What is the formula for calculating the buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid?
F = ρVg
F = mg
F = ρgh
F = Vg

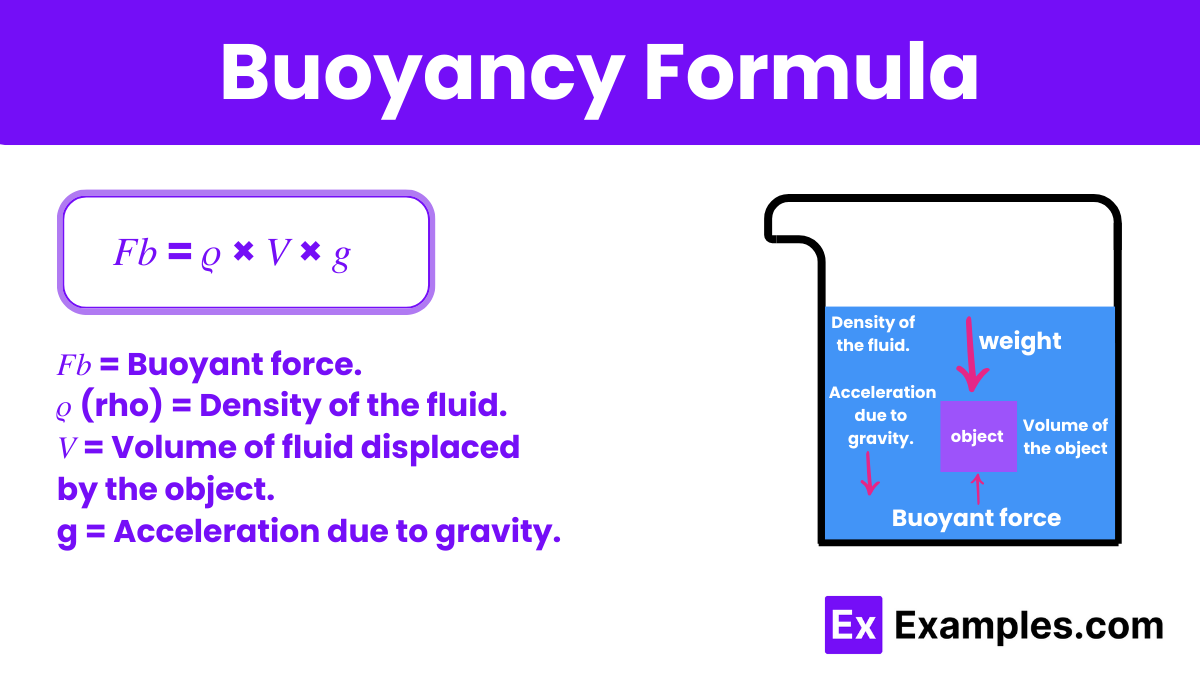
Buoyancy, a fundamental concept in physics, refers to the upward force that a fluid exerts on an object that is partially or wholly immersed in it. This force is crucial for understanding why objects float or sink in water or any other fluid. The formula to calculate buoyancy, also known as the buoyant force, is straightforward and embodies the principle that the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces. Mathematically, it is represented as
The concept and the accompanying formula were first rigorously documented by the ancient Greek scientist Archimedes, making it one of the earliest documented principles in classical physics. His discovery not only laid the groundwork for the study of fluid dynamics but also has practical applications in designing ships and submarines, understanding the behavior of floating and submerged objects, and in various engineering tasks involving fluids.
Problem: A wooden block with a volume of 0.05 m³ is submerged in water. Given that the density of water is 1000 kg/m³, calculate the buoyant force acting on the block.
Solution:
Problem: A metal cylinder weighs 800 N and displaces water weighing 600 N when completely submerged. Calculate the volume of the cylinder using the buoyancy formula.
Solution:
Problem: A lifebuoy has a density of 200 kg/m³ and a volume of 0.15 m³. Determine if it will float in seawater with a density of 1025 kg/m³.
Solution:
Problem: A cube with a side of 0.1 m and a density of 800 kg/m³ is submerged in glycerin (density = 1260 kg/m³). Calculate the buoyant force.
Solution:
To calculate buoyancy, use the formula 𝐹𝑏=𝜌×𝑉×𝑔, where 𝜌 is fluid density, V is displaced volume, and g is gravity.
In the buoyancy formula, “P” typically does not appear; the primary variables are ρ (density), V (volume), and g (gravity).
The basic rule of buoyancy states that an object will float if it displaces a weight of fluid equal to or greater than its own weight.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the formula for calculating the buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid?
F = ρVg
F = mg
F = ρgh
F = Vg
If the density of water is 1000 kg/m³, what is the buoyant force acting on a 0.5 m³ object fully submerged in water?
4900 N
5000 N
4500 N
5200 N
How does the buoyant force change if the volume of the submerged object is doubled while keeping the fluid density and gravity constant?
It remains the same
It doubles
It triples
It halves
What happens to the buoyant force if an object is partially submerged compared to being fully submerged?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
Which principle explains the buoyant force on a submerged object?
Bernoulli's Principle
Pascal's Principle
Archimedes' Principle
Newton's Third Law
What is the buoyant force on an object with a volume of 2 m³ submerged in a fluid with a density of 800 kg/m³?
15680 N
12800 N
16000 N
19600 N
How does the density of the fluid affect the buoyant force on a submerged object?
The buoyant force is independent of the fluid density
The buoyant force decreases with increasing fluid density
The buoyant force increases with increasing fluid density
The buoyant force becomes zero in a denser fluid
What is the unit of buoyant force in the International System of Units (SI)?
Newton
Joule
Pascal
Kilogram
If the acceleration due to gravity on a different planet is 15 m/s², what is the buoyant force on a 3 m³ object submerged in a fluid with a density of 500 kg/m³?
22500 N
30000 N
37500 N
40000 N
How is the buoyant force affected if an object is submerged in oil (density 900 kg/m³) compared to water (density 1000 kg/m³)?
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
It becomes zero
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

