What does the Wiedemann-Franz Law relate?
Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity
Heat capacity and temperature
Voltage and current
Magnetic field and electric field

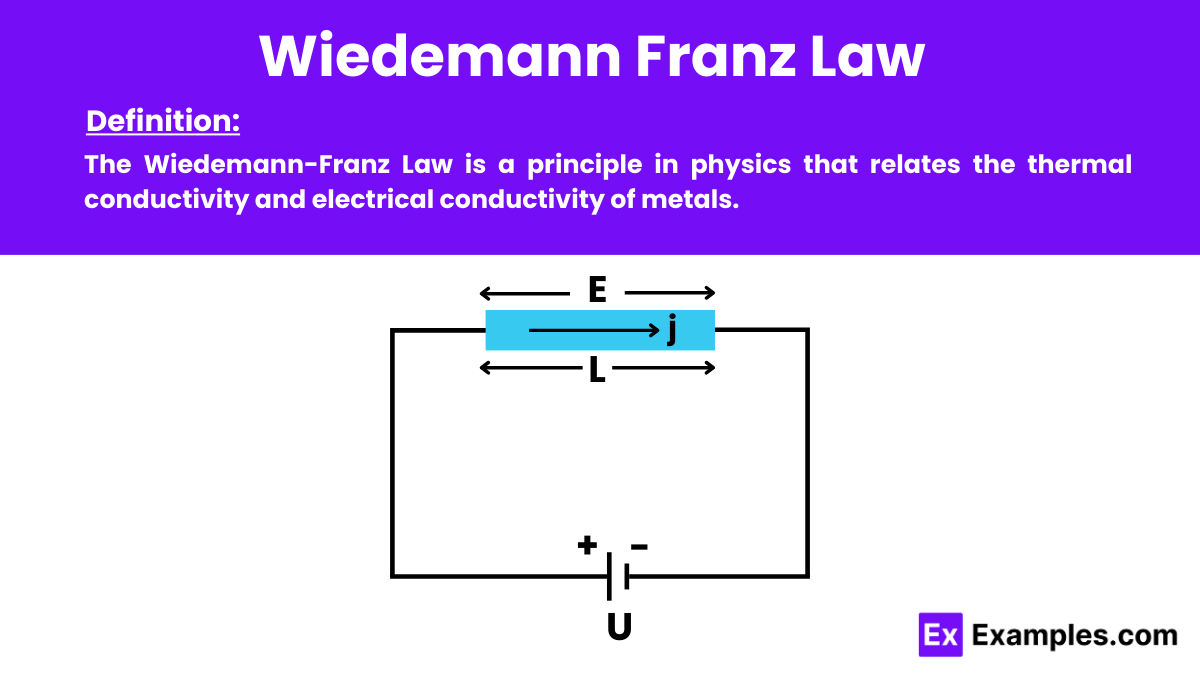
Wiedemann-Franz Law is a principle in physics that establishes a relationship between the thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity of metals. It states that the ratio of thermal conductivity (𝑘) to electrical conductivity (𝜎) is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (𝑇) of the metal.
The formula for the Wiedemann-Franz Law is:
where:
This formula demonstrates that the ratio of thermal conductivity to electrical conductivity is proportional to the temperature of the metal, with the constant 𝐿L remaining consistent for most metals.
The Wiedemann-Franz Law connects the thermal and electrical conductivity of metals. Here’s an outline of its derivation:
Thermal Conductivity (𝑘):
Electrical Conductivity (𝜎):
Linking Thermal and Electrical Conductivity:
The Wiedemann-Franz Law links thermal and electrical conductivities in metals but has notable limitations.
The Wiedemann-Franz Law states that metals have a consistent ratio between thermal and electrical conductivities at a given temperature, reflect the role of free electrons in both processes.
Using the Wiedemann-Franz Law, the Lorenz number is 𝐿≈2.44×10⁻⁸ WΩK⁻², represents the proportionality between heat and electrical conduction in metals.
For the Wiedemann-Franz Law to hold, metals should have a consistent relationship between thermal and electrical conductivities, with any deviations linked to impurity or extreme temperatures.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What does the Wiedemann-Franz Law relate?
Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity
Heat capacity and temperature
Voltage and current
Magnetic field and electric field
What is the proportionality constant in the Wiedemann-Franz Law called?
Boltzmann constant
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
Lorenz number
Planck constant
Which physical principle underlies the Wiedemann-Franz Law?
Conservation of momentum
Quantum mechanics
Classical mechanics
Free electron model of metals
In the Wiedemann-Franz Law, what happens to the ratio of thermal conductivity to electrical conductivity as temperature increases?
Increases
Decreases
Remains constant
Fluctuates randomly
What does the Wiedemann-Franz Law imply about good electrical conductors?
They are poor thermal conductors
They are good thermal conductors
They have high resistivity
They have low density
Which metals closely follow the Wiedemann-Franz Law?
Insulators
Semiconductors
Conductors
Superconductors
What is the formula for the Wiedemann-Franz Law?
κ/σ = LT
κσ = L/T
κ/σ = L/T
κσ = LT
How does the Wiedemann-Franz Law help in determining material properties?
By measuring specific heat
By relating thermal and electrical conductivities
By determining melting point
By measuring thermal expansion
If a metal has a high electrical conductivity, what can be inferred about its thermal conductivity according to the Wiedemann-Franz Law?
It has low thermal conductivity
It has high thermal conductivity
It has constant thermal conductivity
It has zero thermal conductivity
What type of materials does the Wiedemann-Franz Law primarily apply to?
Insulators
Non-metals
Metals
Ceramics
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

