What is the chemical formula for ammonium chloride?
NH4Cl
NH3Cl
NH4Cl2
NH3Cl2


Ammonium chloride is a white crystalline compound that plays a significant role in chemistry. It forms when ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid, resulting in a versatile salt used in various applications. Commonly found in fertilizers, batteries, and cold medicines, ammonium chloride dissolves easily in water and has a salty taste. Its unique properties make it an essential substance in both industrial and laboratory settings, highlighting the diverse nature of chemical compounds and salts.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | NH₄Cl |
| Hill formula | ClH₄N |
| Name | Ammonium chloride |
| Alternate names | Amchlor, Ammoneric, Ammonium muriate, Azanium chloride, Darammon, Sal ammoniac, Salammonite, Salmiac |
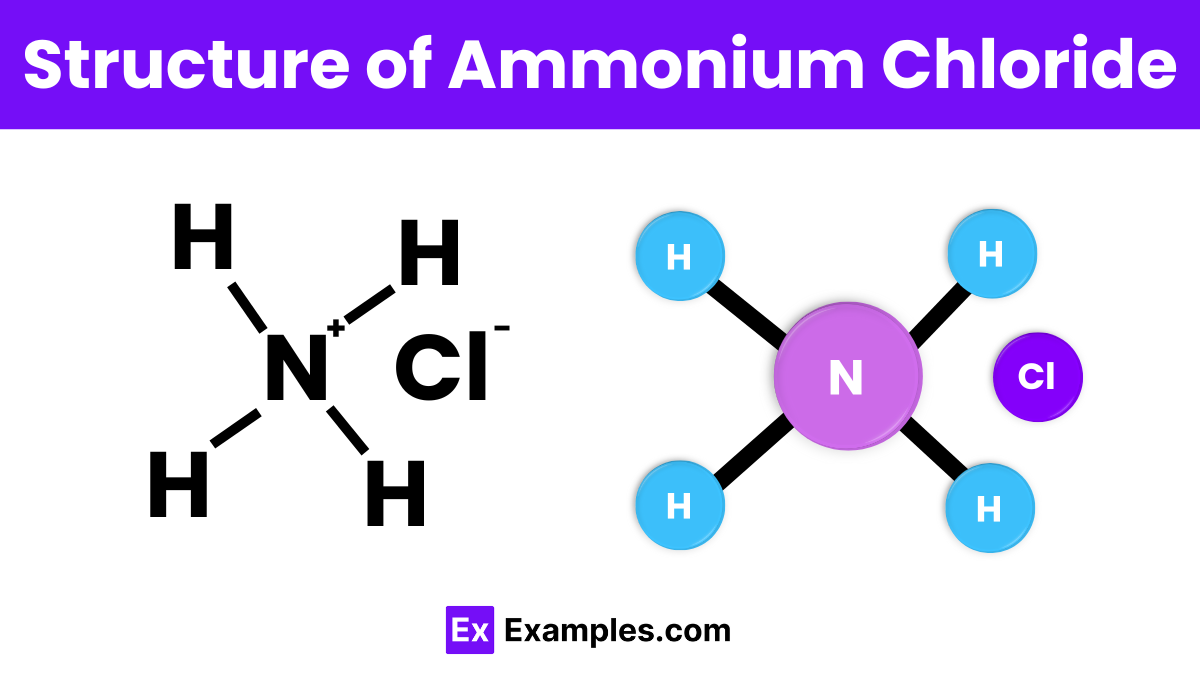
The structure of ammonium chloride consists of an ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) and a chloride ion (Cl⁻). The ammonium ion is formed by a nitrogen atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms in a tetrahedral shape. In ammonium chloride, these ions are held together by ionic bonds, creating a crystal lattice structure. The positively charged ammonium ions and negatively charged chloride ions arrange themselves in a repeating pattern, which helps form the solid crystalline structure of the compound.
To prepare ammonium chloride, you can react ammonia (NH₃) with hydrochloric acid (HCl). When these two substances mix, they form ammonium chloride and water. This reaction is straightforward and commonly used in laboratories. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
In a simple setup, you can bubble ammonia gas into a solution of hydrochloric acid. As the ammonia dissolves, it reacts with the hydrochloric acid to produce ammonium chloride, which then precipitates out of the solution as a white solid. You can filter and dry the solid to obtain pure ammonium chloride.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Molecular Formula | NH₄Cl |
| Molar Mass | 53.49 g/mol |
| Density | 1.527 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 338°C (640°F) |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS registry number | 12125-02-9 |
| Beilstein number | 4371014 |
| PubChem compound ID | 25517 |
| PubChem substance ID | 24855359 |
| SMILES identifier | [NH4+].[Cl-] |
| InChI identifier | InChI=1/ClH.H3N/h1H;1H3/fCl.H4N/h1h;1H/q-1;+1 |
| RTECS number | BP4550000 |
| MDL number | MFCD00011420 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 1 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 0 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
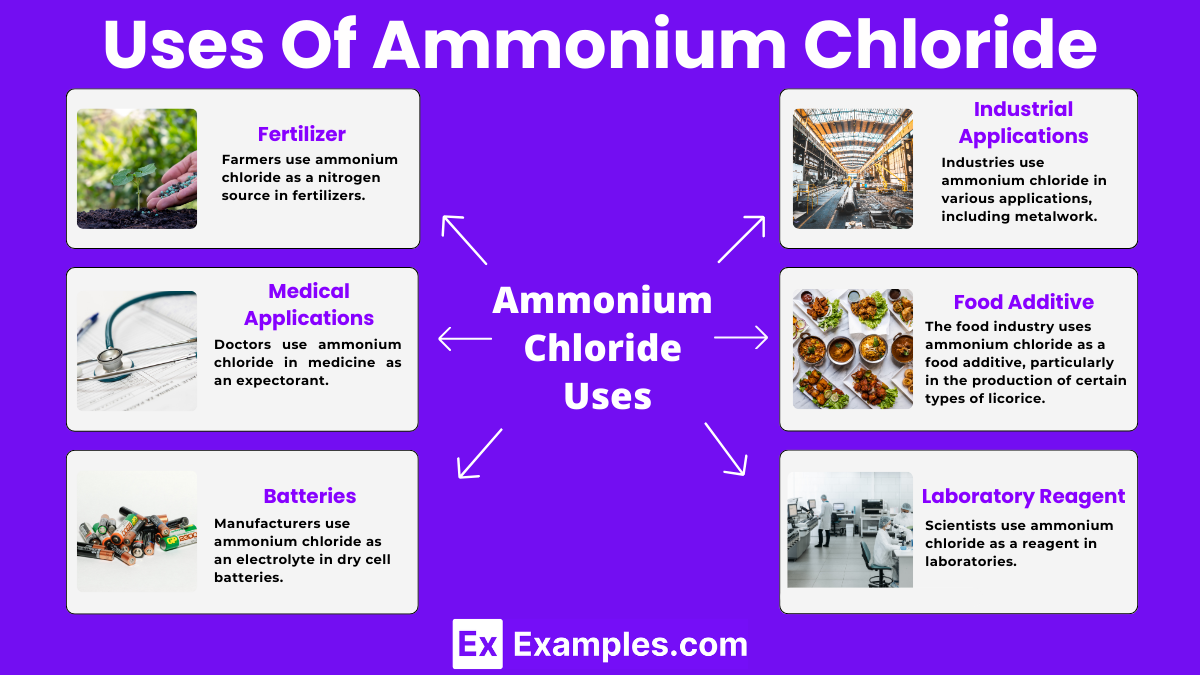
Farmers use ammonium chloride as a nitrogen source in fertilizers. It helps plants grow by providing essential nutrients.
Doctors use ammonium chloride in medicine as an expectorant. It helps relieve coughs by thinning mucus in the respiratory tract.
Industries use ammonium chloride in various applications, including metalwork. It serves as a flux to clean metals during soldering and welding.
Manufacturers use ammonium chloride as an electrolyte in dry cell batteries. It helps conduct electricity and power devices like flashlights and radios.
The food industry uses ammonium chloride as a food additive, particularly in the production of certain types of licorice. It enhances flavor and extends shelf life.
Scientists use ammonium chloride as a reagent in laboratories. It helps in various chemical reactions and experiments, such as buffer solutions and protein purification.
Ammonium chloride can be harmful if inhaled, ingested in large amounts, or contacted with skin and eyes. It can cause respiratory issues, skin irritation, and gastrointestinal problems.
No, ammonium chloride is not a bleach. It is primarily used in fertilizers, batteries, and as a metal cleaner.
Yes, ammonium chloride is safe to eat in licorice in small amounts. It is commonly used in Scandinavian licorice as a flavoring agent.
Ammonium chloride is important for various household uses, including as a cleaning agent, in batteries, and in certain medical applications.
Mixing ammonium chloride with bleach releases toxic chlorine gas. This is dangerous and should be avoided.
Yes, you can mix ammonium chloride with vinegar. The mixture is generally safe and does not produce harmful reactions.
Avoid mixing ammonium chloride with bleach or strong alkalis. These combinations can produce toxic gases or other hazardous reactions.
Mixing vinegar and ammonia produces a neutralization reaction, creating water and ammonium acetate. This reaction is generally safe and non-toxic.
Finnish people eat licorice flavored with ammonium chloride for its unique salty taste, which is a traditional and popular treat in Finland.
Ammonium chloride is used as a flux in metal cleaning. It removes oxides and impurities from metal surfaces during soldering and welding.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula for ammonium chloride?
NH4Cl
NH3Cl
NH4Cl2
NH3Cl2
In which type of reaction is ammonium chloride commonly used?
Neutralization reactions
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Precipitation reactions
Acid-base reactions
What is the state of ammonium chloride at room temperature?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
Plasma
What happens to ammonium chloride when it is heated?
It decomposes into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gas
It melts into a liquid
It sublimates into a gas
It turns into a black solid
Which of the following uses ammonium chloride in its production?
Baking soda
Fire extinguishers
Fertilizers
Cleaning agents
What is the pH of an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride?
Basic
Neutral
Acidic
Alkaline
Ammonium chloride is commonly used in which type of laboratory experiment?
Chromatography
Titration
Spectroscopy
Electrolysis
What is a common method for synthesizing ammonium chloride?
Neutralization of ammonia and hydrochloric acid
Electrolysis of ammonium sulfate
Combustion of ammonium nitrate
Precipitation of ammonium carbonate
In which industry is ammonium chloride used as a flux?
Food industry
Metal industry
Pharmaceutical industry
Textile industry
What is the role of ammonium chloride in certain cold packs?
To act as a heating agent
To provide cooling through an endothermic reaction
To increase the temperature
To provide insulation
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

