What is the chemical formula for lead nitrate?
Pb(NO3)2
Pb(NO3)4
PbNO3
Pb2(NO3)3


Lead nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula Pb(NO₃)₂, commonly found in crystalline form. In chemistry, it appears as a white solid and is highly soluble in water. We often use lead nitrate in laboratories for various experiments and chemical reactions. This compound plays a crucial role in the synthesis of other lead compounds and in the production of fireworks and explosives due to its oxidizing properties. However, it’s important to handle lead nitrate with care, as it is toxic and can cause health hazards if not managed properly.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | Pb(NO₃)₂ |
| Hill Formula | N₂O₆Pb |
| Name | Lead(II) Nitrate |
| IUPAC Name | Plumbous Dinitrate |
| Alternate Names | Lead(+2) Cation Dinitrate, Plumbous Dinitrate |
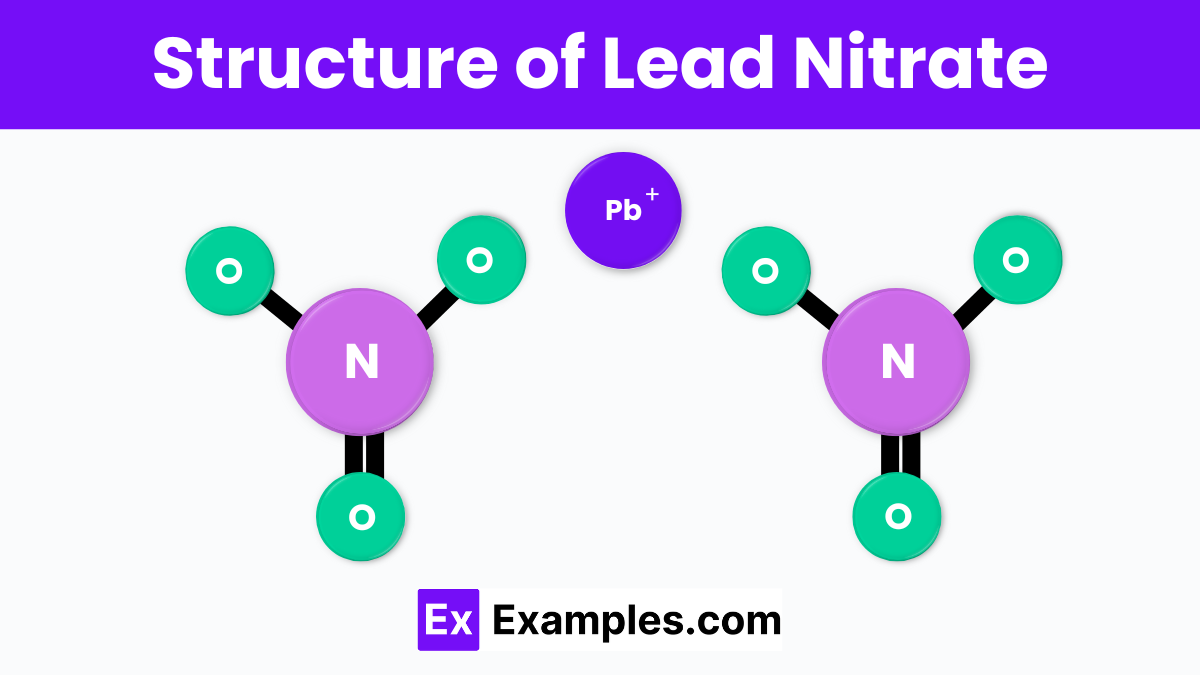
The structure of lead nitrate consists of one lead ion (Pb²⁺) and two nitrate ions (NO₃⁻). In this structure, the lead ion is at the center, and the nitrate ions are arranged around it. Each nitrate ion has one nitrogen atom bonded to three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar shape. The lead ion forms ionic bonds with the nitrate ions, resulting in a stable crystal lattice. This arrangement gives lead nitrate its characteristic crystalline form and solubility in water.
To prepare lead nitrate, you react lead(II) oxide (PbO) or lead(II) carbonate (PbCO₃) with nitric acid (HNO₃). When you add nitric acid to lead(II) oxide, the reaction produces lead nitrate and water. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
Alternatively, when you react lead(II) carbonate with nitric acid, it produces lead nitrate, water, and carbon dioxide. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
In both methods, you dissolve the lead compound in nitric acid, filter out any impurities, and then allow the solution to evaporate. As the water evaporates, lead nitrate crystals form. You can then collect and dry these crystals for use in various applications.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless or white crystalline solid |
| Molecular Weight | 331.2 g/mol |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| Melting Point | 470°C (decomposes) |
| Density | 4.53 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes before boiling |
| Color | Colorless or white |
| Crystal Structure | Orthorhombic |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Hygroscopic Nature | Hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from air) |
| Refractive Index | 1.783 |
| Solubility in Alcohol | Slightly soluble |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 10099-74-8 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 24924 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24852183 |
| SMILES Identifier | N+([O-])[O-].N+([O-])[O-].[Pb+2] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/2NO3.Pb/c22-1(3)4;/q2-1;+2 |
| RTECS Number | OG2100000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00011153 |
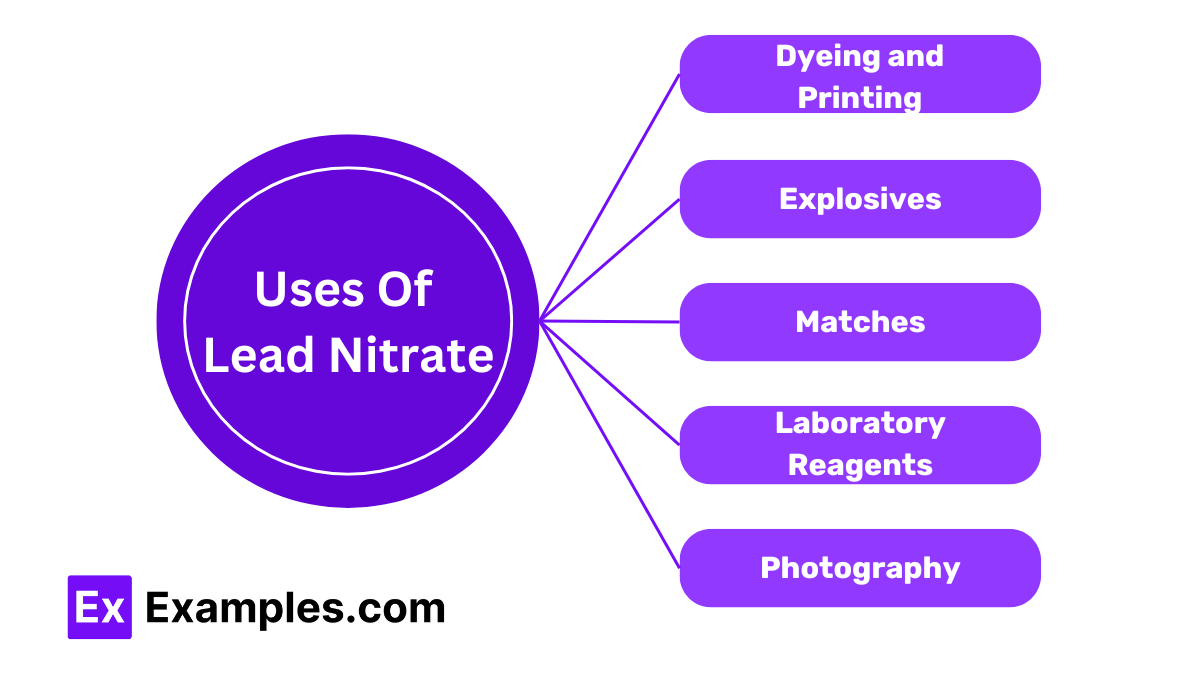
Lead nitrate is used in the textile industry for dyeing and printing fabrics. It helps fix dyes to the fabric, ensuring vibrant and long-lasting colors.
Lead nitrate serves as an oxidizing agent in the production of explosives. It helps facilitate the rapid combustion needed for explosions.
Manufacturers use lead nitrate in the production of matches. It helps in the ignition process, allowing matches to light easily.
Lead nitrate is commonly used as a reagent in chemical laboratories. It aids in various reactions and experiments to test for the presence of certain ions.
In photography, lead nitrate is used in some photographic processes to produce certain types of images. It helps in the development and processing of photographic films.
Lead nitrate is employed in metal finishing processes. It helps in electroplating and other treatments to protect and enhance the appearance of metals.
The formula for lead nitrate is Pb(NO₃)₂, consisting of one lead ion (Pb²⁺) and two nitrate ions (NO₃⁻).
Lead nitrate can act as an oxidizing agent in explosives, contributing to rapid combustion and explosions.
Lead nitrate is not edible. It is highly toxic and can cause severe health problems if ingested.
Lead nitrate is neither an acid nor a base. It is a neutral salt formed from nitric acid and lead.
Lead nitrate is not an acid. It is a salt composed of lead and nitrate ions.
Lead nitrate forms ionic bonds between lead ions (Pb²⁺) and nitrate ions (NO₃⁻).
Lead nitrate is colorless or white in its solid crystalline form.
Lead nitrate dissociates into lead ions (Pb²⁺) and nitrate ions (NO₃⁻) in water.
Ingesting even small amounts of lead nitrate can be toxic. Exposure levels above 0.1 mg/kg body weight are considered dangerous.
Lead nitrate is highly soluble in water, easily dissolving to form a clear solution.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula for lead nitrate?
Pb(NO3)2
Pb(NO3)4
PbNO3
Pb2(NO3)3
In what form is lead nitrate commonly found?
Solid crystals
Gas
Liquid solution
Powder
What is the primary use of lead nitrate in laboratories?
As a disinfectant
As a food preservative
As a pigment in paint
As a reactant in chemical synthesis
How does lead nitrate react when heated?
It decomposes to form lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen
It remains unchanged
It forms lead sulfate
It reacts with water to form lead hydroxide
What safety precaution is essential when handling lead nitrate?
No special precautions are needed
Avoid direct skin contact
Inhalation of fumes is encouraged
Always use in an open area
What is one of the environmental concerns related to lead nitrate?
It is a potent greenhouse gas
It can lead to soil contamination
It depletes the ozone layer
It causes water pollution
What color does lead nitrate produce in a flame test?
Green
Blue
Yellow
Red
What happens to lead nitrate when it reacts with sulfuric acid?
It forms lead sulfate and nitric acid
It forms lead chloride and sulfur dioxide
It forms lead oxide and sulfuric acid
It reacts to form lead nitrate and water
What is the solubility of lead nitrate in water?
Insoluble
Slightly soluble
Moderately soluble
Highly soluble
What is the primary health hazard associated with lead nitrate exposure?
Respiratory issues
Skin rash
Eye irritation
Lead poisoning
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

