What is the chemical formula of ozone?
O₂
O₃
O₁
O₄

Ozone is a special kind of gas. This bond forms what scientists call a covalent compound, which means the atoms share electrons to stay connected. In the world of chemistry, ozone plays a big role in protecting our planet by absorbing the sun’s harmful rays high up in the atmosphere. This gas is not only crucial for life on Earth but also fascinating to study because of its unique properties and the way it interacts with other elements in the air.
Ozone (O₃) is a type of gas found in the Earth’s atmosphere, made up of three oxygen atoms linked together. Unlike the oxygen we breathe, which has two oxygen atoms, ozone has an extra oxygen atom that makes it quite special. This unique structure allows ozone to absorb most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays, providing a protective layer high above us that shields all living things from the sun’s intense energy. In simple terms, ozone acts like the Earth’s sunscreen, playing a crucial role in keeping our planet and its inhabitants safe.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Formula | O₃ |
| Name | ozone |
| Alternate Names | triatomic oxygen, trioxygen |
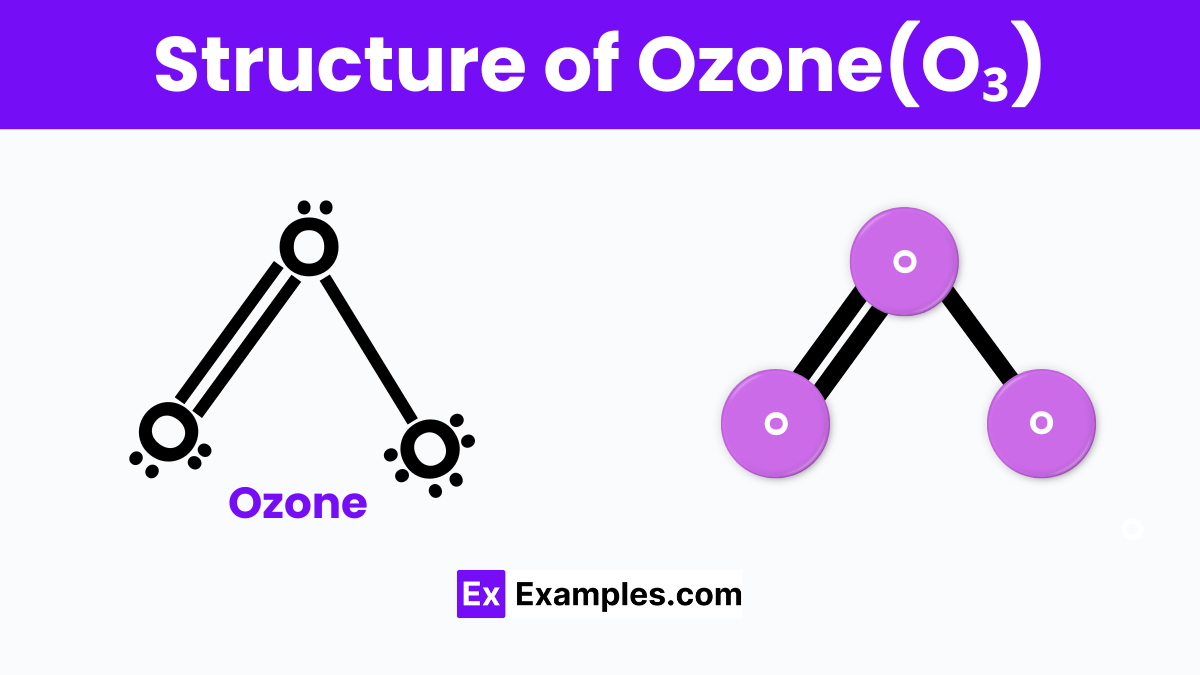
Ozone, or O₃, is a type of oxygen molecule that’s different from the oxygen we breathe, which has two oxygen atoms (O₂). In an ozone molecule, three oxygen atoms are linked together in a way that forms a bent shape. Imagine a boomerang, where the middle oxygen atom is at the tip of the boomerang, and the other two atoms are at the ends. This shape is because of the way electrons are shared between the oxygen atoms, making it a little bit like a stretched-out triangle.
This bent shape of ozone is really important for how it behaves in our atmosphere, especially in the ozone layer, which protects us from the sun’s harmful UV rays. Unlike regular oxygen, ozone can absorb these UV rays, acting like a shield for the Earth. The unique structure of ozone, with its three oxygen atoms, makes all this possible, helping to keep our planet a safe place for all of us to live.
Ozone (O₃) is typically produced by using electric sparks or ultraviolet light to split ordinary oxygen molecules (O₂) into single oxygen atoms. These highly reactive atoms quickly combine with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. The process can be summarized by the equation:
which shows that three molecules of oxygen are converted into two molecules of ozone. In laboratories or industrial settings, this is often done using devices called ozone generators, where a high voltage electric arc is passed through oxygen gas. The electric sparks from the arc break the oxygen molecules into individual atoms, which then combine with other oxygen molecules to form ozone. This method is widely used because it can produce a concentrated amount of ozone efficiently, which is useful for various applications such as water treatment, air purification, and in chemical synthesis.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | O₃ |
| Physical State | Gas at room temperature |
| Color | Pale blue |
| Odor | Sharp, chlorine-like |
| Melting Point | -192.2 °C (-313.96 °F) |
| Boiling Point | -111.9 °C (-169.42 °F) |
| Density | 2.144 g/L (at 0 °C and 101.325 kPa) |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble, but less so than oxygen. The solubility decreases with increasing temperature. |
| Magnetic Susceptibility | Paramagnetic, meaning it is attracted by a magnetic field due to its unpaired electrons. |
Ozone is much more reactive than dioxygen (O₂) due to its molecular structure. It readily reacts with other molecules, making it a powerful oxidizing agent. This property is utilized in water treatment and air purification to break down pollutants.
As an oxidizing agent, ozone can cause metals to corrode and rubber to crack. It reacts with most metals to form metal oxides. For instance:
This equation shows iron (Fe) reacting with ozone to form iron(III) oxide (rust).
Ozone is unstable and tends to decompose back into dioxygen:
This decomposition can be accelerated by the presence of catalysts or high temperatures.
Ozone reacts with many organic compounds in a process known as ozonolysis, breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones. This is particularly useful in organic synthesis and pollution control. For example, in the ozonolysis of alkenes:
This equation illustrates how an alkene reacts with ozone to form two carbonyl compounds.
Ozone can have harmful effects on living tissues. Inhaling ozone can lead to respiratory problems because it reacts with compounds in the respiratory tract. This property underlines the importance of monitoring and regulating ozone levels in the air.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 10028-15-6 |
| PubChem Compound ID | 24823 |
| SMILES Identifier | [O-][O+]=O |
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/O3/c1-3-2 |
| EU Number | 233-069-2 |
| Gmelin Number | 1101 |
| RTECS Number | RS8225000 |
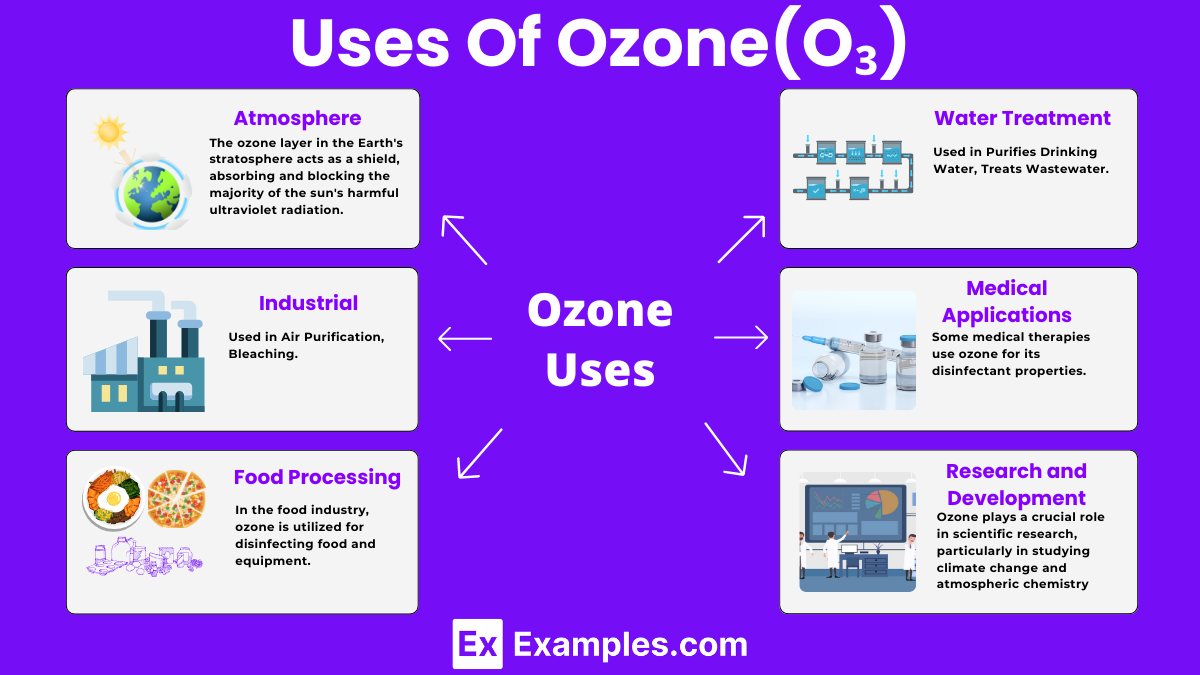
Ozone in the stratosphere absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, protecting living organisms from UV damage, which includes reducing risks of skin cancer and cataracts in humans and safeguarding ecosystems.
Ozone can be harmful, causing respiratory issues and aggravating lung diseases like asthma. High concentrations damage the lungs and throat.
At ground level, ozone is a pollutant, damaging crops, forests, and harming wildlife. It contributes to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Ozone therapy is illegal in some places due to lack of FDA approval and potential health risks like blood vessel damage and lung problems.
Ozone has a distinct sharp, clean smell, often described as similar to chlorine bleach. It’s noticeable after thunderstorms or around electrical equipment
Text prompt
Add Tone
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
What is the chemical formula of ozone?
O₂
O₃
O₁
O₄
Where is the ozone layer primarily located?
Troposphere
Stratosphere
Mesosphere
Thermosph
Ozone is an allotrope of which element?
Nitrogen
Carbon
Oxygen
Hydrogen
What type of bond is found between the oxygen atoms in an ozone molecule?
Single bond
Double bond
Triple bond
One single and one double bond
What is the primary function of the ozone layer?
Reflecting sunlight
Absorbing UV radiation
Trapping heat
Producing oxygen
Which of the following compounds is known to deplete the ozone layer?
CO₂
CH₄
CFCs
H₂O
What is the ozone hole?
A region with no oxygen
A region with no ozone
A region with significantly reduced ozone concentration
A region with extra ozone
What is the main cause of ozone depletion?
Greenhouse gases
Industrial pollution
Emission of CFCs and other halogenated compounds
Natural disasters
Ozone can be harmful to human health at ground level. This is known as:
Stratospheric ozone
Tropospheric ozone
Mesospheric ozone
Thermospheric ozone
Which international agreement aims to reduce the production of ozone-depleting substances?
Kyoto Protocol
Paris Agreement
Montreal Protocol
Basel Convention
Before you leave, take our quick quiz to enhance your learning!

