What is the chemical formula of Calcium Sulfate?
CaSO₃
CaSO₄
CaS
CaS2O₄

Calcium sulfate is a versatile chemical compound composed of calcium, sulfur, and oxygen, known for its widespread use in industries such as construction, food, and medicine. Found naturally as gypsum (dihydrate) and anhydrite (anhydrous), it plays a critical role in making plaster and drywall, acting as a food additive for coagulation and stabilization, and aiding in bone regeneration. This white, solid material highlights the interconnectedness of nature and industry, proving essential in building materials, food production, and healthcare applications.
| Formula | CaSO₄ |
| Hill Formula | CaO₄S |
| Name | Calcium sulfate |
| Alternate Names | Calcium sulfate |
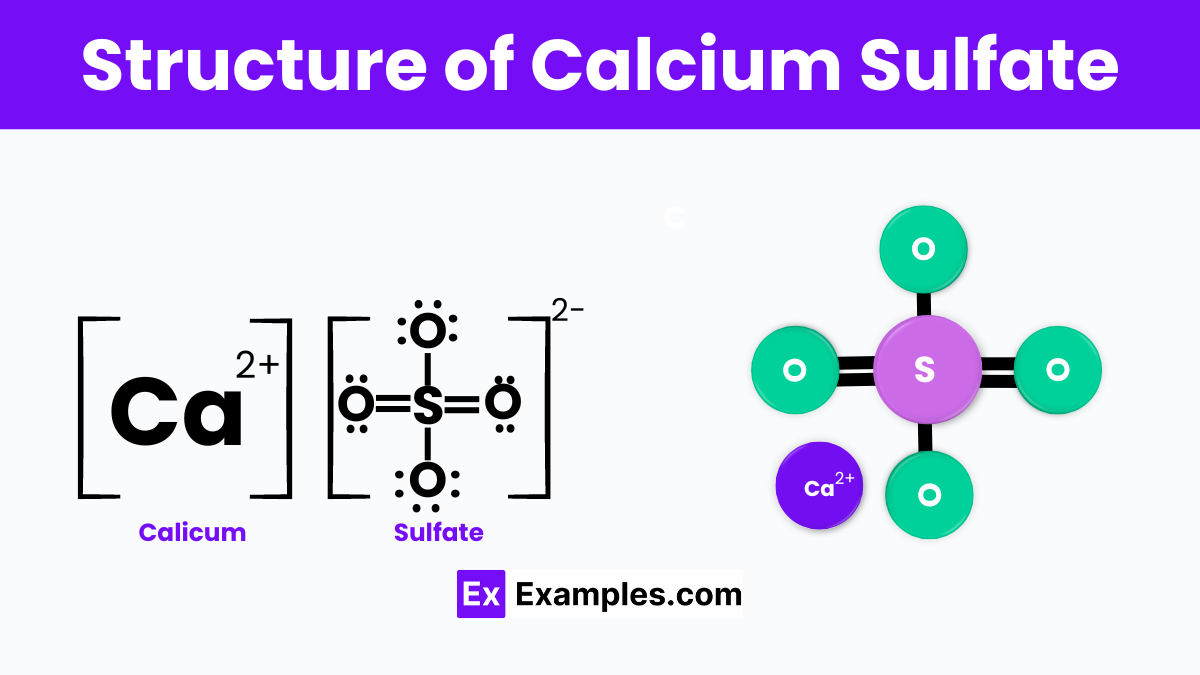
Calcium sulfate, with the chemical formula CaSO₄, is a versatile compound existing in several hydrate forms, including anhydrous calcium sulfate, dihydrate (gypsum), and hemihydrate (plaster of Paris). Each form has distinct properties and applications, making calcium sulfate essential in industries ranging from construction to food additives. Anhydrous calcium sulfate acts as a desiccant, gypsum is used for making plaster and wallboard, and plaster of Paris is utilized for casting molds and decorations due to its quick-setting nature.
The structure of calcium sulfate changes with its hydration level. Anhydrous calcium sulfate has a monoclinic crystal system with calcium ions coordinated by eight oxygen atoms, while gypsum and plaster of Paris have structures that accommodate water molecules, influencing their physical properties. These structural differences make calcium sulfate highly adaptable, serving as a key material in building materials, soil conditioners, food products as an additive (E516), and in pharmaceuticals as an excipient in tablet manufacturing.
Calcium sulfate is synthesized through two primary methods: chemical reaction and dehydration of gypsum. The chemical synthesis process involves reacting calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) with sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) to produce calcium sulfate (CaSO₄), alongside carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), as shown below:
In the dehydration method, gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) is heated, producing either calcium sulfate hemihydrate (plaster of Paris, CaSO₄·0.5H₂O) or anhydrous calcium sulfate (CaSO₄) depending on the temperature. The equations for these reactions are:
Hemihydrate formation:
Anhydrous calcium sulfate formation:
These methods enable the versatile use of calcium sulfate in industries such as construction, where it’s used in materials like drywall and plaster, and in various industrial processes as a desiccant.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 136.14 g/mol (Anhydrous) |
| Appearance | White powder or colorless, crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.96 g/cm³ (Anhydrous), 2.32 g/cm³ (Dihydrate) |
| Melting Point | 1,460°C (Anhydrous), 145°C (Dihydrate loses water) |
| Solubility in Water | 0.21 g/100 mL (20°C, Anhydrous), 2.4 g/L (20°C, Dihydrate) |
| Crystal Structure | Monoclinic (Anhydrous and Dihydrate) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.17 W/(m·K) (Dihydrate) |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 2 (Dihydrate) |
Calcium sulfate is characterized by low reactivity, maintaining stability across various conditions. Being non-flammable and non-toxic, it is utilized in a broad spectrum of applications, including construction materials and food additives.
A significant property of calcium sulfate is its solubility. Dihydrate gypsum has limited water solubility, which decreases with rising temperature. Anhydrite, its anhydrous form, is less soluble, impacting its use in drywall and plaster.
It shows unique thermal properties; gypsum loses water to become plaster of Paris (CaSO4·0.5H2O) upon heating. This dehydration is reversible, enabling plaster to harden when mixed with water. This is utilized in molds and bandages.
Calcium sulfate is pH neutral in aqueous solutions, suitable for applications needing pH stability, like in agriculture for soil conditioning.
It reacts with strong acids and bases, producing calcium salts and sulfuric acid or sulfate salts. This makes it a flexible additive in chemical processes, pharmaceuticals, and food production.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7778-18-9 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 24497 |
| PubChem Substance ID | 24854355 |
| SMILES Identifier | [O-]S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Ca+2] |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/Ca.H2O4S/c;1-5(2,3)4/h;(H2,1,2,3,4)/q+2;/p-2/fCa.O4S/qm;-2 |
| RTECS Number | WS6920000 |
| MDL Number | MFCD00010912 |
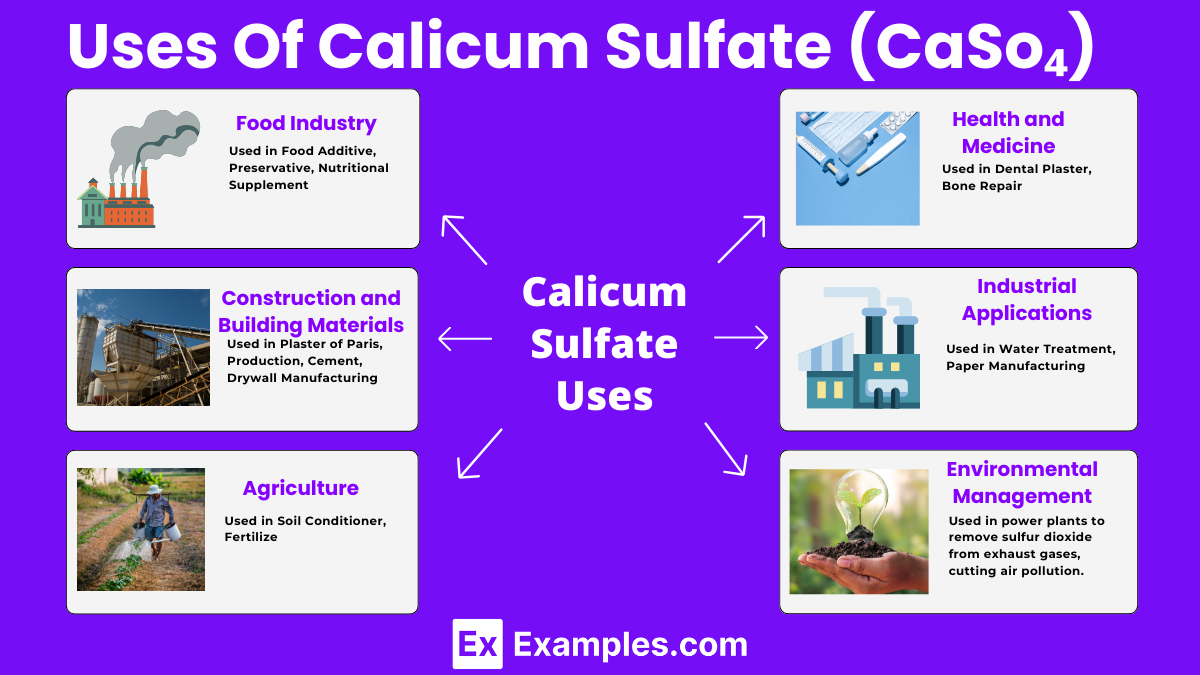
Calcium sulfate is non-toxic and biodegradable, making it environmentally friendly. Its natural occurrence and compatibility with the environment add to its appeal in sustainable practices.
The wide range of applications, from construction materials to food additives, highlights its versatility. This adaptability makes calcium sulfate a valuable resource across different sectors.
In the food industry, calcium sulfate provides a source of dietary calcium, an essential nutrient for bone health and metabolic functions.
Yes, calcium sulfate is safe and commonly used as a food additive, enhancing texture and stability in various products.
Calcium sulfate provides essential nutrients, supporting bone health and cellular function without adverse effects when consumed appropriately.
Calcium sulfate is also known as gypsum when in its mineral form, widely used in industries and agriculture.
In households, calcium sulfate may be known as Plaster of Paris, especially in crafting and repair works.
Calcium sulfate naturally occurs in the mineral gypsum, extensively mined from the earth’s crust for various applications.
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of Calcium Sulfate?
CaSO₃
CaSO₄
CaS
CaS2O₄
What is the common name for hydrated Calcium Sulfate?
Limestone
Epsom salt
Gypsum
Quicklime
What is the primary use of Calcium Sulfate in the construction industry?
Insulation
Cement additive
Drywall production
Paint pigment
Which of the following is a property of anhydrous Calcium Sulfate?
Highly soluble in water
Hygroscopic
Reactive with acids
Low melting point
What happens to Gypsum when it is heated to about 150°C?
It converts to Plaster of Paris
It melts
It decomposes into calcium oxide
It becomes highly reactive
Which form of Calcium Sulfate is used as a coagulant in the production of tofu?
Anhydrous calcium sulfate
Hemihydrate calcium sulfate
Dihydrate calcium sulfate
Gypsum
What is the solubility of Calcium Sulfate in water at 25°C?
Highly soluble
Moderately soluble
Sparingly soluble
Insoluble
Calcium Sulfate is commonly found in which type of rock?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Volcanic
What is the molar mass of Calcium Sulfate (CaSO₄)?
120.17 g/mol
136.14 g/mol
152.17 g/mol
172.20 g/mol
Which of the following industries uses Calcium Sulfate as a drying agent?
Pharmaceutical
Textile
Food processing
Metal casting
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

