What is the primary use of toluene in industrial applications?
As a refrigerant
As a solvent
As a food preservative
As a fuel additive

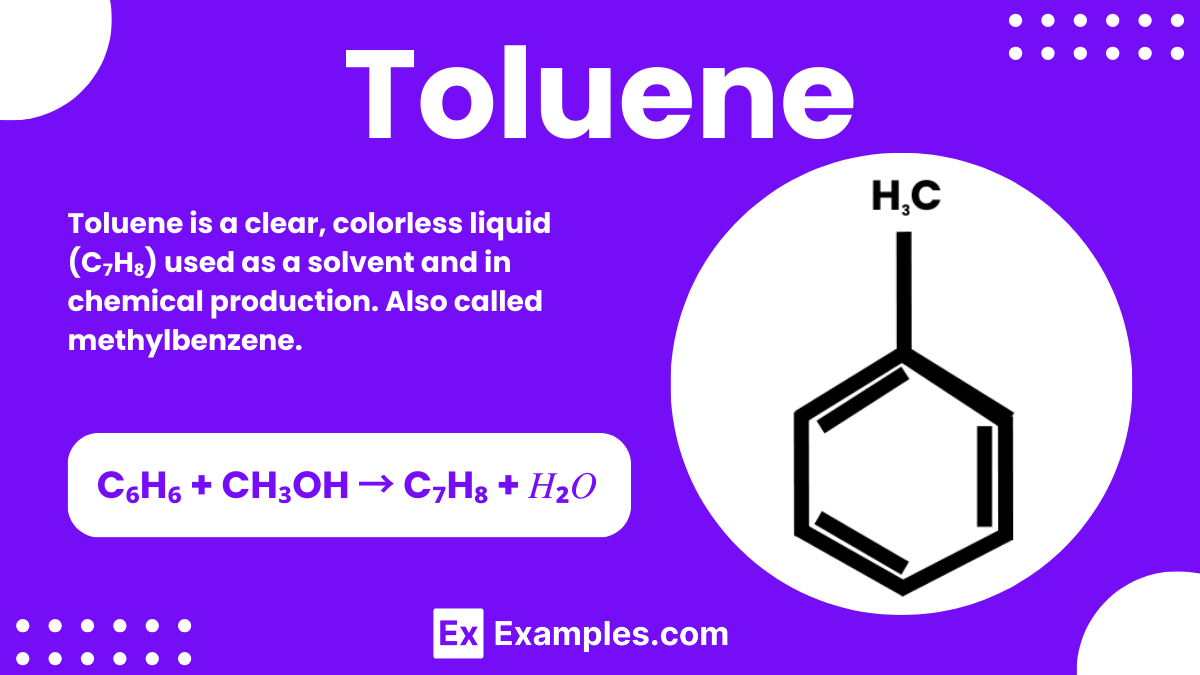
Toluene is a clear, colorless liquid commonly used in chemistry as a solvent and an important starting material for making other compounds. It has a sweet, pungent smell and is found in paint thinners, nail polish removers, and some types of glue. Chemists often work with toluene because it can dissolve many substances without reacting with them. Being a hydrocarbon, it consists of a benzene ring with a single methyl group attached, making it a key compound in organic chemistry.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | C₆H₅CH₃ |
| Hill Formula | C₇H₈ |
| Name | Toluene |
| IUPAC Name | Methylbenzene |
| Alternate Names | Meth Acid E, Methane Phenyl-, Methylbenzene, Methylbenzol, Phenylmethane, Toluol |
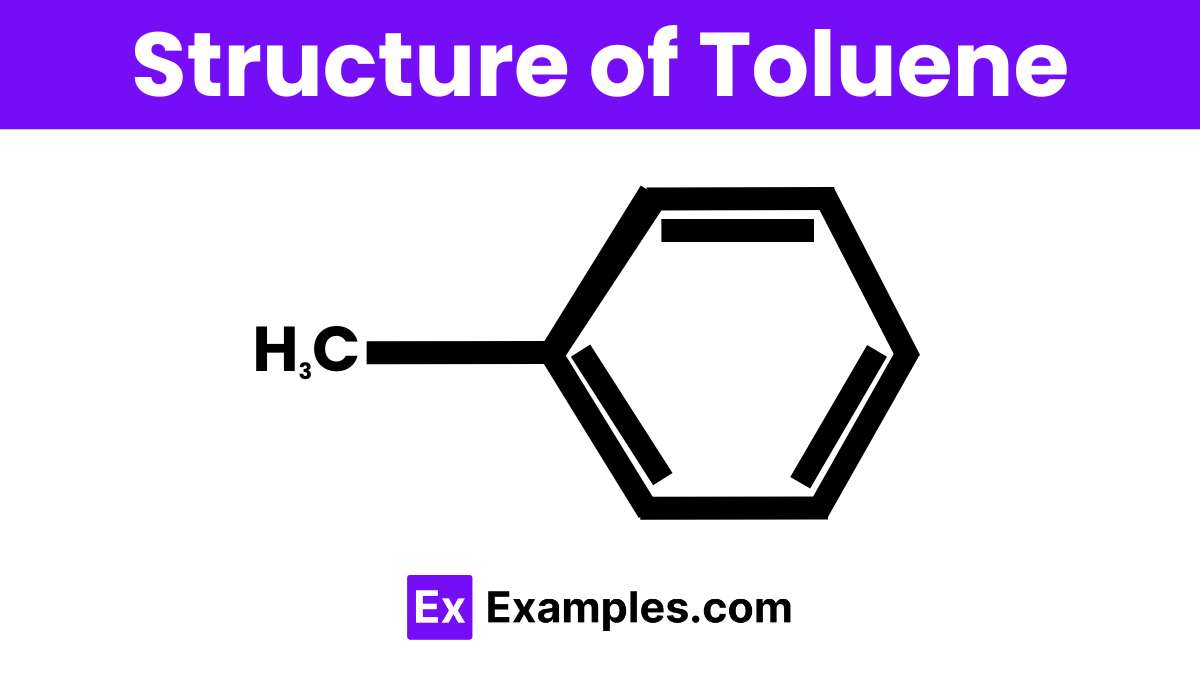
Toluene has a simple and distinctive structure consisting of a benzene ring bonded to a single methyl group (CH₃). This means that six carbon atoms form a hexagonal ring with alternating double bonds, while one carbon of this ring is attached to a group of three hydrogen atoms. This structure gives toluene its chemical properties and makes it an important compound in various industrial applications.
To prepare toluene, we primarily use the catalytic reforming of petroleum naphtha. In this process, you heat and pressurize naphtha in the presence of a catalyst, usually platinum or rhenium, which rearranges the hydrocarbons to produce toluene. The reaction is efficient and commonly used in the petrochemical industry to obtain toluene from crude oil derivatives.
Another method involves the methylation of benzene. By reacting benzene (C₆H₆) with methanol (CH₃OH) in the presence of a catalyst, toluene (C₇H₈) is produced along with water. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
These methods ensure the commercial availability of toluene for various applications in industries like manufacturing and pharmaceuticals.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Distinctive, sweet smell |
| Molecular Weight | 92.14 g/mol |
| Melting Point | -95°C (-139°F) |
| Boiling Point | 110.6°C (231.1°F) |
| Density | 0.87 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in Water | Slightly soluble |
| Vapor Pressure | 28.4 mmHg at 25°C (77°F) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 108-88-3 |
| Beilstein Number | 635760 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 1140 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24850838 |
| SMILES Identifier | CC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C7H8/c1-7-5-3-2-4-6-7/h2-6H, 1H3 |
| InChI Key | YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYAT |
| RTECS Number | XS5250000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00008512 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| NFPA Health Rating | 2 |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 3 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 |
Toluene acts as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives. It effectively dissolves many organic compounds, making it ideal for these applications.
Toluene is used as a fuel additive to improve octane ratings in gasoline. This helps engines run more smoothly and efficiently.
Industries use toluene as a starting material in the synthesis of chemicals such as benzene, xylene, and TNT (trinitrotoluene). Its reactivity makes it valuable in producing these compounds.
Toluene serves as a cleaning agent for machinery and electronic equipment. It removes grease and other residues effectively.
In the pharmaceutical industry, toluene is used as a solvent in the production of various medicines. Its purity and effectiveness make it suitable for this purpose.
Yes, toluene is legal and widely used in industrial applications. However, regulations control its usage and exposure due to its potential health risks.
Drinking toluene can cause severe health issues, including stomach pain, nausea, dizziness, and central nervous system damage. It requires immediate medical attention.
Toluene can affect the central nervous system, causing symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and nausea. Long-term exposure may lead to more serious health issues, including organ damage.
Toluene is highly flammable. It can easily ignite and burn, making it essential to handle it with care and store it away from open flames and heat sources.
Toluene is toxic if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Prolonged exposure can cause significant health problems, including liver and kidney damage, and requires careful handling.
Toluene is only slightly soluble in water. When mixed, it forms a separate layer, with toluene floating on top due to its lower density.
People are exposed to toluene through inhalation of fumes, skin contact, or ingestion. Common sources include industrial solvents, paints, and gasoline.
Yes, toluene is one of the many chemicals found in cigarette smoke. It contributes to the harmful effects of smoking on health.
Yes, you can smell toluene. It has a distinct, sweet, and pungent odor, which makes it noticeable even at low concentrations.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the primary use of toluene in industrial applications?
As a refrigerant
As a solvent
As a food preservative
As a fuel additive
What is the chemical formula of toluene?
C6H5OH
C6H6
C7H8
C8H10
Which of the following is a common safety precaution when handling toluene?
Ensuring adequate ventilation
Using it in open containers
Direct contact with skin
Ignoring spill procedures
Toluene is primarily derived from which process in the petrochemical industry?
Distillation
Hydrogenation
Cracking
Reforming
What physical state is toluene at room temperature?
Solid
Gas
Liquid
Plasma
Which of the following properties of toluene makes it useful as a solvent?
Its high boiling point
Its high solubility in water
Its ability to dissolve many organic substances
Its low vapor pressure
Toluene is commonly used as a raw material in the production of which compound?
Acetone
Terephthalic acid
Ethanol
Methanol
Which of the following is a potential health effect of exposure to toluene?
Respiratory irritation
Improved cognitive function
Enhanced vision
Reduced appetite
In which industry is toluene most commonly used as a component of gasoline?
Automotive
Pharmaceutical
Food and beverage
Textile
What is one of the main environmental concerns associated with toluene?
Its role in ozone depletion
Its contribution to water pollution
Its impact on soil erosion
Its effect on climate change
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

