What is the atomic number of Rhodium?
43
44
45
46
Dive into the fascinating world of Rhodium, the rare and precious metal renowned for its exceptional properties and diverse applications. This comprehensive guide illuminates Rhodium’s significance, from its unparalleled ability to reflect and resist corrosion to its pivotal role in catalytic converters and fine jewelry. Discover how Rhodium’s scarcity and high performance make it a sought-after element in various industries, including automotive, jewelry, and chemical sectors. Through real-world examples, you’ll learn about Rhodium’s impact and why it remains a symbol of luxury and innovation in modern technology and design
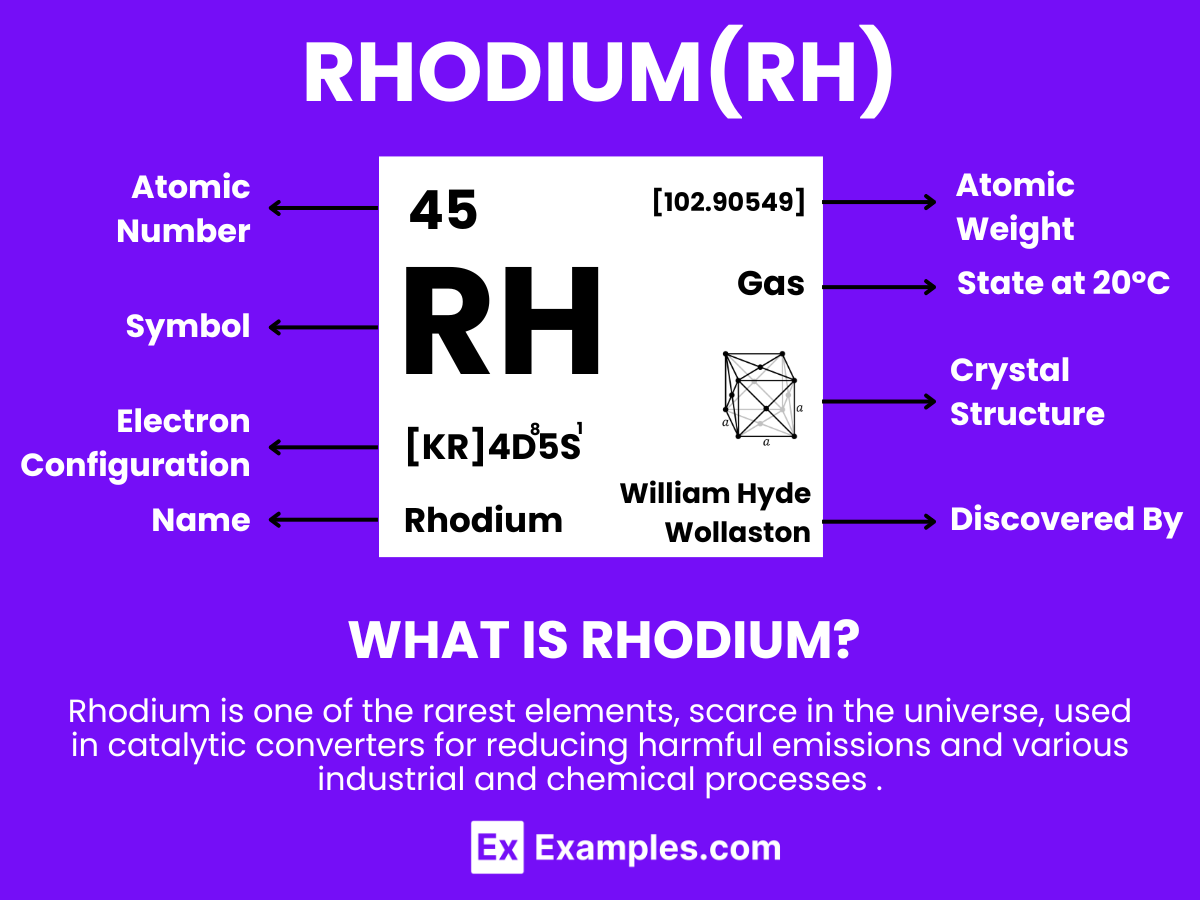
Rhodium is a rare, silvery-white metallic element that is highly reflective and known for its exceptional resistance to corrosion. With the atomic number 45. Rhodium stands out for its rarity and the high cost associated with its extraction and use. This element is not found as a free metal in nature but is usually obtained as a byproduct of platinum and nickel mining. Rhodium’s primary use is in the automotive industry for manufacturing catalytic converters, which help reduce harmful emissions. Additionally, it is used in the jewelry industry for plating to provide a reflective white surface and enhance durability. Rhodium’s ability to withstand corrosion and its high reflectivity also make it valuable in optical instruments and as a catalyst in certain chemical reactions.
Rhodium, with the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45, is a rare, silver-white, hard transition metal that is highly reflective and resistant to corrosion. As a member of the platinum group metals (PGMs) in the periodic table, rhodium shares some characteristics with its neighbors. Understanding the atomic structure of rhodium provides insights into its unique properties and applications. Here’s a detailed overview:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 45 |
| Atomic Weight | 102.90550 |
| Melting Point | 1,966 °C (3,571 °F) |
| Boiling Point | 3,700 °C (6,692 °F) |
| Density at 20°C | 12.41 g/cm³ |
| State at 20 °C | Solid |
| Color | Silvery-white metallic |
| Electrical Conductivity | 2.3×10⁶ S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150 W/(m·K) |
| Heat of Fusion | 21.5 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 494 kJ/mol |
| Atomic Radius | 134 pm |
| Crystal Structure | Face-centered cubic (fcc) |
| Oxidation States | -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1964°C (3567°F) |
| Boiling Point | 3695°C (6683°F) |
| Heat of Fusion | 21.5 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 493 kJ/mol |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 24.98 J/(mol·K) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 12.41 g/cm³ |
| Mohs Hardness | 6 |
| Young’s Modulus | 380 GPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150 W/(m·K) |
| Electrical Resistivity | 4.3 µΩ·m (at 20 °C) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High; conductivity decreases with temperature increase |
| Magnetic Susceptibility | Weakly paramagnetic at room temperature |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Natural Isotopes | Rh-103 (100% abundance) |
| Neutron Cross Section | 144.8 barns (for Rh-103) |
| Primary Decay Mode | Stable (Rh-103) |
| Isotope | Natural Abundance (%) | Half-Life | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh-103 | 100 | Stable | Only naturally occurring isotope, used in industrial applications |
| Rh-99 | — | 16.1 days | Used in medical research |
| Rh-101 | — | 3.3 years | Used in scientific studies |
| Rh-102m | — | 2.9 years | Used in nuclear physics experiments |
| Rh-105 | — | 35.36 hours | Potential use in cancer treatment |
The presented table and descriptions of Rhodium’s physical properties and chemical compounds showcase the element’s unique attributes and versatility in industrial and scientific applications. Highlighting Rhodium’s remarkable durability, catalytic efficiency, and role in advanced technologies, this summary encapsulates its significance in pushing the boundaries of material science and chemical engineering.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the atomic number of Rhodium?
43
44
45
46
Rhodium is most commonly used in which industry?
Electronics
Automotive
Agriculture
Textile
What is the chemical symbol for Rhodium?
Rh
Ro
Rd
Rm
What property makes Rhodium suitable for use in catalytic converters?
High reactivity
High melting point
High corrosion resistance
Low density
Which of the following is a characteristic property of Rhodium?
Soft and malleable
High reflectance
Brittle
Magnetic
What is the primary source of Rhodium?
Gold ores
Platinum ores
Copper ores
Iron ores
Which of the following is NOT a common use of Rhodium?
Jewelry plating
Electrical contacts
Solar panels
Chemical industry catalysts
What is the color of pure Rhodium?
Yellow
Grayish-white
Black
Blue
What is the melting point of Rhodium?
1064°C
1455°C
1964°C
2237°C
Rhodium is often alloyed with which metal for use in jewelry?
Gold
Silver
Platinum
Copper
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

