What does the term "Megahertz" (MHz) measure?
Voltage
Frequency
Resistance
Power

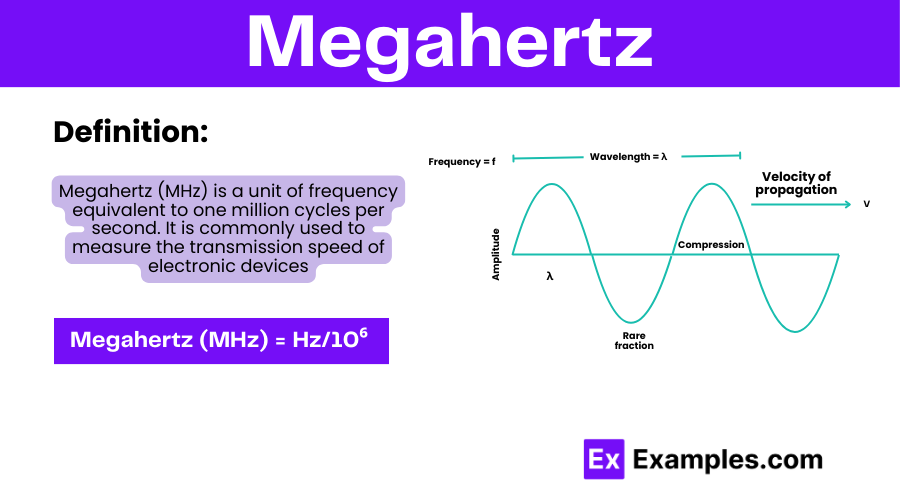
Megahertz (MHz) is a unit of frequency measurement that is commonly used to describe the speed or frequency of electronic devices, such as processors and radio wave transmissions. The term “megahertz” means one million cycles per second.
Megahertz (MHz ) = Hz/10⁶
Wavelength and Frequency Relation:
Where:
. λ is the wavelength (in meters),
. c is the speed of light in vacuum (approximately 3×10⁸ meters/second),
. f is the frequency in hertz (Hz).
For frequency in megahertz:λ= 3×10⁸/f×10⁶ meters
Period and Frequency:
As previously mentioned, the period T of a wave, which is the time for one complete cycle, is the inverse of the frequency:
Where f is in hertz.
For frequency in megahertz:
T= 1/f×10⁶ seconds
Energy of a Photon (in the context of electromagnetic waves):
Where:
. E is the energy of the photon (in joules),
. ℎ is Planck’s constant (6.626×10⁻³⁴ joule-seconds),
. f is the frequency in hertz.
. For frequency in megahertz: E=h×(f×10⁶ )
| Submultiple Value | SI Symbol | Sub Name | Multiple Value | SI Symbol | Multiple Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10⁻³⁶ (MHz) | qHz | Quectohertz | 10²⁴ (MHz) | QHz | Quettahertz |
| 10⁻³³ (MHz) | rHz | Rontohertz | 10²¹ (MHz) | RHz | Ronnahertz |
| 10⁻³⁰ (MHz) | yHz | Yoctohertz | 10¹⁸ (MHz) | YHz | Yottahertz |
| 10⁻²⁷ (MHz) | zHz | Zeptohertz | 10¹⁵ (MHz) | ZHz | Zettahertz |
| 10⁻²⁴ (MHz) | aHz | Attohertz | 10¹² (MHz) | EHz | Exahertz |
| 10⁻²¹ (MHz) | fHz | Femtohertz | 10¹⁹ (MHz) | PHz | Petahertz |
| 10⁻¹⁸ (MHz) | pHz | Picohertz | 10⁶ (MHz) | THz | Terahertz |
| 10⁻¹⁵ (MHz) | nHz | Nanohertz | 10³ (MHz) | GHz | Gigahertz |
| 10⁻¹² (MHz) | μHz | Microhertz | 11 (MHz) | MHz | Megahertz |
| 10⁻⁹ (MHz) | mHz | Millihertz | 10⁻³ (MHz) | kHz | Kilohertz |
| 10⁻⁸ (MHz) | cHz | Centihertz | 10⁻⁴ (MHz) | hHz | Hectohertz |
| 10⁻⁷ (MHz) | dHz | Decihertz | 10⁻⁵ (MHz) | daHz | Decahertz |
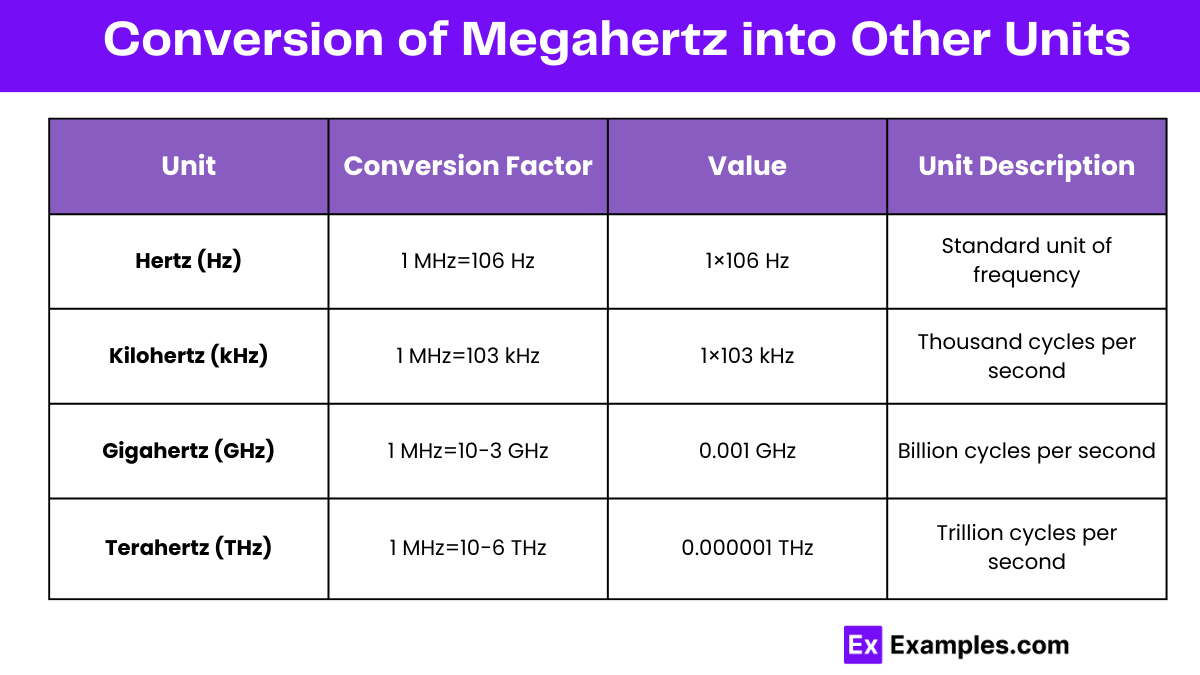
To convert Megahertz (MHz) into other frequency units, you can refer to the table below which displays the conversion of 1 MHz into various units across four columns:
| Unit | Conversion Factor | Value | Unit Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hertz (Hz) | 1 MHz=106 Hz | 1×106 Hz | Standard unit of frequency |
| Kilohertz (kHz) | 1 MHz=103 kHz | 1×103 kHz | Thousand cycles per second |
| Gigahertz (GHz) | 1 MHz=10−3 GHz | 0.001 GHz | Billion cycles per second |
| Terahertz (THz) | 1 MHz=10−6 THz | 0.000001 THz | Trillion cycles per second |
One Megahertz (MHz) equals one million Hertz (Hz). It is a unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) used to measure signal speed.
One Megahertz (MHz) is equivalent to one thousand Kilohertz (kHz). This conversion is used in measuring frequencies, where higher values like MHz are commonly used in radio, telecommunications, and computing to indicate cycles per second at millions or thousands respectively.
The statement “1 Megahertz (MHz) = 0.001 Gigahertz (GHz)” describes the relationship between two units of frequency measurement. One megahertz, which is equivalent to one million hertz, is one thousandth of a gigahertz. This conversion is crucial for understanding frequency scales in various technological contexts.
1 Megahertz (MHz) = 0.000001 Terahertz (THz)” defines the relationship between megahertz and terahertz. One megahertz equals one millionth of a terahertz, illustrating how these units of frequency measurement relate at vastly different scales.
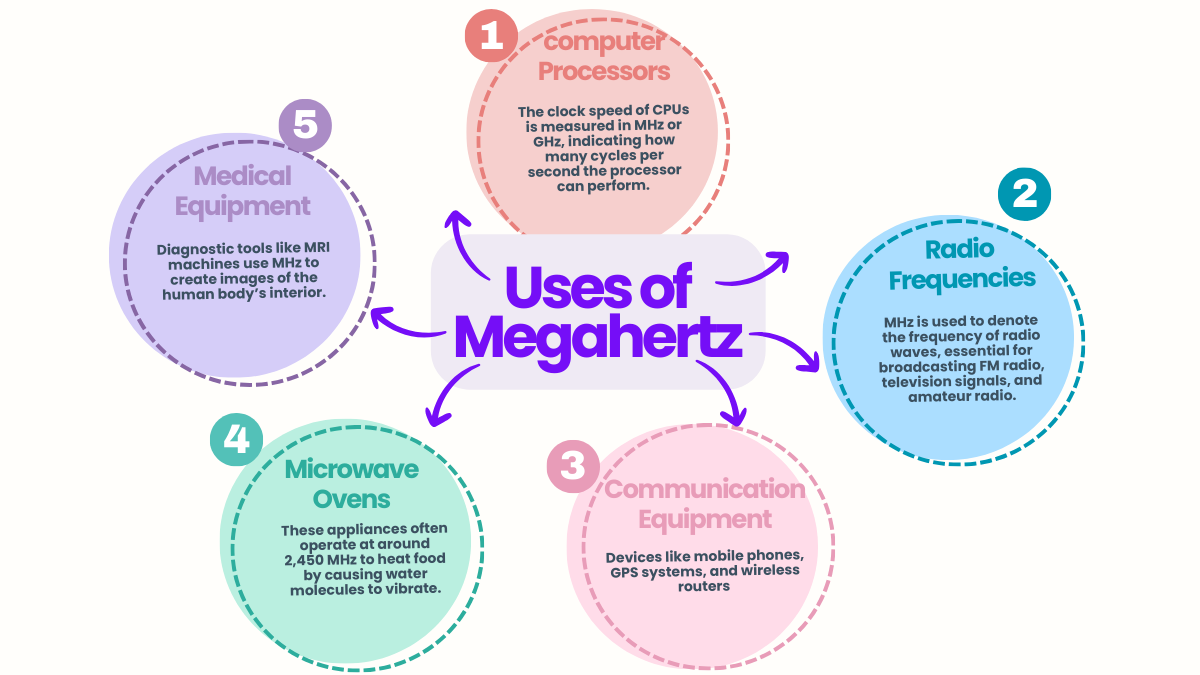
Megahertz (MHz) isn’t a measure of length; it’s a unit of frequency. It indicates the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon, typically used to describe wave frequencies and the speed of electronic devices.
Gigahertz (GHz) is larger than megahertz. One gigahertz equals one thousand megahertz. Gigahertz is commonly used to describe higher frequencies, like those of modern computer processors.
Yes, MHz is often used to measure clock speed in computers and other electronics. Clock speed, measured in MHz, indicates how many cycles per second a computer processor can perform, affecting its overall performance.
1 megahertz means one million cycles per second. It is a frequency unit used to measure the rate at which an electronic device operates or the frequency of electromagnetic waves.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does the term "Megahertz" (MHz) measure?
Voltage
Frequency
Resistance
Power
1 Megahertz (MHz) is equal to how many Hertz (Hz)?
10³ Hz
10⁴ Hz
10⁵ Hz
10⁶ Hz
Which device commonly operates in the range of Megahertz frequencies?
Microwave oven
Light bulb
Radio transmitter
Electric motor
If a signal has a frequency of 2000 kHz, what is its frequency in MHz?
0.2 MHz
2 MHz
20 MHz
200 MHz
Which of the following frequencies is higher?
500 kHz
1 MHz
1500 kHz
2000 Hz
What is the frequency of a signal with 5 million cycles per second?
5 kHz
5 MHz
50 MHz
500 MHz
Which band of the electromagnetic spectrum includes frequencies in the Megahertz range?
Visible light
X-rays
Radio waves
Gamma rays
A processor operates at 3 GHz. How many MHz is this?
300 MHz
3000 MHz
30,000 MHz
300,000 MHz
In the context of digital communication, what does a higher frequency in MHz typically allow for?
Higher data transmission speed
Lower power consumption
Increased signal range
Improved signal clarity
Which of the following frequencies is equivalent to 2.5 MHz?
2500 Hz
25,000 Hz
250,000 Hz
2,500,000 Hz
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

