What is the symbol for rutherfordium?
Rf
Rd
Ru
Rh
Discover the fascinating world of Rutherfordium, a synthetic element that captures the imagination of scientists and enthusiasts alike. This guide delves into the essence of Rutherfordium, offering comprehensive insights into its definition, applications, and unique compounds. With practical examples and a clear, accessible approach, we illuminate the significance of this elusive element in the periodic table. Ideal for students, researchers, and curious minds, our exploration of Rutherfordium paves the way for a deeper understanding of its role in modern science.
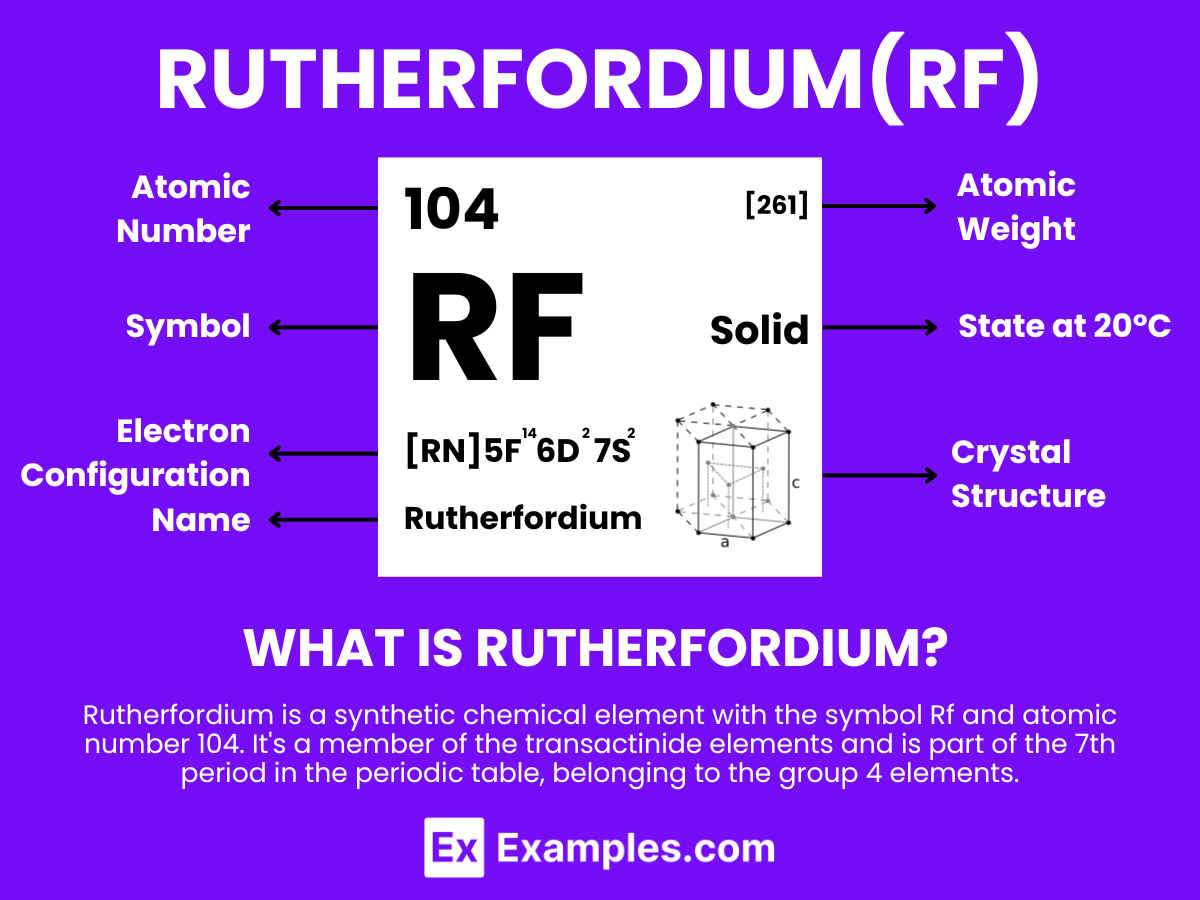
Rutherfordium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Rf and atomic number 104. It’s a member of the transactinide elements and is part of the 7th period in the periodic table, belonging to the group 4 elements. Rutherfordium is a radioactive, highly unstable element that does not occur naturally and is produced artificially in particle accelerators through the fusion of lighter atoms. Named after the renowned New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford, known for his pioneering work in nuclear physics, Rutherfordium was first synthesized in the 1960s by teams of scientists in the United States and the Soviet Union, leading to a dispute over its discovery and naming.
Rutherfordium, with the symbol Rf and atomic number 104, is a highly radioactive, synthetic element that occupies a place among the transactinide elements within the periodic table. It’s categorized under the group 4 transition metals, sharing this designation with elements such as titanium, zirconium, and hafnium, located in the 7th period.
Being synthetic, rutherfordium is produced in laboratories through intricate nuclear reactions, and it doesn’t exist naturally. The atomic structure of rutherfordium is an area of intense scientific interest, though the element’s brief half-life—particularly of its most stable isotope, ²⁶⁷Rf, which has a half-life around 1.3 hours—presents substantial challenges for detailed study.
The anticipated electron configuration for rutherfordium is [Rn] 5f¹⁴ 6d² 7s² This configuration indicates that rutherfordium is the inaugural element in the 6d series of transition metals, suggesting that it shares several characteristics with its lighter counterparts within group 4. Typically, rutherfordium is expected to exhibit a +4 oxidation state, which is consistent with the oxidation states observed in other group 4 elements.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 104 |
| Atomic Weight | [267] (most stable isotope) |
| Melting Point | About 2400 K (estimated) |
| Boiling Point | Unknown (estimated to be 5800 K) |
| Density | Unknown (estimated to be around 23.2 g/cm³) |
| State at Room Temperature | Solid (predicted) |
| Electronic Configuration | [Rn] 5f¹⁴ 6d² 7s² (predicted) |
| Oxidation States | +4 (most stable), +3 (predicted) |
| Crystal Structure | Unknown (hcp expected) |
Rutherfordium (Rf) is a superheavy element with the atomic number 104. It belongs to group 4 of the periodic table, sharing its group with titanium, zirconium, hafnium, and is expected to display some chemical properties similar to those of its lighter congeners, albeit modified significantly by relativistic effects. Due to its position, given the extremely short half-life and the limited quantities in which rutherfordium has been produced, much of what is known about its chemical properties is theoretical, based on calculations and comparisons with other group 4 elements.
Rutherfordium is predicted to exhibit a +4 oxidation state, similar to hafnium, its nearest lighter homologue. However, due to strong relativistic effects influencing its electrons, rutherfordium might also be capable of stabilizing in other oxidation states under certain conditions. The +3 and +2 oxidation states are theoretically possible and might be more stable for rutherfordium than for its lighter congeners due to these effects.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Half-Life | Depends on the isotope; shortest observed ~1.3 milliseconds, longest ~13 hours |
| Decay Modes | Alpha decay, Spontaneous fission, Electron capture |
| Isotopes | Known isotopes range from Rf-253 to Rf-270 |
| Nuclear Spin | Unknown |
Rutherfordium, with the atomic number 104, is a superheavy element that does not occur naturally and has no stable isotopes. It is exclusively produced through artificial nuclear reactions in particle accelerators. The preparation of rutherfordium involves highly specialized techniques, primarily involving the bombardment of target materials with accelerated particles. Below are the primary methods used in the preparation of rutherfordium:
| Isotope | Mass Number | Half-life | Decay Modes | Decay Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rutherfordium-261 | 261 | 1.08 minutes | Alpha decay | Nobelium-257 |
| Rutherfordium-262 | 262 | 2.1 seconds | Alpha decay, Spontaneous fission | Nobelium-258, various |
| Rutherfordium-263 | 263 | 10 minutes | Alpha decay | Nobelium-259 |
| Rutherfordium-264 | 264 | ~0.8 seconds | Spontaneous fission | Various |
| Rutherfordium-265 | 265 | 1-2 minutes | Alpha decay | Nobelium-261 |
| Rutherfordium-266 | 266 | ~10 hours | Alpha decay, Electron capture | Nobelium-262, Dubnium-266 |
| Rutherfordium-267 | 267 | ~1.3 hours | Alpha decay | Nobelium-263 |
The exploration of rutherfordium’s isotopes reveals a fascinating but complex element at the frontier of nuclear science. While its practical applications are limited by its radioactivity and short-lived existence, rutherfordium plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of superheavy elements, challenging scientists to expand the boundaries of the periodic table and atomic theory.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the symbol for rutherfordium?
Rf
Rd
Ru
Rh
Rutherfordium is classified as which type of element?
Alkali metal
Alkaline earth metal
Transition metal
Noble gas
Who is rutherfordium named after?
Marie Curie
Ernest Rutherford
Dmitri Mendeleev
Niels Bohr
In which year was rutherfordium first synthesized?
1960
1964
1969
1974
Rutherfordium was first synthesized by bombarding which element with neon ions?
Uranium
Plutonium
Californium
Curium
What is the most stable isotope of rutherfordium?
Rf-257
Rf-261
Rf-263
Rf-267
What is the primary method used to study the chemical properties of rutherfordium?
Mass spectrometry
X-ray diffraction
Gas-phase chromatography
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Rutherfordium is located in which period of the periodic table?
Period 6
Period 7
Period 8
Period 9
Which laboratory first confirmed the synthesis of rutherfordium?
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Rutherfordium is primarily used for:
Industrial applications
Medical treatments
Scientific research
Consumer products
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

