22+ Qualitative Data Examples to Download
The scientific method prides itself on the fact that this practice can verify and produce knowledge and information using uncovered evidence and facts surrounding the research topic. People lead very different lives with subjective points of view that affect their attitudes, behaviors, core values, and core beliefs. The subjective data these people can provide to researchers is called qualitative data.
1. Qualitative Data Analysis Plan Template

2. Qualitative Data Analysis
3. Qualitative Data Analysis Overall Report
4. Sample Qualitative Data Analysis
5. Qualitative Data Analysis Workshop
6. Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
7. Communication Qualitative Data Analysis Report
8. Analyzing and Reporting Qualitative Data
9. Consulting Qualitative Data Report
10. Thematic Analysis of Qualitative Data
11. Qualitative Analysis of Video Data
12. Simple Qualitative Data Analysis
13. Qualitative Data for Evaluation Report
14. Qualitative Data Analysis Report Template
15. General Qualitative Data Analysis Report
16. Qualitative Data Analysis Report
17. Qualitative Data Analysis Example
18. Analyzing Qualitative Data in Heath Care
19. Qualitative Research Data Analysis Report
20. Qualitative Data Analysis Report
21. Qualitative Data Interim Analysis Report
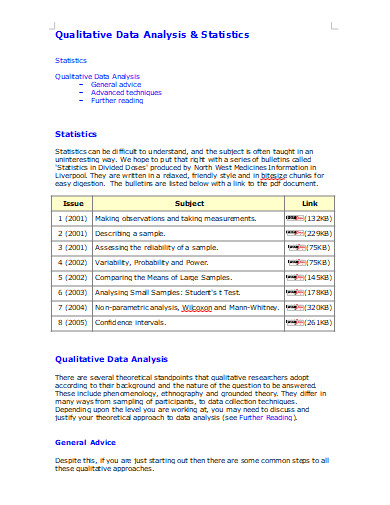
22. Qualitative Data Analysis and Statistics
23. Qualitative Data Analysis Report in PDF
What Are Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data are not objectively true, meaning researchers cannot apply this data to all cases. The insight one can gain from qualitative data allows the researcher to induce a correlation or cause-and-effect relationship from two or more variables that would otherwise be very hard to measure quantitatively. To use qualitative data, the research question should be a qualitative topic and will require the researcher’s use of encoding specific keywords and feelings from the qualitative data.
How to Obtain Qualitative Data
Qualitative data can come in many forms, which the qualitative research method will determine. For example, a case study will yield multiple pages of perspective information about the subject’s life, thought process, and actions. If you want more qualitative data examples, samples, and articles, you may use any of the links in the sections above as your reference.
Step 1: Determine Your Qualitative Method
Your qualitative method should be appropriate for the qualitative research question you are trying to answer. These qualitative methods can span a specific amount of time and will require the researcher to do specific actions according to the theme, tone, and context of the qualitative method. For example, if the qualitative method is an interview, then the researcher will need to create interview questions as the means to obtain the qualitative data.
Step 2: Determine the Length of the Application of the Qualitative Method
A qualitative method may range from a couple of days to years of application of the research method. A qualitative survey will require the researcher to spend days obtaining responses from the target population, while a case study might require the researcher to spend years in a specific environment. You must determine the length of the application of the chosen qualitative method.
Step 3: Use the Qualitative Method You Have Chosen
You must apply the qualitative method you have chosen to your target population at the chosen time. The qualitative method you have chosen will also determine the amount of data you will acquire in a given time.
Step 4: Write Down or Record the Qualitative Data You will Obtain from the Use of the Qualitative Method
You must write down or record the qualitative data you will collect through the usage of the qualitative method. Be sure to ensure that you accurately and precisely record the information onto your recording software or notepad.
FAQs
Quantitative data is a type of data that is highly objective and factual; often, this type of data requires numerous responses to establish the objectivity of the data. Qualitative data is a type of data that is highly subjective and is true to a specific individual or group of individuals.What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative data?
Yes, surveys that require nuanced and in-depth answers can obtain and create highly-qualitative data, which the person can use for their research efforts. The answers will be free-form and will require the person to look for various codes in the excerpts.Can I use surveys to obtain qualitative data?
There are two types of qualitative data a person can obtain which are nominal and ordinal. The latter is a type of data that has no natural value, rank, or order, while ordinal data is a type of quantitative data that has a specific predetermined or specific order.What are the two types of qualitative data?
Qualitative data is a set of information or knowledge that the researcher has obtained through the use of qualitative research methods. It is important for the researcher to know how to obtain qualitative data for their research as it provides the backbone for the conclusion and knowledge the research will provide.