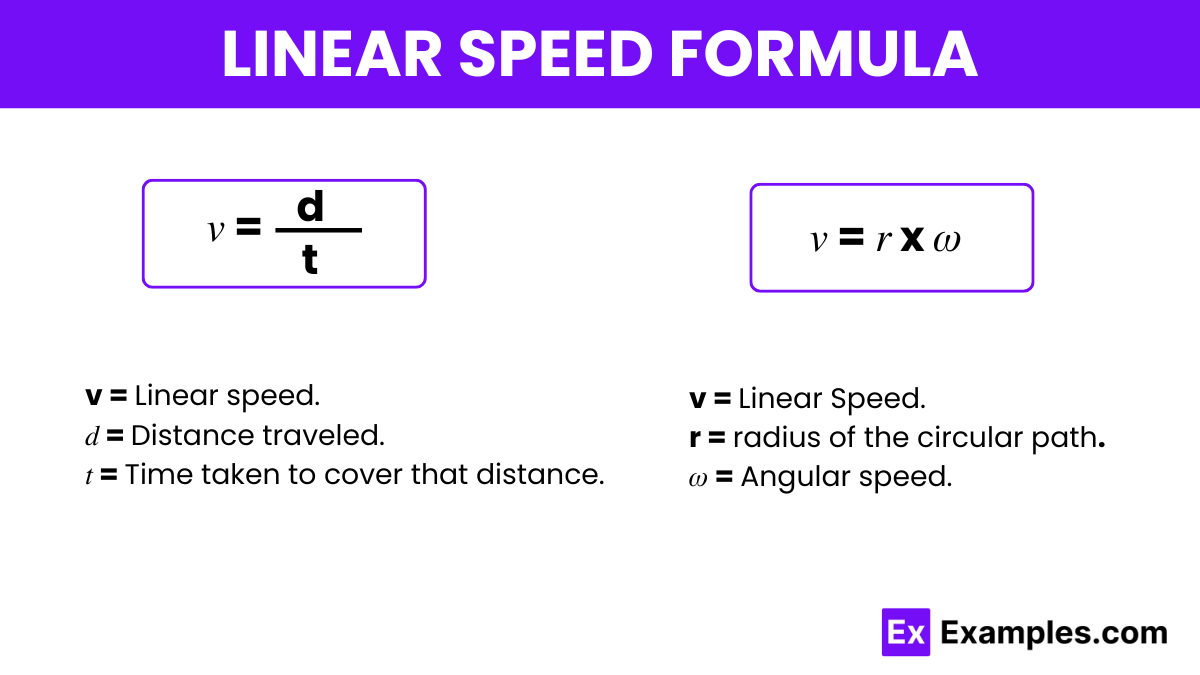
Linear speed, often simply referred to as speed, is a measure of the distance traveled per unit of time by an object moving along a straight or curved path. In physics, the linear speed formula is crucial for understanding how objects move in space. The formula for linear speed (𝑣) is expressed as
The relationship between linear speed and angular speed also forms an integral part of kinematics in physics. Linear Speed Formula, in the sense of angular speed, is articulated as
This formula highlights how the linear speed increases with both the radius of the path and the rate at which an object moves around the path. This specific articulation was developed from the broader understanding of motion and kinematics, dating back to the foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton and other key figures in classical mechanics.
Question: A car travels a distance of 150 kilometers in 3 hours. What is the average speed of the car?
Solution: To find the average speed, use the formula: 𝑣=𝑑 / 𝑡 Where:
Substitute the values into the formula: 𝑣=150 km / 3 hours=50 km/hour
Answer: The average speed of the car is 50 km/hour.
Question: A bicycle rides along a circular track with a radius of 30 meters. If the rider completes one full circle in 2 minutes, what is the linear speed of the bicycle?
Solution: First, convert the time from minutes to seconds: 𝑡 = 2 minutes = 120 seconds
Calculate the circumference of the circle, which is the distance traveled:
𝑑 = 2𝜋 x 𝑟=2𝜋 x (30) = 60𝜋 meters
Now, use the linear speed formula:
𝑣 = 𝑑 / 𝑡 = 60𝜋 meters / 120 seconds=𝜋 / 2 meters/second
Answer: The linear speed of the bicycle is 𝜋 / 2 meters/second, approximately 1.57 meters/second.
Question: A wheel rotates at an angular speed of 100 radians per minute. If the radius of the wheel is 0.5 meters, what is the linear speed at the rim of the wheel?
Solution: First, convert the angular speed from radians per minute to radians per second: 𝜔=100 radians/minute=100 / 60 radians/second
Now, use the formula connecting linear speed and angular speed:
𝑣=𝑟𝜔=0.5 × (100 / 60) = 50 / 60 meters/second
Simplify: 𝑣 = 25 / 30 meters/second ≈ 0.83 meters/second
Answer: The linear speed at the rim of the wheel is approximately 0.83 meters/second.
Calculate linear speed with the formula 𝑣=𝑑t, where 𝑑 is distance and 𝑡 is time.
In trigonometric terms, we express linear speed 𝑣v as 𝑣=𝑟𝜔, linking the radius r with the angular speed ω.
Yes, linear speed refers to the magnitude of velocity, indicating how fast an object travels along a path.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for linear speed in terms of distance and time?
v = d/t
v = t/d
v = d*t
v = 2d/t
If a car travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours, what is its linear speed?
25 km/h
50 km/h
75 km/h
100 km/h
What is the unit of linear speed in the International System of Units (SI)?
meters per second (m/s)
kilometers per hour (km/h)
miles per hour (mph)
feet per second (ft/s)
How does increasing the distance affect the linear speed, assuming the time remains constant?
Linear speed decreases
Linear speed remains the same
Linear speed increases
Linear speed becomes zero
What is the linear speed of an object that covers 60 meters in 3 seconds?
15 m/s
10 m/s
20 m/s
5 m/s
If the time taken to cover a certain distance is halved, how does the linear speed change?
It is halved
It remains the same
It doubles
It quadruples
Which of the following correctly defines linear speed?
The rate at which an object changes its position
The total distance traveled by an object
The time taken by an object to travel a certain distance
The acceleration of an object
How does the linear speed change if both the distance and time are doubled?
It remains the same
It doubles
It halves
It quadruples
What is the formula for linear speed in terms of angular speed (ω) and radius (r)?
v = ωr
v = ω/r
v = r/ω
v = ωr²
If an object has an angular speed of 2 rad/s and a radius of 3 meters, what is its linear speed?
6 m/s
3 m/s
2 m/s
5 m/s
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

