What is the primary source of natural light energy on Earth?
Stars
The Moon
Artificial Lights
Fire

Light energy, also known as radiant energy, is a form of energy that is visible to the human eye and is emitted by sources such as the sun, light bulbs, and lasers. It travels in waves and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes other types of waves such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. It often interacts with other forms of energy, such as electrical energy in solar panels and chemical energy in photosynthesis and various light-emitting reactions.
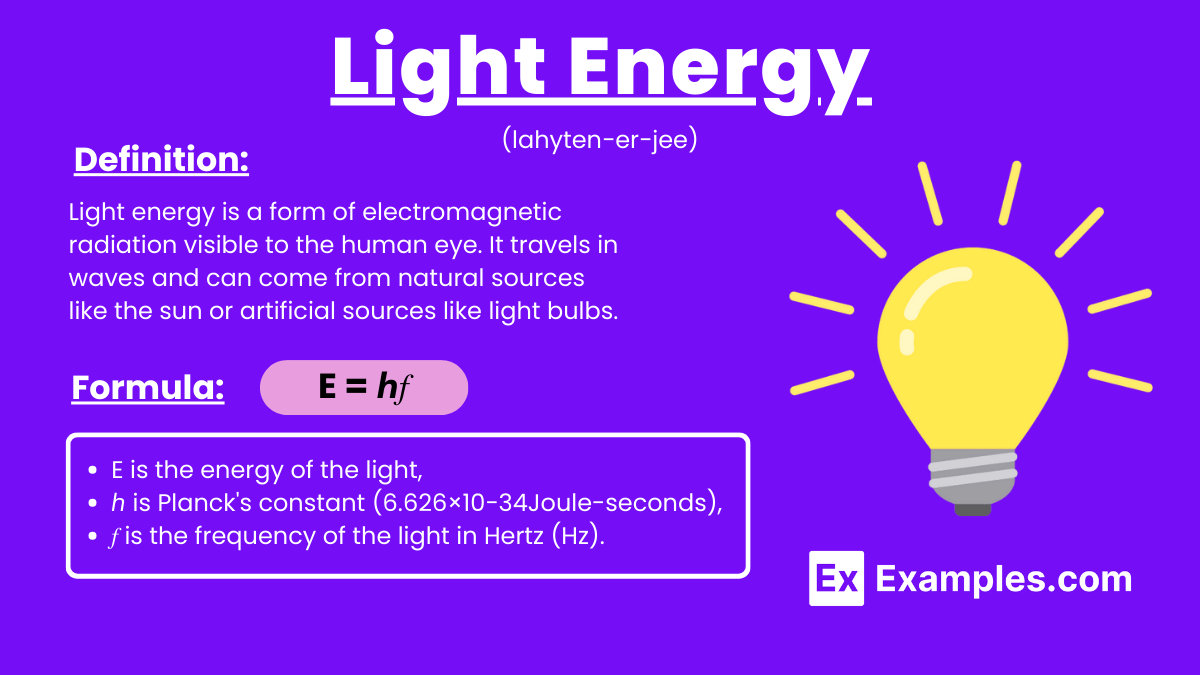
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye. It travels in waves and can come from natural sources like the sun or artificial sources like light bulbs. This energy is essential for processes like photosynthesis and vision.
The formula for light energy is derived from the relationship between energy (E), Planck’s constant (h), and the frequency of light (f):
E is the energy of the light,
ℎ is Planck’s constant (6.626×10−34Joule-seconds),
𝑓 is the frequency of the light in Hertz (Hz).
| Unit | Symbol | Description | Context of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Joules | J | Standard unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI) | Measuring total energy |
| Electron Volts | eV | Unit of energy often used in atomic and particle physics | Measuring photon energy |

Light energy, also known as electromagnetic radiation, comes in various forms. Each type of light energy has unique properties and applications. Here are the main types:
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. It consists of a range of colors, each with a different wavelength, from red (longest wavelength) to violet (shortest wavelength). Applications include:
Vision: Enabling humans and animals to see.
Lighting: Used in homes, streets, and vehicles.
Communication: Fiber optic cables use visible light for data transmission.
Infrared radiation has longer wavelengths than visible light and is experienced as heat. It’s divided into near, mid, and far-infrared.
Remote Controls: Used in TVs and other electronic devices.
Thermal Imaging: Used in night-vision equipment and medical diagnostics.
Heating: Infrared heaters are used in saunas and industrial processes.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation has shorter wavelengths than visible light. It is divided into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
Sterilization: UV light kills bacteria and viruses.
Tanning: UV light causes skin tanning and can lead to sunburn.
Fluorescent Lamps: Used in lighting and insect traps.
X-rays have even shorter wavelengths and higher energy than UV rays. They are divided into soft X-rays and hard X-rays.
Medical Imaging: Used to view inside the human body, such as in X-ray machines.
Security: Used in airport security scanners.
Industrial Inspection: Used to inspect the integrity of materials and structures.
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and the highest energy of all types of light energy.
Medical Treatment: Used in cancer treatment through radiation therapy.
Astronomy: Used to observe celestial phenomena.
Sterilization: Used to sterilize medical equipment and food products.
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are divided into different bands such as AM, FM, and microwaves.
Communication: Used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, and Wi-Fi.
Radar: Used in navigation, weather forecasting, and speed detection.
MRI Scans: Used in medical imaging to produce detailed images of the body.
Microwaves are a subset of radio waves with shorter wavelengths.
Cooking: Used in microwave ovens to heat food.
Communication: Used in satellite and mobile phone networks.
Radar Technology: Used in radar guns and weather radar systems.
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy. This process is essential for the production of oxygen and glucose, which are vital for the survival of most life forms on Earth.
Light energy enables vision in humans and animals. The human eye captures light and converts it into electrical signals that are processed by the brain, allowing us to see the world around us.
Solar power harnesses light energy from the sun to generate electricity. Solar panels made of photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electrical energy, providing a renewable and eco-friendly energy source.
Light energy is used in various medical applications, including:
Light energy is used in fiber optic communications, where light pulses transmit data over long distances with high speed and minimal loss. This technology is the backbone of the internet and telecommunication networks.
Photography relies on light to capture images. Digital cameras and imaging devices convert light into electronic signals to produce pictures. Imaging techniques like X-rays and MRIs also use light energy to visualize the inside of the human body.
Light travels in straight lines as electromagnetic waves. It can move through a vacuum, air, and various media like water and glass.
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s), or about 186,282 miles per second (mi/s).
The Sun is the primary source of natural light energy. Other sources include stars, fire, and artificial lights like bulbs and LEDs.
Natural light comes from the Sun and stars, while artificial light is produced by human-made devices such as light bulbs and LEDs.
Light can be reflected, refracted, absorbed, or transmitted depending on the material it encounters. For example, mirrors reflect light, and lenses refract it.
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, changing its speed. This is why objects appear bent in water.
Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, as seen in mirrors.
We see different colors because objects absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect others. The reflected light determines the color we perceive.
White light is a mixture of all visible wavelengths of light. When passed through a prism, it splits into the colors of the rainbow.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays, including visible light.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary source of natural light energy on Earth?
Stars
The Moon
Artificial Lights
Fire
Which type of light is used in fiber optic communication?
Infrared Light
Ultraviolet Light
Visible Light
X-rays
How does the speed of light in a vacuum compare to its speed in water?
Faster in water
Slower in water
The same in both
Depends on the type of water
What phenomenon occurs when light changes direction as it passes from air into water?
Reflection
Diffraction
Refraction
Polarization
What is the name of the effect where light is bent around objects?
Reflection
Refraction
Diffraction
Absorption
Which color of light has the shortest wavelength?
Red
Green
Blue
Violet
What is the primary reason for the blue color of the sky?
Reflection of the ocean
Scattering of blue light by the atmosphere
Absorption of other colors
Presence of blue pigments
Which device is used to split white light into its component colors?
Prism
Lens
Mirror
Filter
What is the name of the effect where light is absorbed and transformed into heat?
Transmission
Reflection
Absorption
Scattering
Which of the following is true about laser light?
It is incoherent
It is diffused
It has a single wavelength
It scatters in all directions
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

